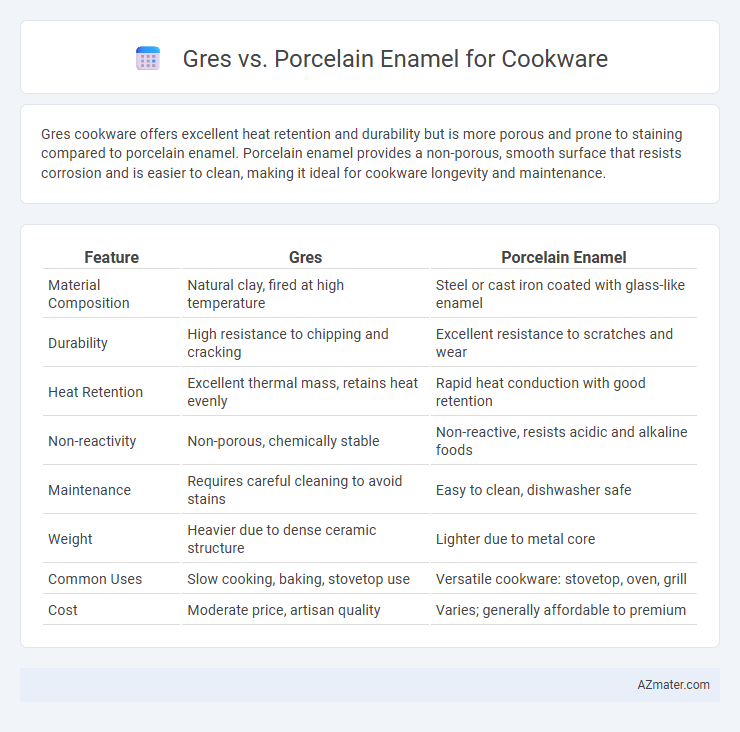
Gres cookware offers excellent heat retention and durability but is more porous and prone to staining compared to porcelain enamel. Porcelain enamel provides a non-porous, smooth surface that resists corrosion and is easier to clean, making it ideal for cookware longevity and maintenance.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Gres | Porcelain Enamel |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Natural clay, fired at high temperature | Steel or cast iron coated with glass-like enamel |
| Durability | High resistance to chipping and cracking | Excellent resistance to scratches and wear |
| Heat Retention | Excellent thermal mass, retains heat evenly | Rapid heat conduction with good retention |
| Non-reactivity | Non-porous, chemically stable | Non-reactive, resists acidic and alkaline foods |
| Maintenance | Requires careful cleaning to avoid stains | Easy to clean, dishwasher safe |
| Weight | Heavier due to dense ceramic structure | Lighter due to metal core |
| Common Uses | Slow cooking, baking, stovetop use | Versatile cookware: stovetop, oven, grill |
| Cost | Moderate price, artisan quality | Varies; generally affordable to premium |
Gres vs Porcelain Enamel: An Overview
Gres cookware, made from dense stoneware clay, offers exceptional heat retention and durability ideal for slow cooking and high-temperature baking. Porcelain enamel cookware features a vitreous coating fused to metal, providing a non-porous, stain-resistant surface that resists corrosion and metal reactivity. Both materials excel in durability, but gres is prized for its natural, rustic finish and thermal stability, while porcelain enamel stands out for its versatility and ease of maintenance.
Material Composition and Manufacturing Process
Gres cookware is typically made from natural clay materials fired at lower temperatures, resulting in a porous ceramic body that requires a glazing layer for durability and non-stick properties. Porcelain enamel cookware consists of a metal core, often cast iron or steel, coated with a smooth layer of powdered glass fused at high temperatures, creating a non-reactive and highly durable enamel surface. The manufacturing process of porcelain enamel involves fusing glass particles onto metal through intense heat, whereas gres relies on ceramic firing techniques that emphasize mineral composition and glaze application.
