Zirconia offers superior fracture toughness and wear resistance compared to alumina, making it more durable for hip replacements. Alumina provides excellent biocompatibility and low wear rates but is more brittle, leading to a higher risk of fracture in long-term use.
Table of Comparison
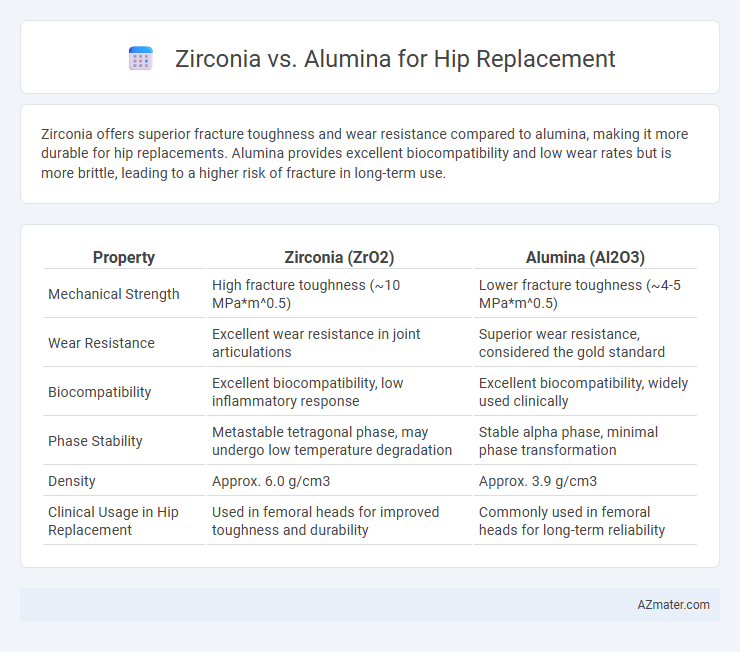
| Property | Zirconia (ZrO2) | Alumina (Al2O3) |
|---|---|---|
| Mechanical Strength | High fracture toughness (~10 MPa*m^0.5) | Lower fracture toughness (~4-5 MPa*m^0.5) |
| Wear Resistance | Excellent wear resistance in joint articulations | Superior wear resistance, considered the gold standard |
| Biocompatibility | Excellent biocompatibility, low inflammatory response | Excellent biocompatibility, widely used clinically |
| Phase Stability | Metastable tetragonal phase, may undergo low temperature degradation | Stable alpha phase, minimal phase transformation |
| Density | Approx. 6.0 g/cm3 | Approx. 3.9 g/cm3 |
| Clinical Usage in Hip Replacement | Used in femoral heads for improved toughness and durability | Commonly used in femoral heads for long-term reliability |
Introduction to Hip Replacement Materials
Zirconia and alumina are two advanced ceramic materials commonly used in hip replacement implants due to their exceptional biocompatibility and wear resistance. Zirconia offers superior toughness and fracture resistance, making it suitable for high-impact environments, while alumina provides outstanding hardness and excellent resistance to wear and corrosion. The selection between these materials impacts implant longevity, patient outcomes, and overall prosthetic performance.
Overview of Zirconia Ceramics
Zirconia ceramics are widely used in hip replacements due to their high fracture toughness, excellent biocompatibility, and resistance to wear and corrosion. Their unique crystal structure provides superior mechanical strength compared to alumina, making zirconia an ideal choice for load-bearing orthopedic implants. The material's ability to reduce implant loosening and extend prosthesis lifespan significantly improves patient outcomes in hip arthroplasty.
Overview of Alumina Ceramics
Alumina ceramics for hip replacement are highly valued for their exceptional biocompatibility, wear resistance, and mechanical strength, making them a preferred material in orthopedic implants. Their high hardness and low friction coefficient contribute to reduced wear debris generation, which lowers the risk of osteolysis and implant loosening. Alumina's stable chemical properties and resistance to corrosion ensure long-term implant durability and patient safety in hip arthroplasty procedures.
Mechanical Properties Comparison
Zirconia exhibits higher fracture toughness and better resistance to crack propagation compared to alumina, making it more durable under repetitive stress in hip replacements. Alumina, while possessing superior hardness and wear resistance, tends to be more brittle, increasing the risk of catastrophic failure under high mechanical loads. Both ceramics offer biocompatibility and corrosion resistance, but zirconia's enhanced toughness provides improved longevity and mechanical performance in load-bearing orthopedic applications.
Wear Resistance and Longevity
Zirconia exhibits superior wear resistance compared to alumina, reducing particle generation and minimizing osteolysis risks in hip replacements. The enhanced toughness of zirconia contributes to increased longevity of implants by resisting crack propagation under cyclic loading. Alumina, while biocompatible and hard, tends to be more brittle, potentially limiting its lifespan in high-stress joint environments.
Biocompatibility and Biological Response
Zirconia exhibits superior biocompatibility compared to alumina, with lower cytotoxicity and enhanced osseointegration in hip replacement applications. Alumina is highly inert but may demonstrate less favorable biological responses, including a higher risk of wear debris-induced inflammation. Clinical studies indicate zirconia's ability to reduce immune response and promote long-term implant stability, making it a preferable choice for minimizing adverse biological reactions.
Fracture Risk and Material Failure
Zirconia exhibits superior fracture toughness compared to alumina, significantly reducing the risk of catastrophic material failure in hip replacements. Alumina, while highly biocompatible and wear-resistant, is more brittle and prone to microcracks that can propagate under cyclic loading, increasing fracture risk. Advances in zirconia toughened alumina composites offer an optimal balance of fracture resistance and durability, minimizing implant failure rates in orthopedic applications.
Clinical Outcomes and Patient Satisfaction
Zirconia exhibits superior fracture toughness and wear resistance compared to alumina, leading to reduced risk of implant failure in hip replacement procedures. Clinical outcomes demonstrate lower incidence of osteolysis and aseptic loosening with zirconia components, enhancing long-term implant stability. Patient satisfaction rates are higher with zirconia due to improved implant longevity and decreased postoperative complications.
Cost and Availability Considerations
Zirconia hip replacements typically have higher costs due to advanced manufacturing processes and material properties, while alumina remains more affordable and widely available in the market. Alumina components are favored for their cost-effectiveness and easier access, especially in regions with limited medical resources. Cost and availability significantly impact the selection between zirconia and alumina, influencing both patient affordability and hospital procurement decisions.
Future Perspectives in Hip Replacement Materials
Advancements in hip replacement materials emphasize the potential of zirconia for its superior wear resistance and biocompatibility compared to alumina, which, while historically popular, faces challenges related to brittleness and long-term durability. Research is increasingly focused on developing zirconia-toughened composites that combine the mechanical strength of alumina with zirconia's fracture toughness, promising enhanced implant longevity and reduced revision rates. The integration of nanotechnology and surface engineering in these ceramics is expected to further optimize osseointegration and minimize inflammatory responses, shaping the future landscape of hip replacement biomaterials.
Infographic: Zirconia vs Alumina for Hip Replacement
 azmater.com
azmater.com