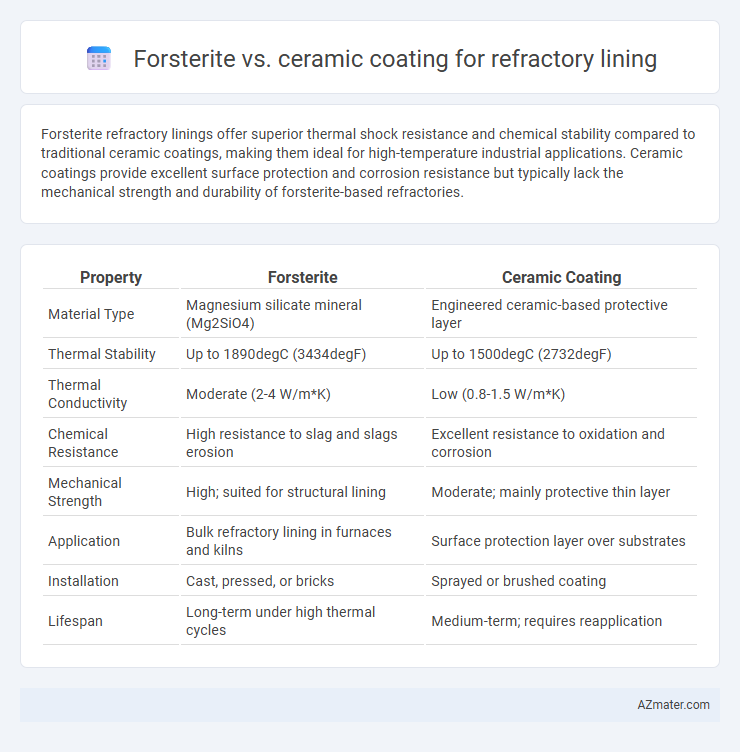
Forsterite refractory linings offer superior thermal shock resistance and chemical stability compared to traditional ceramic coatings, making them ideal for high-temperature industrial applications. Ceramic coatings provide excellent surface protection and corrosion resistance but typically lack the mechanical strength and durability of forsterite-based refractories.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Forsterite | Ceramic Coating |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Magnesium silicate mineral (Mg2SiO4) | Engineered ceramic-based protective layer |
| Thermal Stability | Up to 1890degC (3434degF) | Up to 1500degC (2732degF) |
| Thermal Conductivity | Moderate (2-4 W/m*K) | Low (0.8-1.5 W/m*K) |
| Chemical Resistance | High resistance to slag and slags erosion | Excellent resistance to oxidation and corrosion |
| Mechanical Strength | High; suited for structural lining | Moderate; mainly protective thin layer |
| Application | Bulk refractory lining in furnaces and kilns | Surface protection layer over substrates |
| Installation | Cast, pressed, or bricks | Sprayed or brushed coating |
| Lifespan | Long-term under high thermal cycles | Medium-term; requires reapplication |
Introduction to Forsterite and Ceramic Coatings
Forsterite, a magnesium silicate mineral (Mg2SiO4), serves as a high-temperature refractory material with excellent thermal stability and resistance to slag attack, commonly used in furnace linings. Ceramic coatings, composed of advanced oxides such as alumina or zirconia, offer protective layers for refractory linings by enhancing wear resistance, thermal insulation, and chemical inertness. Both materials improve the durability and performance of refractory linings in industrial applications, with Forsterite primarily providing bulk thermal resistance and ceramic coatings delivering surface protection.
Material Composition and Properties
Forsterite refractory lining primarily consists of magnesium orthosilicate (Mg2SiO4), offering excellent thermal stability and resistance to slag corrosion, making it ideal for high-temperature environments. Ceramic coatings, typically composed of alumina (Al2O3), silica (SiO2), or zirconia (ZrO2), provide enhanced surface hardness, wear resistance, and chemical inertness, protecting substrates from oxidation and abrasion. Forsterite's inherent structural stability contrasts with ceramic coatings' superior surface durability, influencing selection based on operational temperature, mechanical stress, and chemical exposure.
