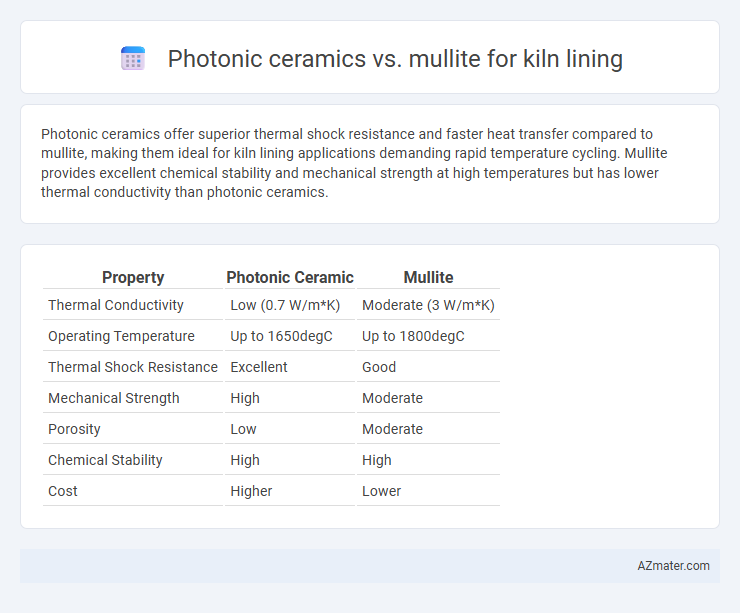
Photonic ceramics offer superior thermal shock resistance and faster heat transfer compared to mullite, making them ideal for kiln lining applications demanding rapid temperature cycling. Mullite provides excellent chemical stability and mechanical strength at high temperatures but has lower thermal conductivity than photonic ceramics.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Photonic Ceramic | Mullite |
|---|---|---|
| Thermal Conductivity | Low (0.7 W/m*K) | Moderate (3 W/m*K) |
| Operating Temperature | Up to 1650degC | Up to 1800degC |
| Thermal Shock Resistance | Excellent | Good |
| Mechanical Strength | High | Moderate |
| Porosity | Low | Moderate |
| Chemical Stability | High | High |
| Cost | Higher | Lower |
Introduction to Kiln Lining Materials
Photonic ceramic and mullite are commonly used kiln lining materials with distinct thermal and mechanical properties. Photonic ceramic offers superior thermal shock resistance and insulation efficiency, enhancing kiln energy savings and durability. Mullite provides excellent high-temperature stability and chemical resistance, making it ideal for prolonged exposure in harsh kiln environments.
Overview of Photonic Ceramic
Photonic ceramic, an advanced material engineered with superior thermal insulation and high-temperature stability, offers enhanced durability and energy efficiency compared to traditional mullite for kiln linings. Its unique microstructure reduces heat loss, improving kiln performance and lifespan under extreme operating conditions up to 1600degC. Photonic ceramic's lightweight and low thermal conductivity properties make it a cutting-edge alternative for modern industrial kilns requiring optimal thermal management.
Understanding Mullite in Kiln Applications
Mullite is a critical material for kiln linings due to its exceptional thermal stability, low thermal expansion, and high resistance to thermal shock, making it ideal for high-temperature environments. Its composition, primarily alumina and silica, provides mechanical strength and chemical inertness, which enhances kiln durability and energy efficiency. Compared to photonic ceramics, mullite offers superior resistance to deformation and longer lifespan under extreme firing conditions, ensuring consistent kiln performance.
Thermal Performance Comparison
Photonic ceramic exhibits superior thermal insulation properties with lower thermal conductivity (around 0.15 W/m*K) compared to mullite, which typically ranges between 1.5 to 3.0 W/m*K, enabling better heat retention and energy efficiency in kiln lining applications. Mullite offers excellent thermal shock resistance and mechanical strength but allows more heat transfer, leading to higher energy consumption during firing cycles. Photonic ceramic's enhanced insulation reduces heat loss, improving kiln operating temperatures and lifespan while maintaining structural stability under high thermal loads.
Mechanical Strength and Durability
Photonic ceramic offers higher mechanical strength compared to mullite, with superior resistance to thermal shock and mechanical wear, making it ideal for high-stress kiln lining applications. Mullite, while also thermally stable, exhibits lower fracture toughness and can degrade faster under cyclic thermal loads, reducing its long-term durability. The enhanced mechanical properties of photonic ceramics contribute to extended service life and improved reliability in industrial kiln environments.
Resistance to Chemical Attack
Photonic ceramics exhibit superior resistance to chemical attack compared to mullite, making them ideal for kiln linings exposed to aggressive atmospheres containing alkalis and acids. Their dense microstructure minimizes porosity, reducing chemical infiltration and prolonging service life under corrosive conditions. Mullite, while offering good thermal stability, tends to degrade faster when exposed to molten salts and acidic vapors, limiting its durability in harsh chemical environments.
Energy Efficiency and Heat Retention
Photonic ceramic outperforms mullite in kiln lining due to its superior energy efficiency and exceptional heat retention properties, reducing fuel consumption significantly. Its advanced microstructure offers lower thermal conductivity and enhanced insulation, ensuring stable internal temperatures and faster heating cycles. Mullite, while durable, exhibits higher thermal conductivity which leads to increased heat loss and less efficient energy use during prolonged kiln operation.
Cost Analysis and Lifespan
Photonic ceramic offers a higher initial cost compared to mullite but provides superior thermal shock resistance and longer service life, reducing replacement frequency in kiln lining applications. Mullite, while more cost-effective upfront, tends to wear faster under extreme thermal conditions, leading to increased maintenance expenses over time. Evaluating total cost of ownership shows photonic ceramic's durability often offsets its premium price through lower lifecycle costs and minimized downtime.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Photonic ceramic offers superior thermal insulation with lower energy consumption during kiln operation, resulting in reduced carbon emissions compared to mullite. Mullite, while durable and resistant to thermal shock, generally requires higher firing temperatures, increasing fuel usage and environmental impact. The enhanced energy efficiency and recyclability of photonic ceramic materials contribute to a more sustainable kiln lining solution.
Choosing the Best Material for Kiln Lining
Photonic ceramic offers superior thermal shock resistance and durability compared to mullite, making it ideal for high-temperature kiln lining applications that demand longevity and efficiency. Mullite, while providing good thermal insulation and structural stability, tends to have lower resistance to thermal cycling and mechanical stress under extreme conditions. Selecting photonic ceramic enhances kiln operational performance by reducing maintenance frequency and energy consumption, whereas mullite may suit less demanding environments with moderate temperatures.
Infographic: Photonic ceramic vs Mullite for Kiln lining
 azmater.com
azmater.com