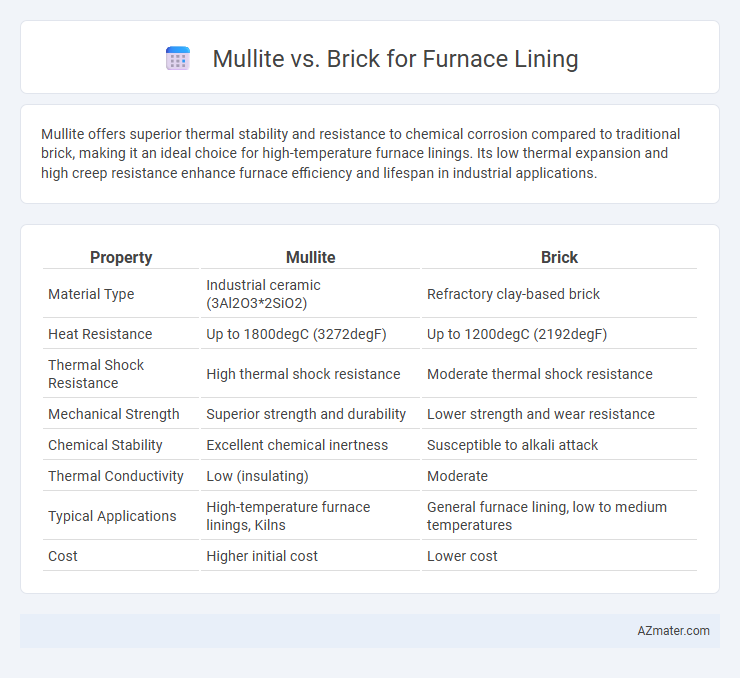
Mullite offers superior thermal stability and resistance to chemical corrosion compared to traditional brick, making it an ideal choice for high-temperature furnace linings. Its low thermal expansion and high creep resistance enhance furnace efficiency and lifespan in industrial applications.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Mullite | Brick |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Industrial ceramic (3Al2O3*2SiO2) | Refractory clay-based brick |
| Heat Resistance | Up to 1800degC (3272degF) | Up to 1200degC (2192degF) |
| Thermal Shock Resistance | High thermal shock resistance | Moderate thermal shock resistance |
| Mechanical Strength | Superior strength and durability | Lower strength and wear resistance |
| Chemical Stability | Excellent chemical inertness | Susceptible to alkali attack |
| Thermal Conductivity | Low (insulating) | Moderate |
| Typical Applications | High-temperature furnace linings, Kilns | General furnace lining, low to medium temperatures |
| Cost | Higher initial cost | Lower cost |
Introduction to Furnace Lining Materials
Mullite and brick are prominent furnace lining materials known for their high-temperature resistance and thermal stability. Mullite, a synthetic crystalline aluminosilicate, offers superior mechanical strength and thermal shock resistance compared to traditional firebrick, improving furnace longevity. Firebrick remains cost-effective and widely used for moderate to high-temperature applications but lacks the enhanced durability and insulating properties of mullite linings.
Overview of Mullite and Traditional Brick
Mullite is an advanced refractory material characterized by high thermal stability, excellent resistance to thermal shock, and low thermal expansion, making it ideal for furnace lining applications. Traditional fire bricks, composed mainly of alumina and silica, offer robust structural integrity and good heat resistance but have lower thermal shock resistance compared to mullite. The superior chemical stability and mechanical strength of mullite often result in increased furnace longevity and efficiency compared to conventional brick linings.
Key Thermal Properties: Mullite vs Brick
Mullite offers superior thermal stability with a melting point of approximately 1840degC compared to traditional firebrick, which melts around 1780degC, making it ideal for high-temperature furnace linings. Its low thermal conductivity (around 3 W/m*K) ensures better insulation, reducing heat loss and energy consumption, whereas firebrick typically exhibits higher thermal conductivity, resulting in greater heat transfer. Mullite's excellent thermal shock resistance and low creep rate enhance furnace durability under cyclical heating and cooling conditions, outperforming standard firebrick materials.
Mechanical Strength and Durability Comparison
Mullite exhibits superior mechanical strength compared to traditional brick, with a higher resistance to thermal shock and mechanical wear, making it ideal for furnace linings exposed to extreme temperatures. Its low thermal expansion and high melting point contribute to enhanced durability and prolonged service life in high-stress industrial environments. Brick, while cost-effective, often falls short in long-term structural stability and erosion resistance under continuous thermal cycling conditions.
Chemical Resistance and Corrosion Protection
Mullite offers superior chemical resistance and corrosion protection compared to traditional brick, making it ideal for furnace linings exposed to acidic gases and slag. Its high alumina content and stable crystalline structure resist chemical attack and minimize degradation under harsh thermal cycles. In contrast, standard firebrick is more susceptible to corrosion and chemical erosion, reducing its lifespan in aggressive furnace environments.
Insulation Efficiency: Energy Savings Analysis
Mullite offers superior insulation efficiency compared to traditional brick in furnace linings due to its low thermal conductivity and high refractoriness, resulting in reduced heat loss and lower energy consumption. Furnaces lined with mullite typically demonstrate energy savings of up to 15-20%, enhancing operational cost-effectiveness in high-temperature applications. The material's ability to maintain structural integrity at elevated temperatures further contributes to improved energy retention and prolonged furnace lifespan.
Installation & Maintenance Requirements
Mullite furnace linings offer superior thermal stability and resistance to chemical attack, resulting in less frequent maintenance compared to traditional brick linings. Installation of mullite linings requires specialized techniques, including precise casting or gunning to ensure optimal density and strength, whereas brick linings involve more labor-intensive stacking and mortar application. Maintenance demands for brick linings are higher due to potential spalling and cracking under thermal cycling, leading to more frequent inspections and repairs.
Cost-effectiveness: Initial vs Lifetime Expense
Mullite furnace linings offer higher initial costs compared to traditional bricks due to advanced manufacturing and superior thermal properties. Despite the upfront investment, mullite's enhanced durability and resistance to thermal shock reduce maintenance and replacement expenses, lowering the overall lifetime cost. Bricks may appear cost-effective initially but often incur higher long-term expenses from frequent repairs and shorter service life in high-temperature applications.
Suitability for Different Furnace Applications
Mullite offers superior thermal stability and resistance to thermal shock, making it ideal for high-temperature furnace linings in industries like steelmaking and glass production. Brick linings, particularly firebricks, provide cost-effective insulation suitable for lower temperature applications such as ceramic kilns and domestic furnaces. Selection between mullite and brick depends on operating temperature, mechanical stress, and chemical environment, with mullite preferred for extreme conditions and bricks favored for moderate use.
Choosing the Right Lining: Mullite or Brick?
Mullite offers superior thermal stability and chemical resistance compared to traditional fire brick, making it ideal for high-temperature furnace linings exposed to aggressive environments. Fire bricks, typically composed of alumina and silica, provide excellent mechanical strength and are cost-effective for general-purpose applications with moderate thermal loads. Selecting the right furnace lining depends on operational temperature, chemical exposure, and budget constraints, with mullite favored for demanding conditions and fire brick preferred for standard industrial use.
Infographic: Mullite vs Brick for Furnace Lining
 azmater.com
azmater.com