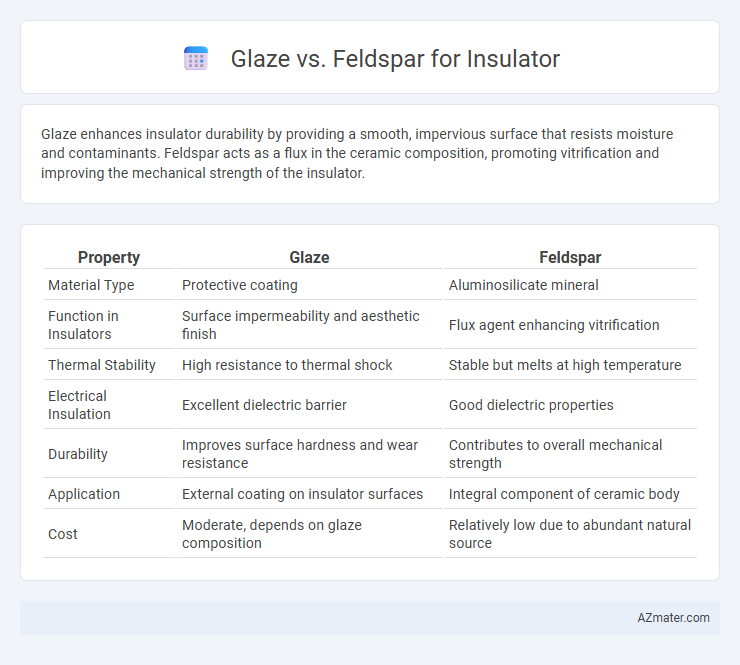
Glaze enhances insulator durability by providing a smooth, impervious surface that resists moisture and contaminants. Feldspar acts as a flux in the ceramic composition, promoting vitrification and improving the mechanical strength of the insulator.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Glaze | Feldspar |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Protective coating | Aluminosilicate mineral |
| Function in Insulators | Surface impermeability and aesthetic finish | Flux agent enhancing vitrification |
| Thermal Stability | High resistance to thermal shock | Stable but melts at high temperature |
| Electrical Insulation | Excellent dielectric barrier | Good dielectric properties |
| Durability | Improves surface hardness and wear resistance | Contributes to overall mechanical strength |
| Application | External coating on insulator surfaces | Integral component of ceramic body |
| Cost | Moderate, depends on glaze composition | Relatively low due to abundant natural source |
Introduction to Insulators: Glaze and Feldspar
Glaze and feldspar are essential materials in the production of ceramic insulators, each contributing distinct properties to durability and electrical insulation. Feldspar acts as a fluxing agent, lowering the melting temperature and enhancing the vitrification process, which provides mechanical strength and resistance to thermal shock. Glaze forms a glassy surface layer that improves insulator waterproofing, prevents contamination, and ensures high dielectric strength under various environmental conditions.
Composition Differences: Glaze vs Feldspar
Glaze for insulators primarily consists of silica, alumina, and fluxing agents that form a glassy, non-porous surface to enhance electrical insulation and weather resistance. Feldspar, a key raw material in many glaze formulations, is rich in alkali metal oxides and alumina, serving as a flux to lower melting temperatures and improve the glaze's durability and adhesion. The main composition difference lies in glaze being a processed mixture tailored for specific functional properties, while feldspar is a naturally occurring mineral contributing essential fluxing oxides in ceramic insulator production.
Role of Glaze in Electrical Insulators
Glaze plays a critical role in electrical insulators by providing a smooth, glassy surface that enhances dielectric properties and protects against environmental degradation such as moisture and contamination. Unlike feldspar, which primarily acts as a flux to lower the melting temperature during the manufacturing process, glaze directly improves the insulator's electrical resistance and mechanical durability. The optimized combination of glaze composition and firing conditions ensures superior performance and longevity in high-voltage insulation applications.
Feldspar’s Importance in Insulator Manufacturing
Feldspar plays a critical role in insulator manufacturing by acting as a flux that lowers the melting temperature of the ceramic mix, enhancing the vitrification process for improved mechanical strength and electrical resistance. Unlike glaze, which primarily serves as a surface coating to improve aesthetics and provide a protective layer, feldspar integrates into the bulk material, contributing to the overall durability and thermal stability of the insulator. The presence of feldspar ensures that the insulator maintains structural integrity under high voltage and environmental stress, making it indispensable in high-performance ceramic insulator production.
Physical Properties Comparison
Glaze and feldspar differ significantly in physical properties relevant to insulators, with feldspar exhibiting higher melting points around 1150-1250degC, providing better thermal stability compared to glazes that typically soften at lower temperatures. Feldspar's crystalline structure enhances mechanical strength and durability, essential for insulators exposed to mechanical stress and environmental factors. In contrast, glazes offer smooth surfaces and aesthetic finishes but generally lack the robustness and electrical resistance that feldspar contributes to ceramic insulators.
Impact on Electrical Performance
Glaze composition significantly affects the dielectric strength and insulation resistance of insulators by modifying surface smoothness and porosity, thus reducing leakage currents and enhancing electrical performance. Feldspar, as a key flux in glaze formulations, lowers the melting temperature and promotes vitrification, which improves the insulator's density and dielectric properties. The optimized balance of glaze and feldspar ensures superior electrical insulation by minimizing defects and improving thermal stability under high voltage conditions.
Durability and Weather Resistance
Glaze provides a protective coating that enhances the durability of insulators by reducing surface porosity and preventing moisture absorption, which is critical for maintaining long-term electrical performance. Feldspar, a key component in the ceramic body, contributes to the structural strength and thermal stability of the insulator but offers limited surface protection compared to glaze. The combination of glaze and feldspar improves weather resistance, with glaze acting as a barrier against environmental factors such as UV rays, temperature fluctuations, and pollutants, while feldspar ensures mechanical integrity under various stress conditions.
Cost Efficiency and Availability
Feldspar offers superior cost efficiency compared to glaze for insulator manufacturing due to its abundant natural availability and lower raw material costs. Glaze requires additional processing and specialized application, increasing production expenses and limiting its use to high-performance or decorative insulators. Feldspar's widespread availability and affordability make it the preferred choice for bulk insulator production in industries prioritizing economic feasibility.
Environmental and Safety Considerations
Glaze materials for insulators often contain heavy metals and volatile organic compounds that can pose environmental hazards during manufacturing and disposal, whereas feldspar is a naturally occurring mineral with lower toxic emissions and better recyclability. Feldspar-based insulators demonstrate improved thermal stability and reduced leaching of harmful substances, enhancing workplace safety and minimizing ecological impacts. Selecting feldspar over traditional glaze reduces the carbon footprint and supports sustainable production in the electrical insulation industry.
Which Is Better for Insulators: Glaze or Feldspar?
Feldspar is generally better for insulators due to its excellent fluxing properties, which help lower the melting temperature and create a strong, durable ceramic body with high electrical insulation. Glaze enhances surface smoothness and waterproofing but does not significantly improve the core insulating properties compared to feldspar. Therefore, feldspar is preferred as the primary material for the insulating base, while glaze serves as a protective and aesthetic surface layer.
Infographic: Glaze vs Feldspar for Insulator
 azmater.com
azmater.com