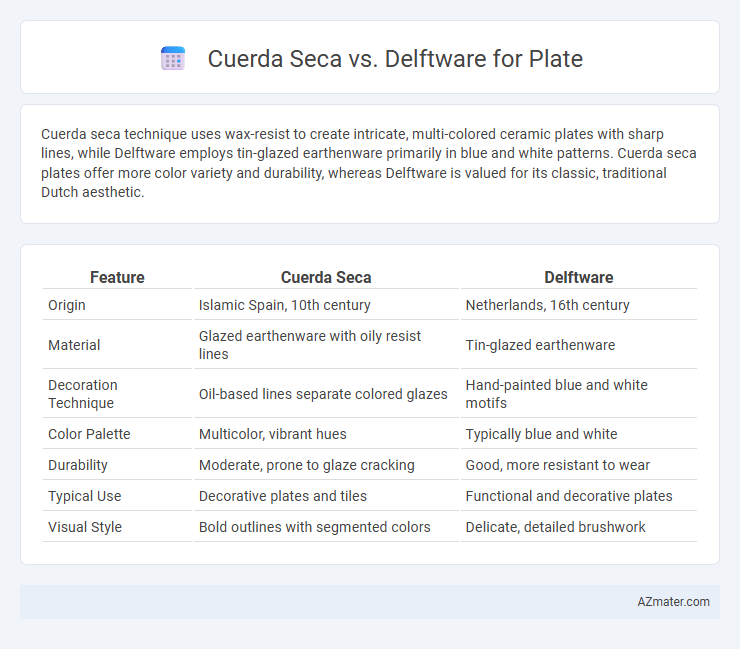
Cuerda seca technique uses wax-resist to create intricate, multi-colored ceramic plates with sharp lines, while Delftware employs tin-glazed earthenware primarily in blue and white patterns. Cuerda seca plates offer more color variety and durability, whereas Delftware is valued for its classic, traditional Dutch aesthetic.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Cuerda Seca | Delftware |
|---|---|---|
| Origin | Islamic Spain, 10th century | Netherlands, 16th century |
| Material | Glazed earthenware with oily resist lines | Tin-glazed earthenware |
| Decoration Technique | Oil-based lines separate colored glazes | Hand-painted blue and white motifs |
| Color Palette | Multicolor, vibrant hues | Typically blue and white |
| Durability | Moderate, prone to glaze cracking | Good, more resistant to wear |
| Typical Use | Decorative plates and tiles | Functional and decorative plates |
| Visual Style | Bold outlines with segmented colors | Delicate, detailed brushwork |
Introduction to Decorative Plate Techniques
Cuerda seca and Delftware are distinctive ceramic decoration techniques used in decorative plates, each reflecting unique cultural and artistic traditions. Cuerda seca, originating from Islamic pottery, employs a greasy resist line that separates vibrant colored glazes, creating intricate patterns without color bleeding. Delftware, rooted in Dutch craftsmanship, features tin-glazed earthenware painted predominantly in blue and white, showcasing detailed scenes and floral motifs with a smooth, glossy finish.
What is Cuerda Seca?
Cuerda seca is a traditional ceramic glazing technique originating from Spain and widely used in Islamic art, characterized by using oily substances to separate different colored glazes on pottery, preventing the colors from mixing during firing. Contrastingly, Delftware is a Dutch tin-glazed pottery known for its blue and white designs, relying on a smooth, plaque-like surface without the color separation lines seen in cuerda seca. The cuerda seca process allows intricate multicolored designs with crisp, black outlines, offering a distinct visual texture compared to the soft, blended look of Delftware.
What is Delftware?
Delftware is a distinctive type of Dutch tin-glazed pottery featuring intricate blue and white designs, traditionally produced in Delft since the 16th century. This ceramic technique involves applying a white tin glaze to create a smooth, opaque surface that enhances the hand-painted cobalt blue motifs, often depicting landscapes, floral patterns, or scenes from daily life. Delftware plates are prized for their delicate artistry and historical significance, contrasting with the more geometric and colorful patterns found in the Spanish-Moorish cuerda seca style.