Heat Distribution and Retention Properties
Gres cookware offers excellent heat retention thanks to its thick ceramic composition, making it ideal for slow, even cooking. Porcelain enamel cookware, coated on cast iron or steel, provides superior heat distribution due to the metal core but retains heat less effectively than gres. Both materials excel in durability and aesthetics, but for optimal heat performance, gres is preferred for steady warmth, while porcelain enamel ensures quick, uniform cooking temperatures.
Durability and Resistance to Damage
Gres cookware offers robust durability with excellent resistance to chipping and cracking, making it suitable for everyday use and high-heat cooking. Porcelain enamel cookware, while also durable, features a glass-like coating that is highly resistant to scratches, stains, and acidic food damage but can chip if dropped or handled roughly. Both materials provide long-lasting performance, but gres excels in impact resistance whereas porcelain enamel is superior in maintaining a non-reactive, easy-to-clean surface.
Non-Stick Performance and Cooking Experience
Porcelain enamel cookware offers superior non-stick performance due to its smooth, glass-like surface that prevents food from sticking and facilitates easy cleaning compared to gres, which is more porous and prone to food adhesion. The non-reactive nature of porcelain enamel ensures even heat distribution, enhancing cooking experience by reducing hotspots and allowing precise temperature control. Gres cookware may require more oil or butter to prevent sticking, which can affect the flavor and texture of dishes, making porcelain enamel the preferred choice for non-stick efficiency in culinary applications.
Maintenance and Ease of Cleaning
Gres cookware, typically made from stoneware, requires careful hand washing to prevent chipping and cracking, with mild detergent and non-abrasive sponges recommended for maintaining its surface. Porcelain enamel cookware offers superior ease of cleaning due to its smooth, non-porous surface that resists staining and is often dishwasher safe, reducing the need for intensive scrubbing. Both materials benefit from avoiding metal utensils to preserve the finish, but porcelain enamel stands out for durability in routine maintenance and stain resistance.
Aesthetic Appeal and Design Options
Gres cookware offers a rustic, artisanal aesthetic with natural earth tones and textured finishes that appeal to those seeking a traditional, handcrafted look. Porcelain enamel cookware boasts vibrant, glossy surfaces available in a wide range of colors and patterns, providing versatile design options to complement modern kitchens. The smooth, non-porous finish of porcelain enamel also allows for intricate detailing and long-lasting color retention, enhancing its visual appeal over time.
Safety, Health Concerns, and Reactivity
Gres cookware, made from natural stoneware clay, offers excellent safety with its non-toxic, lead-free composition that resists chemical reactions and does not leach harmful substances into food. Porcelain enamel cookware, coated with a glass-like layer fused to metal, provides a hygienic, non-reactive surface that prevents metallic taste transfer and exposure to heavy metals such as nickel or cadmium. Both materials ensure food safety, but porcelain enamel can chip, potentially exposing reactive metal beneath, whereas gres's dense, vitrified structure minimizes health risks related to surface damage and reactivity.
Price Comparison and Value for Money
Gres cookware typically offers a more affordable price point compared to porcelain enamel, making it an attractive option for budget-conscious buyers seeking durable kitchenware. Porcelain enamel, while often more expensive, provides superior resistance to chipping and a longer lifespan, potentially delivering better value for money over time. Evaluating initial cost against durability and maintenance needs helps determine the most cost-effective choice for individual cooking preferences.
Choosing the Right Cookware: Gres or Porcelain Enamel?
Gres cookware offers excellent heat retention and durability, making it ideal for slow cooking and baking, while porcelain enamel provides a non-reactive, easy-to-clean surface perfect for acidic foods and vibrant aesthetics. When choosing between gres and porcelain enamel, consider your cooking style: gres excels in rustic, high-heat applications, whereas porcelain enamel suits versatile, everyday use with low maintenance. Prioritize cookware that matches your stovetop compatibility, thermal performance, and the ease of cleaning required for your kitchen routine.
Infographic: Gres vs Porcelain Enamel for Cookware
 azmater.com
azmater.com