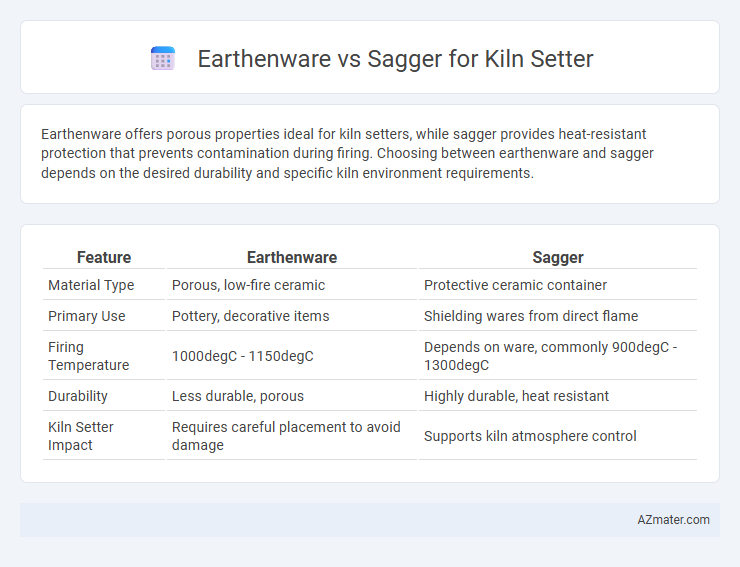
Earthenware offers porous properties ideal for kiln setters, while sagger provides heat-resistant protection that prevents contamination during firing. Choosing between earthenware and sagger depends on the desired durability and specific kiln environment requirements.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Earthenware | Sagger |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Porous, low-fire ceramic | Protective ceramic container |
| Primary Use | Pottery, decorative items | Shielding wares from direct flame |
| Firing Temperature | 1000degC - 1150degC | Depends on ware, commonly 900degC - 1300degC |
| Durability | Less durable, porous | Highly durable, heat resistant |
| Kiln Setter Impact | Requires careful placement to avoid damage | Supports kiln atmosphere control |
Introduction to Earthenware and Sagger
Earthenware is a common type of ceramic fired at lower temperatures, typically between 1,000degC and 1,150degC, known for its porous nature and warm, earthy tones. Saggers are protective containers used in kilns to shield delicate earthenware from direct flame and ash, ensuring even firing and preventing damage or contamination. Using saggers with earthenware improves the final product's surface quality and structural integrity during the firing process.
Understanding Kiln Setters
Kiln setters are essential devices that control the firing process and prevent overfiring by shutting off the kiln at a preset temperature. Earthenware kilns often utilize saggers--protective containers made from refractory materials--to shield delicate pottery from direct flame and ash deposits during firing. Understanding the compatibility of kiln setters with saggers or earthenware environments ensures precise temperature regulation and improved ceramic results.
What Is Earthenware?
Earthenware is a type of porous ceramic fired at low temperatures between 1,000degC and 1,150degC, commonly used for pottery and decorative items due to its durability and earthy texture. It contrasts with a sagger, which is a protective container made from refractory materials used in kilns to shield delicate pieces from direct flame and ash during firing. Understanding the firing range and material properties of earthenware is crucial for selecting appropriate sagger usage in kiln setters to ensure optimal results and prevent damage.
What Is a Sagger?
A sagger is a protective container or casing used inside a kiln to shield delicate ceramic pieces, such as earthenware, from direct flame and ash during firing. Made from refractory materials like fireclay or silicon carbide, saggers create a controlled microenvironment that prevents contamination and ensures even heat distribution. Unlike earthenware, which is the ceramic material being fired, saggers serve as a durable barrier that enhances the quality and finish of kiln-fired ceramics.
Key Differences: Earthenware vs Sagger
Earthenware is a porous, low-fired ceramic often used for pottery and tableware, while sagger is a protective container used inside kilns to shield ceramics from direct flame and ash during high-temperature firing. Earthenware typically fires between 1,000degC and 1,150degC, whereas saggers withstand higher temperatures above 1,200degC to protect delicate wares. The primary difference lies in function: earthenware is the fired product, while saggers are kiln accessories designed to preserve the surface quality of ceramics during firing.
Advantages of Using Earthenware as Kiln Setter
Earthenware as a kiln setter offers exceptional thermal insulation and durability, effectively protecting kiln elements from high-temperature damage. Its porous structure provides superior heat resistance and minimizes thermal shock, extending the lifespan of kiln components. Furthermore, earthenware is cost-effective and easy to shape, making it an ideal material for custom kiln setters in ceramic firing processes.
Benefits of Sagger for Kiln Setting
Saggers provide excellent protection for earthenware during kiln firing by preventing direct contact with flames and debris, ensuring cleaner and more uniform finishes. They enhance temperature control and reduce the risk of warping or cracking by creating a stable microenvironment within the kiln setter. Their reusability and heat resistance make saggers a cost-effective choice for consistent and high-quality kiln firings.
Best Applications for Each Material
Earthenware is ideal for kiln setters when producing decorative pottery and low-fire ceramics, as its porous nature withstands thermal shock without damaging fragile pieces. Saggars excel in high-temperature firings and industrial applications by providing a protective barrier against oxidation and flame damage, ensuring precise kiln atmosphere control. Choosing earthenware suits artisans prioritizing aesthetic glazes, while saggars benefit mass production requiring consistent, high-quality finishes.
Durability and Performance Comparison
Earthenware typically exhibits lower durability due to its porous structure compared to the dense, heat-resistant properties of saggers used in kiln setters. Saggers provide superior thermal insulation and protection against direct flame contact, enhancing overall kiln setter performance and longevity. This results in saggers maintaining structural integrity longer in high-temperature environments, making them more reliable for repeated firing cycles.
Choosing the Right Kiln Setter: Earthenware or Sagger
Choosing the right kiln setter between earthenware and sagger depends on the firing temperature and the type of ceramics being produced, as earthenware typically requires lower temperatures around 1000-1150degC while sagger can withstand higher heat up to cone 10 (about 1300degC). Earthenware kiln setters are often preferred for porous, thinner pieces that need controlled oxidation atmospheres, whereas sagger setters offer superior protection for delicate designs and reduce ash or gas deposits during firing. Selecting a kiln setter optimized for the intended clay body and firing atmosphere ensures consistent results and protects the kiln elements from damage.
Infographic: Earthenware vs Sagger for Kiln Setter
 azmater.com
azmater.com