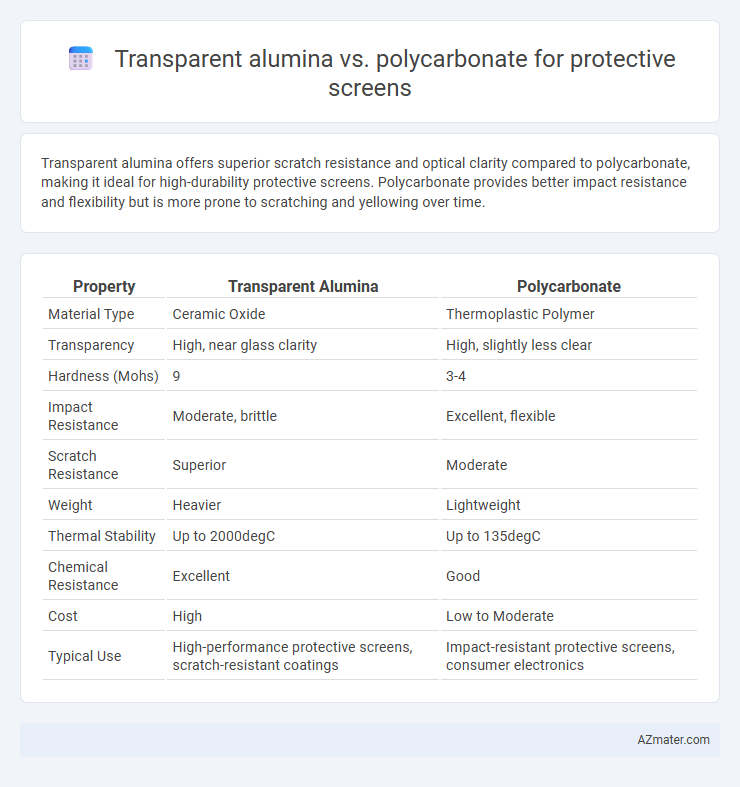
Transparent alumina offers superior scratch resistance and optical clarity compared to polycarbonate, making it ideal for high-durability protective screens. Polycarbonate provides better impact resistance and flexibility but is more prone to scratching and yellowing over time.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Transparent Alumina | Polycarbonate |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Ceramic Oxide | Thermoplastic Polymer |
| Transparency | High, near glass clarity | High, slightly less clear |
| Hardness (Mohs) | 9 | 3-4 |
| Impact Resistance | Moderate, brittle | Excellent, flexible |
| Scratch Resistance | Superior | Moderate |
| Weight | Heavier | Lightweight |
| Thermal Stability | Up to 2000degC | Up to 135degC |
| Chemical Resistance | Excellent | Good |
| Cost | High | Low to Moderate |
| Typical Use | High-performance protective screens, scratch-resistant coatings | Impact-resistant protective screens, consumer electronics |
Overview of Transparent Alumina and Polycarbonate
Transparent alumina, a crystalline form of aluminum oxide, offers exceptional hardness, optical clarity, and high resistance to abrasion and impact, making it ideal for protective screens in rugged environments. Polycarbonate is a lightweight, thermoplastic polymer known for excellent impact resistance, flexibility, and good optical transparency but is more prone to scratching compared to transparent alumina. Both materials balance transparency and protection, with transparent alumina excelling in durability and polycarbonate favored for cost-effectiveness and ease of fabrication.
Material Composition and Structure
Transparent alumina, composed primarily of aluminum oxide (Al2O3), exhibits a crystalline ceramic structure that provides exceptional hardness and scratch resistance, making it highly durable for protective screens. Polycarbonate is a thermoplastic polymer made from bisphenol A and phosgene, characterized by its amorphous, lightweight, and impact-resistant structure, offering superior shatter resistance but lower hardness compared to transparent alumina. The dense crystalline lattice of transparent alumina yields higher optical clarity and chemical stability, while polycarbonate's molecular chains allow flexibility and ease of fabrication in protective screen applications.