Thermal Resistance and Performance
Forsterite exhibits excellent thermal resistance withstanding temperatures up to 1900degC, making it ideal for high-temperature refractory linings in industrial furnaces. Ceramic coatings also provide superior thermal insulation and protection against thermal shock, enhancing the durability and lifespan of refractory materials by preventing surface degradation. The choice between Forsterite and ceramic coatings depends on specific performance requirements, with Forsterite favored for intrinsic heat resistance and ceramics for protective layering and extended operational efficiency.
Chemical Stability in Refractory Applications
Forsterite demonstrates superior chemical stability in refractory lining applications due to its high resistance to alkali and slag infiltration, maintaining structural integrity at temperatures exceeding 1500degC. Ceramic coatings offer enhanced protection by forming a dense, impermeable barrier that minimizes chemical attack and erosion from molten slags and corrosive gases. The combination of forsterite's inherent stability and the protective properties of advanced ceramic coatings significantly extends the lifespan of refractory linings in harsh chemical environments.
Installation and Application Methods
Forsterite refractories require precise dry pressing or casting methods followed by controlled sintering for optimal installation, ensuring high thermal stability and resistance to slag corrosion. Ceramic coatings for refractory linings are typically applied via spray, brush, or trowel methods, providing a protective barrier that enhances surface durability and extends service life. Installation of ceramic coatings is faster and more flexible compared to Forsterite lining but may require periodic reapplication to maintain performance under high thermal cycling.
Durability and Lifespan
Forsterite refractory lining exhibits superior thermal stability and resistance to slag corrosion, extending its durability in high-temperature industrial applications beyond 15 years. Ceramic coatings, while providing excellent surface protection against oxidation and wear, typically offer a shorter lifespan of 5 to 10 years due to their susceptibility to cracking under thermal cycling. The enhanced longevity of Forsterite is attributed to its dense crystalline structure and chemical inertness, making it ideal for demanding refractory environments.
Cost Comparison and Economic Considerations
Forsterite refractory linings typically offer a lower initial material cost compared to advanced ceramic coatings, making Forsterite more economical for large-scale applications where budget constraints are critical. Ceramic coatings, while generally more expensive upfront, provide longer service life and enhanced thermal resistance, potentially reducing maintenance expenses and downtime over time. Economic considerations should weigh initial expenses against durability and performance benefits, with Forsterite favored for cost-sensitive projects and ceramic coatings suitable for high-temperature environments requiring extended lifespan.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Forsterite refractories exhibit superior environmental sustainability due to their natural mineral composition and recyclability, resulting in reduced carbon emissions during production compared to ceramic coatings, which often rely on synthetic materials with higher energy-intensive manufacturing processes. The longer lifespan and thermal stability of forsterite decrease the frequency of relining, minimizing waste generation and resource consumption, whereas ceramic coatings may require more frequent maintenance, contributing to environmental burdens. Forsterite's compatibility with eco-friendly disposal and lower toxicity enhances its role in sustainable refractory applications, making it a preferable choice for minimizing environmental impact in industrial settings.
Industrial Use Cases and Suitability
Forsterite refractories, with high thermal conductivity and excellent resistance to slag corrosion, are widely used in steelmaking and glass industries where high-temperature durability is critical. Ceramic coatings, offering superior abrasion resistance and chemical inertness, are preferred for lining equipment exposed to aggressive slags and molten metals in petrochemical and cement industries. Industrial suitability depends on operational temperature ranges and chemical environments, with forsterite favored in high-temperature applications and ceramic coatings excel in protecting surfaces from mechanical wear and corrosive media.
Choosing the Optimal Refractory Lining Material
Forsterite offers excellent thermal stability and resistance to slag corrosion, making it ideal for high-temperature refractory lining applications in steel and glass industries. Ceramic coatings provide enhanced surface protection, improved thermal insulation, and reduced wear, extending the lifespan of refractory linings under aggressive conditions. Choosing the optimal refractory lining material depends on factors such as operating temperature, chemical environment, mechanical stress, and cost-effectiveness to ensure durability and performance.
Infographic: Forsterite vs Ceramic coating for Refractory lining
 azmater.com
azmater.com