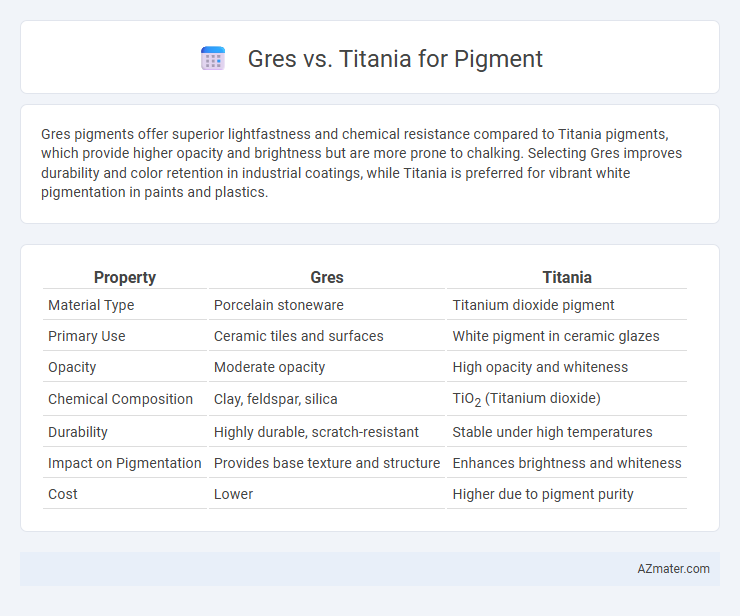
Gres pigments offer superior lightfastness and chemical resistance compared to Titania pigments, which provide higher opacity and brightness but are more prone to chalking. Selecting Gres improves durability and color retention in industrial coatings, while Titania is preferred for vibrant white pigmentation in paints and plastics.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Gres | Titania |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Porcelain stoneware | Titanium dioxide pigment |
| Primary Use | Ceramic tiles and surfaces | White pigment in ceramic glazes |
| Opacity | Moderate opacity | High opacity and whiteness |
| Chemical Composition | Clay, feldspar, silica | TiO2 (Titanium dioxide) |
| Durability | Highly durable, scratch-resistant | Stable under high temperatures |
| Impact on Pigmentation | Provides base texture and structure | Enhances brightness and whiteness |
| Cost | Lower | Higher due to pigment purity |
Introduction to Gres and Titania Pigments
Gres pigments are known for their high durability and resistance to fading, making them ideal for ceramic applications requiring long-lasting color stability. Titania pigments, primarily composed of titanium dioxide, offer exceptional brightness and opacity, widely used in coatings and plastics for enhanced whiteness and coverage. Both pigments serve distinct industrial purposes, with Gres favored in ceramics and Titania dominating in paint and polymer industries.
Chemical Composition and Structure
Gres pigments primarily consist of aluminum silicates combined with metal oxides, providing high stability and resistance to chemical reactions in ceramic applications. Titania pigments are based on titanium dioxide (TiO2), renowned for its strong opacity, whiteness, and UV resistance due to its crystalline anatase or rutile structure. The chemical stability and crystalline structure of Titania offer superior brightness, while Gres pigments provide enhanced durability and resistance to heat and wear.
Color Properties and Stability
Gres pigments exhibit superior color intensity and enhanced UV resistance compared to Titania pigments, ensuring longer-lasting vibrancy in ceramic applications. Titania pigments offer excellent whiteness and brightness but tend to fade faster under prolonged sunlight exposure. The chemical stability of Gres pigments in high-temperature conditions surpasses that of Titania, making them ideal for durable, heat-resistant coatings.
Lightfastness and Weather Resistance
Gres pigments offer superior lightfastness with excellent resistance to fading under prolonged exposure to sunlight, making them ideal for outdoor use. Titania pigments, while highly reflective and bright, generally exhibit lower weather resistance and may degrade faster when subjected to harsh environmental conditions. For applications requiring durable color retention and long-term performance, Gres pigments are the preferred choice due to their stable chemical composition and enhanced weatherproof properties.
Opacity and Hiding Power Comparison
Titania pigment offers superior opacity and hiding power compared to Gres, making it a preferred choice for applications requiring strong coverage and vibrant whiteness. Gres pigments, while cost-effective, often fall short in achieving the same level of opacity, resulting in the need for additional layers to cover substrates effectively. The higher titanium dioxide content in Titania directly correlates with enhanced hiding power, ensuring minimal pigment usage for maximum visual impact.
Environmental and Health Considerations
Gres pigment production generates lower levels of volatile organic compounds (VOCs) compared to Titania, resulting in reduced environmental pollution and occupational exposure risks. Titania, while offering superior opacity and brightness, is associated with concerns related to nanoparticle inhalation, which may pose respiratory health hazards during manufacturing and application processes. Selecting Gres pigments can minimize eco-toxicological impacts and improve workplace safety due to their inherently less hazardous composition and lower emission profiles.
Cost and Availability in the Market
Gres pigment offers competitive pricing and is widely available in various industrial markets, making it a cost-effective choice for large-scale manufacturing. Titania pigment, although generally more expensive due to higher purity and brightness, maintains strong market presence with steady availability from leading suppliers. Businesses seeking an optimal balance between cost and availability often weigh Gres's affordability against Titania's premium quality and consistent supply chain.
Industrial Applications and Usage
Gres pigments, known for their high durability and resistance to chemicals, are widely used in industrial ceramics, coatings, and construction materials due to their stable color performance under extreme conditions. Titania pigments, particularly titanium dioxide, offer superior whiteness and opacity, making them essential in paints, plastics, and paper industries for enhancing brightness and UV resistance. Both pigments provide critical functional properties tailored to industrial applications, with Gres favored for heat and abrasion resistance, while Titania is preferred for optical clarity and protective coatings.
Performance in Various Mediums
Gres pigments are highly valued for their exceptional durability and color retention in ceramics, offering superior resistance to high temperatures and chemical reactions, making them ideal for both stoneware and porcelain. Titania pigments provide excellent opacity and brightness, performing well across various mediums such as paints and plastics, while maintaining stability under UV exposure. In comparative performance, Gres excels in high-heat and structural applications, whereas Titania stands out for surface finishes requiring vivid opacity and resistance to fading.
Future Trends and Innovations in Pigments
Gres and Titania are pivotal in the evolution of pigment technology, with Gres focusing on natural mineral-based pigments offering enhanced durability and environmental compatibility. Titania, primarily known for its titanium dioxide pigments, leads innovations in high-opacity, UV-resistant coatings supporting sustainability and energy efficiency in various industries. Future trends indicate a convergence of bio-based solutions from Gres and nano-enhanced Titania pigments, driving the next generation of eco-friendly, high-performance colorants.
Infographic: Gres vs Titania for Pigment
 azmater.com
azmater.com