Optical Clarity and Light Transmission
Transparent alumina offers superior optical clarity with high light transmission rates above 85%, making it ideal for protective screens requiring exceptional visibility and minimal distortion. Polycarbonate, while providing good transparency and light transmission around 88-90%, tends to exhibit more surface abrasion and slight haze over time, which can reduce optical performance. The choice between transparent alumina and polycarbonate hinges on the need for durability and long-term clarity versus cost-effectiveness and impact resistance.
Impact Resistance and Durability
Transparent alumina offers superior impact resistance with a hardness level reaching 9 on the Mohs scale, making it highly resistant to scratches and abrasions compared to polycarbonate, which rates around 3-4. Polycarbonate provides excellent toughness and can absorb significant impacts without shattering, often used in safety glasses and riot shields due to its ability to flex under stress. In terms of durability, transparent alumina resists high temperatures and chemical corrosion better than polycarbonate, which may degrade over time under UV exposure and extreme environmental conditions.
Scratch and Abrasion Resistance
Transparent alumina offers superior scratch and abrasion resistance compared to polycarbonate, making it ideal for protective screens exposed to harsh environments. Its hardness, often rated above 9 on the Mohs scale, significantly reduces surface wear and maintains optical clarity over time. In contrast, polycarbonate, while impact-resistant, is more prone to surface scratches and requires additional coatings to enhance durability.
Weight and Thickness Comparison
Transparent alumina boasts a significantly higher density, resulting in a heavier protective screen compared to polycarbonate, which is renowned for its lightweight properties. In terms of thickness, transparent alumina can achieve comparable strength at thinner profiles due to its superior hardness and rigidity, whereas polycarbonate requires thicker layers to maintain impact resistance. The trade-off between weight and thickness makes polycarbonate ideal for applications demanding lightweight protection, while transparent alumina suits environments prioritizing slim form factors combined with high durability.
Thermal and Chemical Stability
Transparent alumina exhibits superior thermal stability with a melting point above 2,000degC, making it highly resistant to heat deformation compared to polycarbonate, which softens around 150degC. Chemically, transparent alumina is inert and resistant to corrosion from most acids and alkalis, whereas polycarbonate is vulnerable to degradation by certain solvents and UV exposure. These properties position transparent alumina as the preferred material for protective screens requiring high durability in extreme thermal and chemical environments.
Cost and Availability
Transparent alumina offers higher durability and scratch resistance but comes at a significantly higher cost compared to polycarbonate, which is more affordable and widely available. Polycarbonate screens are easier to source in bulk due to established manufacturing processes and lower raw material expenses. Cost efficiency and broad availability make polycarbonate the preferred choice for large-scale protective screen applications despite its lower hardness and scratch resistance.
Common Applications in Protective Screens
Transparent alumina offers exceptional scratch resistance and high thermal stability, making it ideal for protective screens in industrial machinery and harsh environments. Polycarbonate is favored for impact resistance and lightweight properties, commonly used in eyewear, face shields, and automotive windshields. Both materials are essential in protective screens, with transparent alumina suited for extreme durability and polycarbonate for versatility and impact protection.
Future Trends and Innovations
Transparent alumina offers superior scratch resistance, thermal stability, and chemical durability compared to polycarbonate, making it ideal for high-performance protective screens in demanding environments. Emerging innovations focus on enhancing alumina's optical clarity and impact toughness through advanced ceramic processing techniques, pushing its applicability in next-generation display technologies, including flexible and foldable devices. Polycarbonate remains favored for cost-effective, lightweight, and easily moldable solutions, but ongoing developments in nanoparticle reinforcements aim to improve its abrasion resistance and UV protection, narrowing the performance gap with transparent ceramics.
Infographic: Transparent alumina vs Polycarbonate for Protective screen
 azmater.com
azmater.com