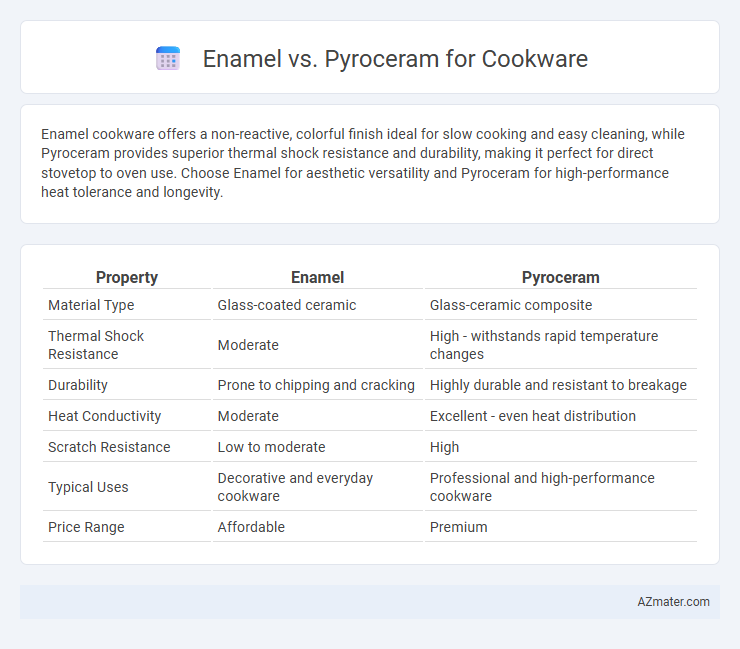
Enamel cookware offers a non-reactive, colorful finish ideal for slow cooking and easy cleaning, while Pyroceram provides superior thermal shock resistance and durability, making it perfect for direct stovetop to oven use. Choose Enamel for aesthetic versatility and Pyroceram for high-performance heat tolerance and longevity.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Enamel | Pyroceram |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Glass-coated ceramic | Glass-ceramic composite |
| Thermal Shock Resistance | Moderate | High - withstands rapid temperature changes |
| Durability | Prone to chipping and cracking | Highly durable and resistant to breakage |
| Heat Conductivity | Moderate | Excellent - even heat distribution |
| Scratch Resistance | Low to moderate | High |
| Typical Uses | Decorative and everyday cookware | Professional and high-performance cookware |
| Price Range | Affordable | Premium |
Introduction to Enamel and Pyroceram Cookware
Enamel cookware features a glass-coated metal base that offers excellent heat retention and a non-reactive cooking surface ideal for acidic foods. Pyroceram cookware, made from a glass-ceramic material, excels in thermal shock resistance and allows for rapid, even heating suitable for stovetop and oven use. Both materials combine durability with unique heat conduction properties, making them popular choices for versatile and long-lasting cookware.
Composition and Manufacturing Differences
Enamel cookware is composed of a metal core, typically cast iron or steel, coated with a layer of glass-like vitreous enamel, which is fused through high-temperature firing to create a durable, non-reactive surface. Pyroceram cookware is made from a glass-ceramic material developed by controlled crystallization of certain glasses, resulting in a highly heat-resistant and thermal shock-resistant surface without the need for additional coatings. Manufacturing enamel involves applying and firing layers of enamel onto metal bases, whereas Pyroceram is produced through a specialized heat-treatment process that transforms glass into a crystalline ceramic structure, enhancing its durability and heat tolerance.
Heat Resistance and Thermal Shock
Pyroceram cookware offers superior heat resistance and exceptional thermal shock capabilities, allowing it to withstand sudden temperature changes without cracking. Enamel cookware, while durable, is more prone to chipping and thermal stress when exposed to rapid temperature fluctuations. The high thermal stability of Pyroceram makes it ideal for use on stovetops, ovens, and even direct flame, outperforming enamel-coated options in maintaining structural integrity under extreme heat conditions.
Non-stick Properties and Cooking Performance
Enamel cookware offers a smooth, non-porous surface that provides moderate non-stick properties, ideal for low to medium-heat cooking and easy cleanup. Pyroceram, a type of glass-ceramic, exhibits superior heat resistance and even heat distribution, minimizing hot spots and enhancing cooking performance, especially for high-temperature searing and baking. While Pyroceram typically requires seasoning or additional coating for non-stick efficiency, enamel's inherent coating resists food sticking without chemical additives.
Durability and Longevity
Enamel cookware offers excellent resistance to scratching and corrosion due to its glass-coated surface, but it can chip or crack if dropped or exposed to sudden temperature changes. Pyroceram cookware, made from a crystalline glass-ceramic, provides superior durability with high resistance to thermal shock, making it ideal for direct stovetop to oven use without damage. Longevity-wise, Pyroceram maintains its integrity and appearance over time better than enamel, which may degrade with heavy usage or impact.
Maintenance and Cleaning Requirements
Enamel cookware requires gentle cleaning with non-abrasive sponges to prevent chipping and preserve its glossy finish, and it is safe for dishwasher use but may gradually dull over time. Pyroceram cookware is highly resistant to stains and scratches, allowing for easier cleaning often with just warm water and mild detergent, and it can withstand high heat scrubbing without damage. Both materials benefit from avoiding metal utensils and harsh chemicals to maintain longevity and performance.
Aesthetic Appeal and Design Options
Enamel cookware offers a vibrant range of colors and glossy finishes that enhance kitchen aesthetics with a classic, timeless look. Pyroceram cookware features sleek, smooth surfaces with a modern, minimalist design often in neutral tones, appealing to contemporary tastes. Both materials provide durable, eye-catching options, but enamel excels in bold, decorative styles while Pyroceram emphasizes subtle elegance and modernity.
Safety and Health Considerations
Enamel cookware offers a non-reactive, glass-coated surface that prevents food from leaching harmful metals, ensuring safer cooking especially for acidic dishes. Pyroceram, a type of glass-ceramic, provides excellent thermal shock resistance and does not release toxins when heated, making it a health-conscious choice for diverse cooking methods. Both materials are free from harmful chemicals like PFOA and PTFE, prioritizing user safety and reducing risks of chemical contamination.
Cost and Availability Comparison
Enamel cookware offers a broad range of affordable options, often found readily in both online and brick-and-mortar retail stores, making it accessible to most consumers. Pyroceram cookware, known for its superior thermal shock resistance, tends to be more expensive and less widely available, usually found in specialty kitchenware shops or through specific brands like CorningWare. The cost difference and availability impact buyer choice, where enamel suits budget-conscious shoppers and Pyroceram appeals to those seeking durability and performance.
Conclusion: Choosing Between Enamel and Pyroceram
Enamel cookware offers vibrant aesthetics and excellent heat retention, making it ideal for slow cooking and high-temperature searing, while Pyroceram provides superior thermal shock resistance and lightweight durability suited for rapid temperature changes and stovetop-to-oven transitions. Selecting between enamel and Pyroceram depends on cooking style preferences and care requirements; enamel demands cautious handling to avoid chipping, whereas Pyroceram resists breakage and is easier to maintain. For versatile everyday use with less maintenance, Pyroceram is preferable, but for classic appearance and robust heat distribution, enamel remains a popular choice.
Infographic: Enamel vs Pyroceram for Cookware
 azmater.com
azmater.com