Historical Origins and Development
Cuerda seca technique, originating in the Islamic art of the 9th century, uses oily substances mixed with pigment to create separated color segments on ceramic plates, facilitating intricate multicolor designs without color bleeding. Delftware emerged in the 16th century in the Netherlands, inspired by Chinese blue-and-white porcelain, evolving into tin-glazed earthenware famous for its distinctive cobalt blue motifs and floral patterns on white plates. While cuerda seca emphasizes precise color isolation for vibrant patterns rooted in Moorish traditions, Delftware reflects European adaptations of Asian ceramics with a distinctive glaze and painting style suited to local tastes.
Materials and Glazing Differences
Cuerda seca and Delftware plates differ significantly in materials and glazing techniques, with cuerda seca utilizing a wax-resist method that separates brightly colored glazes on terracotta or ceramic bases, preventing color blending during firing. Delftware typically uses tin-glazed earthenware, producing a white, opaque surface decorated with cobalt blue designs, offering a smooth, glossy finish distinct from the textured, multicolored look of cuerda seca. The cuerda seca process allows multiple vivid pigments without bleeding, while Delftware relies on a uniform glaze layer to enhance intricate hand-painted patterns.
Design Styles and Motifs Compared
Cuerda seca plates feature bold, intricate designs characterized by vibrant, contrasting colors with black outlines that prevent color bleeding, reflecting Moorish and Islamic art influences. Delftware plates showcase delicate blue and white motifs inspired by Chinese porcelain, often depicting floral patterns, pastoral scenes, or Dutch cultural elements with a focus on symmetry and subtle shading. The cuerda seca style emphasizes vivid color separation and geometric patterns, while Delftware prioritizes monochromatic elegance and detailed narrative imagery.
Techniques: Process and Skill Requirements
Cuerda seca and Delftware employ distinct ceramic decoration techniques, with cuerda seca involving the use of greasy lines to separate colored glazes, preventing mingling during firing, which requires precise control of wax resist and glaze application. Delftware relies on tin-glazed earthenware painted with cobalt oxide designs, demanding skilled brushwork and careful firing to achieve vivid blue patterns on a white background. Mastery of cuerda seca involves intricate wax line drawing and timed glazing steps, while Delftware artisans focus on steady hand painting and maintaining glaze consistency.
Durability and Practical Use
Cuerda seca plates feature a durable glazed surface that resists chipping and fading, making them suitable for everyday use and frequent handling. Delftware plates, often made from tin-glazed earthenware, are more prone to crazing and chipping due to their delicate glaze and softer clay composition. For practical use, cuerda seca is favored in high-traffic settings, whereas Delftware is typically reserved for decorative purposes or gentle, occasional use.
Popularity and Influence in Modern Ceramics
Cuerda seca and Delftware techniques significantly influence modern ceramic plate designs, with Delftware maintaining widespread popularity due to its iconic blue and white patterns rooted in 17th-century Dutch pottery. Cuerda seca, known for its vibrant, multi-colored glazes separated by wax lines, enjoys niche appeal among artists seeking intricate Islamic-inspired motifs. The enduring legacy of Delftware shapes contemporary ceramics globally, while cuerda seca continues to inspire experimental and artisanal craftsmanship in specialized ceramics markets.
Choosing Between Cuerda Seca and Delftware for Plates
Choosing between cuerda seca and Delftware for plates depends on the desired aesthetic and production technique. Cuerda seca, a Spanish-Moorish method, uses oily resist lines to contain multicolored glazes, resulting in vivid, intricate patterns ideal for decorative and functional use. Delftware, characterized by its blue-and-white tin-glazed pottery from the Netherlands, offers classic, hand-painted motifs with a smooth finish, perfect for traditional and collectible tableware.
Infographic: Cuerda seca vs Delftware for Plate
 azmater.com
azmater.com