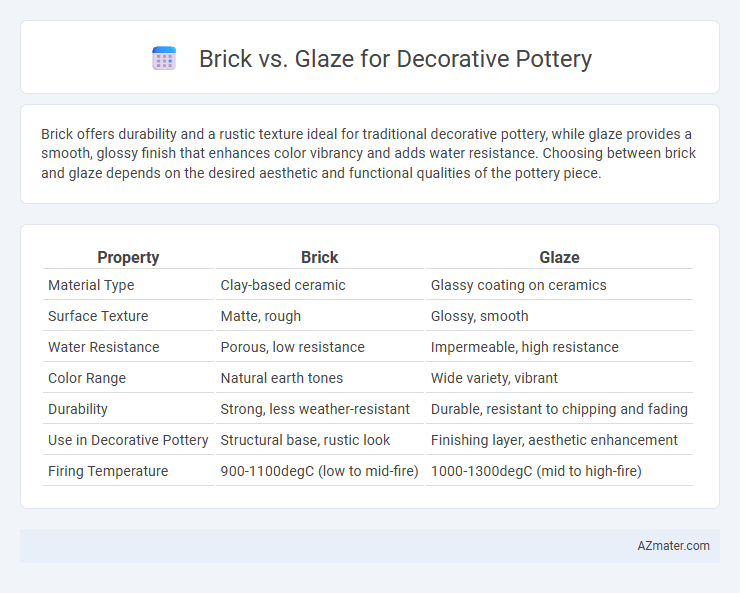
Brick offers durability and a rustic texture ideal for traditional decorative pottery, while glaze provides a smooth, glossy finish that enhances color vibrancy and adds water resistance. Choosing between brick and glaze depends on the desired aesthetic and functional qualities of the pottery piece.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Brick | Glaze |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Clay-based ceramic | Glassy coating on ceramics |
| Surface Texture | Matte, rough | Glossy, smooth |
| Water Resistance | Porous, low resistance | Impermeable, high resistance |
| Color Range | Natural earth tones | Wide variety, vibrant |
| Durability | Strong, less weather-resistant | Durable, resistant to chipping and fading |
| Use in Decorative Pottery | Structural base, rustic look | Finishing layer, aesthetic enhancement |
| Firing Temperature | 900-1100degC (low to mid-fire) | 1000-1300degC (mid to high-fire) |
Introduction to Decorative Pottery Materials
Brick and glaze represent two essential materials in decorative pottery, offering distinct aesthetic and functional properties. Brick provides a sturdy, porous base that enhances the piece's structural integrity while allowing natural textures and earthy tones to shine. Glaze serves as a glassy coating that seals pottery, adding vibrant colors, intricate patterns, and a smooth, waterproof finish that elevates visual appeal and durability.
What is Brick in Pottery?
Brick in pottery refers to a type of clay-based material traditionally used for structural and decorative ceramics, characterized by its coarse texture and high iron content that imparts a reddish hue when fired. It is valued for its durability and rustic appearance, often forming the base or body of decorative pottery pieces before glazing. Unlike glaze, brick itself is not a surface coating but the underlying ceramic material that can be enhanced or protected by various glaze applications.
Understanding Glaze: Definition and Types
Glaze is a vitreous coating fused to pottery surfaces through high-temperature firing, enhancing durability and aesthetic appeal. Types of glazes include gloss, matte, satin, raku, and crystalline, each offering distinct textures and finishes suitable for various decorative styles. Understanding glaze composition, such as silica, flux, and alumina, is essential for achieving desired effects on brick or ceramic pottery.
Aesthetic Differences: Brick vs Glaze
Brick surfaces in decorative pottery offer a raw, earthy aesthetic characterized by matte textures and natural, warm tones that emphasize rustic charm and tactile appeal. In contrast, glaze provides a smooth, glossy finish that enhances color vibrancy and creates reflective surfaces, adding depth and visual sophistication to the pottery. The choice between brick and glaze significantly influences the visual style and perceived quality, with brick embodying traditional, handcrafted aesthetics and glaze delivering modern, polished elegance.
Durability and Longevity Comparison
Brick pottery offers superior durability due to its dense, porous structure that resists chipping and cracking under physical stress. Glaze enhances decorative pottery by providing a glass-like coating that protects against moisture and surface damage, significantly extending its longevity. However, glazed pottery requires careful handling to avoid glaze crazing or chipping, making brick pottery more resilient for long-term use in harsh environments.
Color and Texture Variations
Brick and glaze offer distinct color and texture variations for decorative pottery, with brick providing warm, earthy tones such as reds, oranges, and browns characterized by a matte, rugged surface. Glaze introduces a wide spectrum of vibrant colors including blues, greens, and metallic finishes, accompanied by smooth, glossy, or even crackled textures that enhance visual appeal. The choice between brick and glaze significantly influences the tactile experience and aesthetic depth, allowing artists to tailor the pottery's surface to cultural or stylistic preferences.
Suitability for Indoor and Outdoor Use
Brick pottery exhibits excellent durability and weather resistance, making it highly suitable for outdoor use where it withstands varying climates and moisture exposure. Glazed pottery offers a smooth, protective coating that prevents water absorption and stains, ideal for indoor decorative items and controlled environments. While brick pottery excels in rugged outdoor settings, glazed finishes provide enhanced aesthetic appeal and easier maintenance indoors.
Maintenance and Cleaning Considerations
Brick pottery requires minimal maintenance but can absorb stains easily due to its porous surface, making frequent cleaning necessary with gentle brushes and mild detergents. Glazed pottery offers a smooth, sealed surface that resists stains and moisture, allowing for easier cleaning with just a damp cloth and less risk of damage over time. Proper care for brick pieces involves regular sealing to maintain durability, while glazed items benefit from avoiding abrasive cleaners to preserve their glossy finish.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Brick pottery is often made from locally sourced clay with minimal processing, resulting in lower carbon emissions and reduced energy consumption compared to glaze-coated pottery. Glazing typically involves chemical compounds and firing at higher temperatures, which increases energy use and can release volatile organic compounds (VOCs) harmful to the environment. Sustainable decorative pottery favors unglazed brick materials due to their biodegradability and lower ecological footprint throughout production and disposal.
Choosing the Right Material for Your Pottery Projects
When selecting materials for decorative pottery, the choice between brick and glaze significantly impacts the final appearance and durability. Brick clay offers a robust, earthy texture ideal for rustic, heavyweight pieces, while glaze provides a smooth, vibrant finish that enhances color depth and protects the pottery surface. Understanding the functional requirements and aesthetic goals of your project ensures the optimal material choice, balancing structural integrity with decorative appeal.
Infographic: Brick vs Glaze for Decorative Pottery
 azmater.com
azmater.com