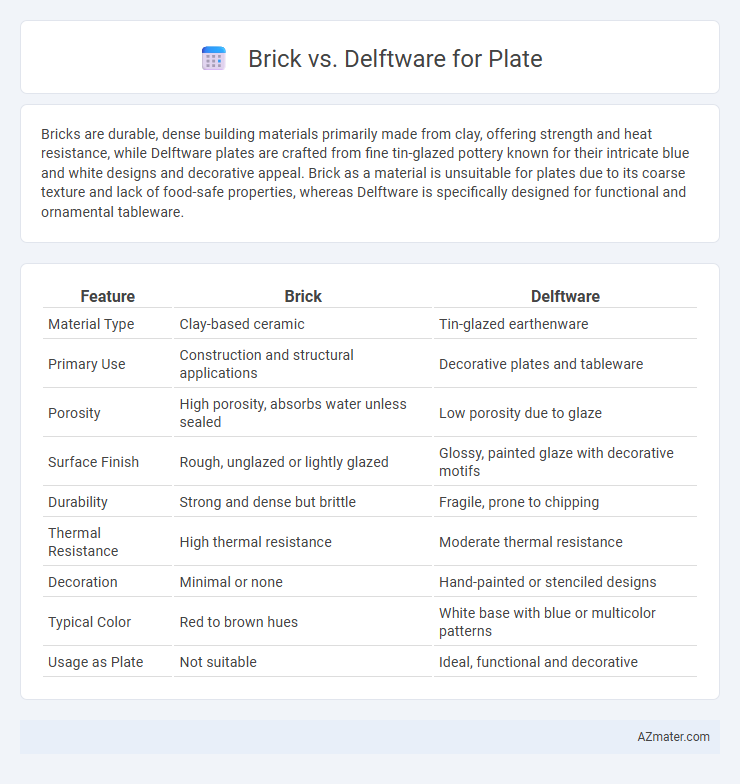
Bricks are durable, dense building materials primarily made from clay, offering strength and heat resistance, while Delftware plates are crafted from fine tin-glazed pottery known for their intricate blue and white designs and decorative appeal. Brick as a material is unsuitable for plates due to its coarse texture and lack of food-safe properties, whereas Delftware is specifically designed for functional and ornamental tableware.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Brick | Delftware |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Clay-based ceramic | Tin-glazed earthenware |
| Primary Use | Construction and structural applications | Decorative plates and tableware |
| Porosity | High porosity, absorbs water unless sealed | Low porosity due to glaze |
| Surface Finish | Rough, unglazed or lightly glazed | Glossy, painted glaze with decorative motifs |
| Durability | Strong and dense but brittle | Fragile, prone to chipping |
| Thermal Resistance | High thermal resistance | Moderate thermal resistance |
| Decoration | Minimal or none | Hand-painted or stenciled designs |
| Typical Color | Red to brown hues | White base with blue or multicolor patterns |
| Usage as Plate | Not suitable | Ideal, functional and decorative |
Introduction to Brick and Delftware Plates
Brick plates, known for their sturdy, rustic texture, are crafted from high-quality clay that undergoes high-temperature firing, resulting in durable and heat-resistant dinnerware ideal for everyday use. Delftware plates originate from the Netherlands, characterized by their distinctive blue and white tin-glazed pottery, often adorned with intricate hand-painted designs inspired by 17th-century Dutch artisans. Both styles offer unique aesthetic and functional qualities, with Brick plates emphasizing robustness and Delftware plates highlighting artistic heritage.
Historical Background of Brick Plates
Brick plates trace their origins to early industrial Europe, where they emerged as durable, utilitarian ceramic tableware primarily used by working-class households. Characterized by a dense, reddish clay composition, brick plates reflect a practical approach to pottery that contrasts with the more ornate and decorative Delftware, which originated in the Netherlands during the 16th century. The historical significance of brick plates lies in their widespread availability and robust construction, catering to everyday use before the rise of more refined ceramic techniques.
Origins and Evolution of Delftware Plates
Brick originated as a durable construction material in ancient Mesopotamia, contrasting with Delftware plates that trace their origins to 16th-century Netherlands, inspired by Chinese porcelain. Delftware plates evolved through the integration of tin-glazed earthenware techniques, combining Dutch artistry with Oriental motifs to create distinctive blue and white designs. Over centuries, Delftware became a symbol of Dutch cultural heritage, reflecting both European craftsmanship and global trade influences.
Material Composition: Brick vs Delftware
Brick plates are typically made from dense clay mixed with iron oxide, resulting in a sturdy, reddish-brown material that is less porous and highly durable. Delftware plates consist of tin-glazed earthenware made from a white clay base coated with a lead glaze containing tin oxide, creating a bright white, smooth surface ideal for detailed blue and white decorations. The material composition of brick provides structural strength and rustic texture, while Delftware's glaze allows for intricate artistry and a delicate finish.
Durability and Longevity Comparison
Brick plates exhibit exceptional durability due to their dense, robust ceramic composition, making them highly resistant to chipping and cracking under regular use. Delftware plates, crafted from tin-glazed earthenware, offer beautiful intricate designs but tend to be more susceptible to wear, chipping, and fading over time. The longevity of brick plates surpasses Delftware, making them more suitable for daily use and long-term durability.
Aesthetic Appeal and Design Differences
Brick plates showcase a rustic, earthy aesthetic characterized by their textured surfaces and warm, natural hues, often reflecting traditional handcrafted techniques. Delftware plates are celebrated for their smooth, glossy finish and iconic blue-and-white motifs, featuring intricate floral or scenic patterns rooted in Dutch artistry. The design contrast lies in Brick plates' organic, tactile appeal versus Delftware's refined, delicate ornamentation, catering to distinct stylistic preferences.
Functional Uses in Daily Life
Brick plates offer durability and heat resistance, making them ideal for everyday use such as serving hot meals and baking. Delftware plates, characterized by their brittle ceramic composition, are better suited for decorative purposes or light serving tasks rather than heavy daily use. The functional difference lies in Brick plates' robustness for frequent handling versus Delftware's aesthetic appeal in formal dining settings.
Maintenance and Care Requirements
Brick plates require minimal maintenance, needing only gentle hand washing with mild detergent to preserve their texture and prevent chipping. Delftware plates demand more careful handling, as their delicate blue-and-white glaze can be sensitive to abrasive cleaners and sudden temperature changes, necessitating soft cloth cleaning and avoiding dishwasher use. Regularly inspecting both types for cracks or damage ensures longevity and maintains their aesthetic appeal.
Cost and Availability Analysis
Brick plates generally have lower production costs due to simpler materials and manufacturing processes, making them more budget-friendly and widely accessible. Delftware plates, crafted with intricate hand-painted designs and higher-quality ceramics, tend to be more expensive and less readily available, especially outside specialty markets. Availability of Brick plates is high in mass retail stores, while Delftware often requires purchase from niche boutiques or online collectors.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Brick plates, often made from fired clay with minimal processing, have a lower environmental impact due to their use of abundant natural materials and energy-efficient production methods. Delftware, characterized by its tin-glazed earthenware and intricate hand-painted designs, involves more resource-intensive firing and glazing processes that may contribute to higher energy consumption and chemical use. Sustainable choice leans towards brick plates for their durability, biodegradability, and reduced reliance on synthetic glazes compared to Delftware's complex artisanal production.
Infographic: Brick vs Delftware for Plate
 azmater.com
azmater.com