Sagger offers high thermal stability and low thermal expansion, making it ideal for insulating materials in high-temperature kiln environments. Alumina insulators exhibit superior mechanical strength and excellent electrical insulation properties, enhancing durability in industrial applications.
Table of Comparison
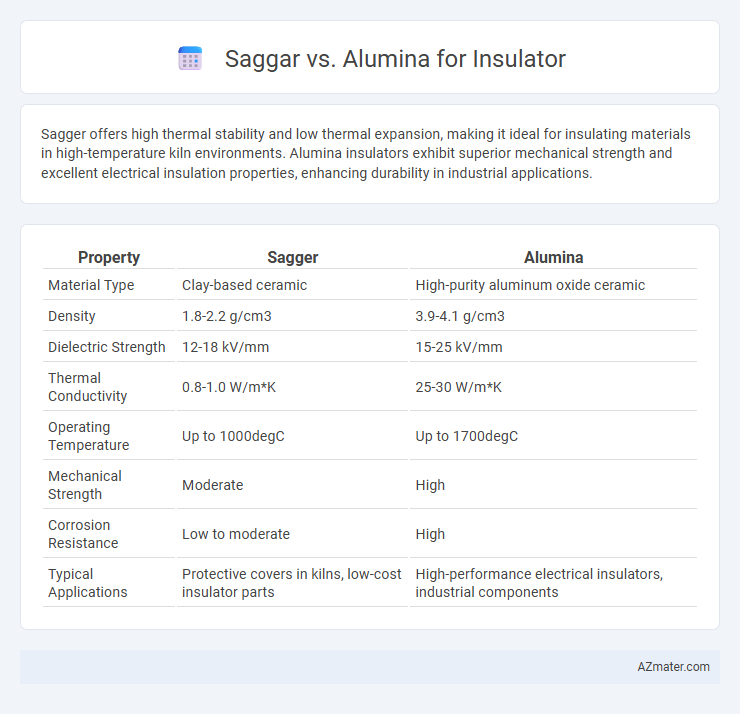
| Property | Sagger | Alumina |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Clay-based ceramic | High-purity aluminum oxide ceramic |
| Density | 1.8-2.2 g/cm3 | 3.9-4.1 g/cm3 |
| Dielectric Strength | 12-18 kV/mm | 15-25 kV/mm |
| Thermal Conductivity | 0.8-1.0 W/m*K | 25-30 W/m*K |
| Operating Temperature | Up to 1000degC | Up to 1700degC |
| Mechanical Strength | Moderate | High |
| Corrosion Resistance | Low to moderate | High |
| Typical Applications | Protective covers in kilns, low-cost insulator parts | High-performance electrical insulators, industrial components |
Introduction to Sagger and Alumina Insulators
Sagger is a refractory ceramic container used to protect materials from direct flame or contamination during high-temperature processes, often made from high-purity alumina or clay-based materials to withstand thermal shocks. Alumina insulators, composed primarily of aluminum oxide (Al2O3), exhibit excellent electrical insulation properties, high thermal conductivity, and outstanding mechanical strength, making them ideal for use in harsh industrial environments. Both sagger and alumina insulators are critical in high-temperature applications, where durability and resistance to thermal degradation ensure optimal performance and longevity.
Material Composition: Sagger vs Alumina
Sagger primarily consists of refractory clay mixed with fire clay and mullite, designed to withstand extreme kiln temperatures and protect ware during firing. Alumina, composed largely of aluminum oxide (Al2O3) with high purity levels ranging from 90% to 99.9%, offers superior thermal conductivity, electrical insulation, and mechanical strength. The distinct material compositions influence their performance where sagger provides insulation through a layered ceramic matrix, while alumina delivers enhanced durability and electrical insulation in high-temperature applications.
Thermal Resistance: Comparative Analysis
Sagger and alumina insulators significantly differ in thermal resistance, with alumina exhibiting superior stability at high temperatures due to its high melting point of 2072degC and thermal conductivity ranging from 20-30 W/mK. Sagger material, primarily made from fireclay or kaolin, has lower thermal conductivity and melting points around 1600-1800degC, resulting in less efficient heat dissipation under extreme conditions. The enhanced thermal resistance of alumina insulators makes them highly suitable for applications demanding prolonged exposure to high thermal stress and electrical insulation.
Electrical Insulation Performance
Sagger and alumina both serve as critical materials in electrical insulation, but alumina offers superior dielectric strength and thermal stability, making it more effective for high-voltage applications. Alumina insulators exhibit lower dielectric loss and higher resistivity compared to sagger, enhancing their performance in minimizing electrical leakage and insulation failure. These electrical insulation properties make alumina the preferred choice for advanced insulator design in power transmission and electronic devices.
Mechanical Strength and Durability
Sagger, made primarily from refractory clay, offers moderate mechanical strength but lower durability compared to alumina, which boasts significantly higher hardness and resistance to thermal shock due to its dense, crystalline structure. Alumina insulators demonstrate superior mechanical strength, with flexural strength values often exceeding 300 MPa, making them ideal for high-stress applications. The enhanced durability of alumina insulators also stems from their excellent resistance to chemical corrosion and wear, resulting in longer service life under extreme conditions.
Chemical Stability in Extreme Conditions
Sagger ceramics exhibit superior chemical stability compared to alumina insulators when exposed to extreme conditions such as high temperatures and aggressive chemical atmospheres. Alumina, although widely used for its hardness and thermal conductivity, can undergo phase transformations and chemical corrosion that degrade its insulating properties. The high purity and dense microstructure of sagger materials resist chemical attack and thermal shock, making them more reliable for demanding industrial applications involving harsh environmental stresses.
Cost-Effectiveness and Availability
Sagger and alumina differ significantly in cost-effectiveness and availability for insulator applications. Sagger, primarily composed of refractory clay, offers a low-cost and widely available option but may lack the superior thermal and electrical properties of alumina. Alumina insulators, though more expensive and less abundant, provide enhanced durability, higher dielectric strength, and better resistance to high temperatures, justifying their cost in demanding industrial environments.
Applications in Industrial Settings
Sagger and alumina both serve crucial roles as insulators in industrial settings, with sagger primarily used in high-temperature furnaces for protecting ceramic ware during firing, while alumina excels in electrical insulation due to its high dielectric strength and thermal stability. Alumina's superior resistance to wear, corrosion, and thermal shock makes it ideal for applications in electronics manufacturing, power plants, and chemical processing equipment. Industries rely on alumina for components such as insulator tubes, substrates, and spark plugs, whereas saggers are essential in ceramics and metallurgy for controlled atmosphere treatments.
Lifespan and Maintenance Requirements
Sagger insulators typically exhibit higher lifespan due to their robust composition, often withstanding extreme thermal cycling and mechanical stress better than alumina insulators. Alumina insulators offer superior electrical properties but generally require more frequent maintenance to address surface contamination and potential brittleness over time. Maintenance for sagger insulators is less intensive, focusing mainly on structural integrity checks, whereas alumina insulators demand regular cleaning and inspection to maintain optimal performance.
Choosing Between Sagger and Alumina Insulators
Choosing between Sagger and Alumina insulators depends on the specific thermal and mechanical requirements of the application. Sagger insulators, typically composed of ceramic materials with high thermal stability, offer excellent protection against contamination and enable uniform heat distribution in kiln processes. Alumina insulators provide superior electrical insulation, high mechanical strength, and resistance to thermal shock, making them ideal for high-temperature industrial environments.
Infographic: Sagger vs Alumina for Insulator
 azmater.com
azmater.com