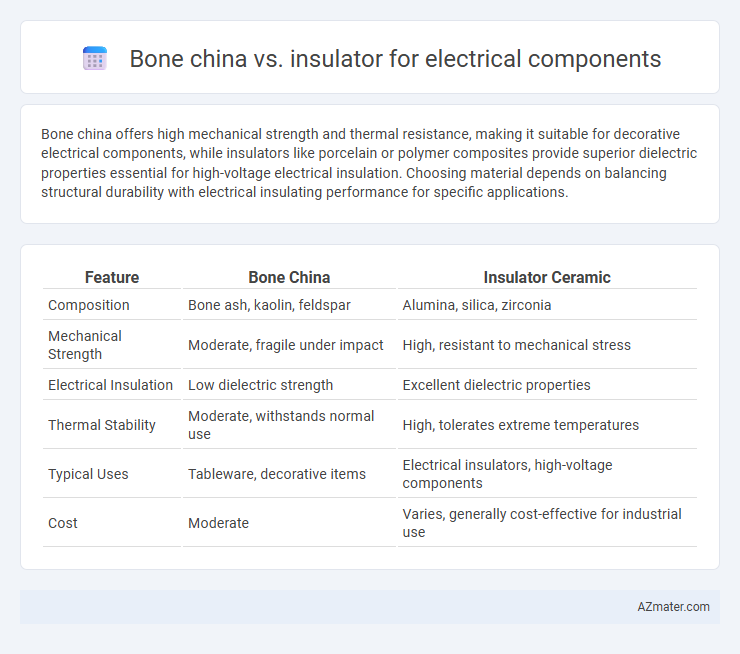
Bone china offers high mechanical strength and thermal resistance, making it suitable for decorative electrical components, while insulators like porcelain or polymer composites provide superior dielectric properties essential for high-voltage electrical insulation. Choosing material depends on balancing structural durability with electrical insulating performance for specific applications.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Bone China | Insulator Ceramic |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Bone ash, kaolin, feldspar | Alumina, silica, zirconia |
| Mechanical Strength | Moderate, fragile under impact | High, resistant to mechanical stress |
| Electrical Insulation | Low dielectric strength | Excellent dielectric properties |
| Thermal Stability | Moderate, withstands normal use | High, tolerates extreme temperatures |
| Typical Uses | Tableware, decorative items | Electrical insulators, high-voltage components |
| Cost | Moderate | Varies, generally cost-effective for industrial use |
Introduction to Bone China and Electrical Insulators
Bone china, a type of porcelain known for its high strength and translucency, is composed mainly of bone ash, feldspar, and kaolin, making it an ideal material for certain electrical insulators due to its excellent mechanical strength and thermal resistance. Electrical insulators, essential for preventing unwanted current flow, commonly utilize materials like ceramic, glass, and polymers, but bone china offers unique advantages such as enhanced durability and dielectric properties under high voltage conditions. Understanding the composition and performance differences between bone china and traditional electrical insulator materials is crucial for optimizing safety and efficiency in electrical component design.
Material Composition: Bone China vs Electrical Insulators
Bone china is a ceramic material composed primarily of bone ash, feldspar, and kaolin, offering exceptional whiteness, translucency, and mechanical strength. Electrical insulators, on the other hand, are made from materials such as porcelain, glass, or polymers, designed to resist electrical conductivity and withstand high voltage stress. The key difference lies in bone china's focus on aesthetic and structural durability, while insulators prioritize dielectric strength and thermal stability for electrical applications.
Electrical Properties Comparison
Bone china exhibits excellent electrical insulation properties due to its high dielectric strength and low electrical conductivity, making it suitable for high-voltage applications. Insulators designed specifically for electrical components, such as porcelain or polymer-based materials, often provide superior mechanical strength and resistance to thermal shock while maintaining comparable dielectric performance. The choice between bone china and conventional insulators depends on balancing electrical resistance, mechanical durability, and operational environment requirements.
Mechanical Strength and Durability
Bone china exhibits high mechanical strength and excellent durability due to its fine microstructure and high vitrification, making it resistant to cracking and mechanical stress in electrical components. Insulators made from bone china offer superior thermal shock resistance compared to traditional ceramic insulators, ensuring long-lasting performance in high-voltage applications. The dense, non-porous nature of bone china enhances its capacity to withstand mechanical wear and electrical arcing, prolonging the operational lifespan of electrical insulators.
Thermal Stability and Heat Resistance
Bone china has limited thermal stability and heat resistance compared to insulators designed for electrical components, as it is primarily a ceramic material optimized for aesthetic and lightweight properties. Electrical insulators, such as porcelain or specially engineered ceramics, exhibit superior thermal stability, withstanding higher temperatures and thermal cycling without degradation. These insulators maintain dielectric strength and structural integrity under prolonged heat exposure, making them ideal for high-voltage and high-temperature applications.
Common Applications in Electrical Components
Bone china is rarely used in electrical components due to its brittleness and limited dielectric strength, making it unsuitable for high-voltage insulators. Insulators, typically made from porcelain or specialized ceramics, provide superior electrical resistance and mechanical durability, making them common in power transmission lines, transformers, and switchgear. These materials prevent electrical current leakage and withstand environmental stresses, ensuring reliable performance in electrical distribution systems.
Cost and Manufacturing Differences
Bone china offers high mechanical strength and smooth surface finish but incurs higher production costs due to the complex firing process and use of bone ash, making it less economical for large-scale electrical insulator manufacturing. Insulators made from traditional ceramic materials, such as alumina or porcelain, benefit from more established, cost-efficient manufacturing techniques including simpler firing cycles and raw materials, leading to lower overall expenses. The cost differential highlights bone china's suitability for specialized applications requiring superior aesthetics and strength, while standard insulators prioritize cost-effectiveness and large-volume production feasibility.
Advantages of Bone China in Electrical Use
Bone china offers superior electrical insulation properties due to its high density and low porosity, making it ideal for electrical components requiring reliable dielectric strength. Its excellent mechanical strength ensures durability under thermal and mechanical stress, reducing the risk of component failure in high-voltage applications. The naturally smooth surface of bone china also minimizes moisture absorption, enhancing its performance as an insulator in humid or variable environmental conditions.
Limitations of Each Material for Electrical Insulation
Bone china offers excellent electrical insulation properties due to its high dielectric strength and low electrical conductivity but suffers from brittleness and mechanical fragility, limiting its use in high-stress electrical components. Insulators such as porcelain or polymer-based materials provide greater mechanical strength and impact resistance but may exhibit lower thermal stability and higher moisture absorption, which can compromise insulation performance over time. Both materials face trade-offs in balancing electrical insulation efficiency, mechanical durability, and environmental resistance, influencing their selection for specific electrical applications.
Which is Better: Bone China or Traditional Insulators?
Bone china, renowned for its high mechanical strength and excellent electrical insulation properties, offers superior performance in electrical components compared to traditional insulators made from materials like porcelain or glass. Its micro-structure provides enhanced resistance to thermal shock and dielectric breakdown, making it ideal for high-voltage applications. Traditional insulators may be more cost-effective but generally lack the durability and insulating efficiency that bone china consistently delivers in demanding electrical environments.
Infographic: Bone china vs Insulator for Electrical component
 azmater.com
azmater.com