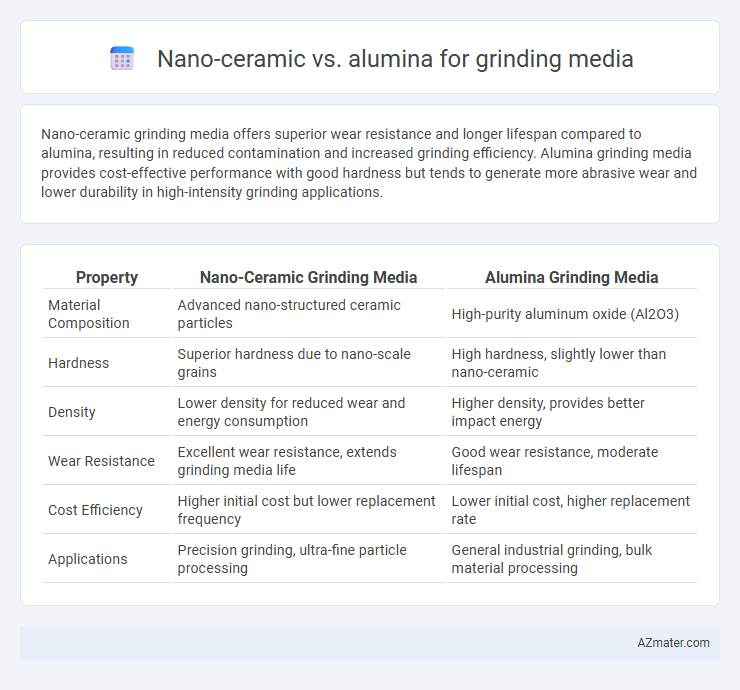
Nano-ceramic grinding media offers superior wear resistance and longer lifespan compared to alumina, resulting in reduced contamination and increased grinding efficiency. Alumina grinding media provides cost-effective performance with good hardness but tends to generate more abrasive wear and lower durability in high-intensity grinding applications.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Nano-Ceramic Grinding Media | Alumina Grinding Media |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Advanced nano-structured ceramic particles | High-purity aluminum oxide (Al2O3) |
| Hardness | Superior hardness due to nano-scale grains | High hardness, slightly lower than nano-ceramic |
| Density | Lower density for reduced wear and energy consumption | Higher density, provides better impact energy |
| Wear Resistance | Excellent wear resistance, extends grinding media life | Good wear resistance, moderate lifespan |
| Cost Efficiency | Higher initial cost but lower replacement frequency | Lower initial cost, higher replacement rate |
| Applications | Precision grinding, ultra-fine particle processing | General industrial grinding, bulk material processing |
Introduction to Grinding Media Materials
Nano-ceramic and alumina grinding media exhibit distinct physical and chemical properties essential for optimized milling performance. Nano-ceramics offer high hardness, superior wear resistance, and enhanced grinding efficiency due to their fine particle size and uniform microstructure. Alumina grinding media, commonly composed of high-purity aluminum oxide, provide excellent chemical inertness and mechanical strength, making them suitable for diverse industrial applications such as mineral processing and chemical manufacturing.
Overview of Nano-Ceramic Grinding Media
Nano-ceramic grinding media consist of ultra-fine ceramic particles engineered at the nanometer scale, offering superior hardness, wear resistance, and toughness compared to conventional alumina media. These properties enhance grinding efficiency and reduce contamination in high-precision applications such as electronics and pharmaceuticals. Nano-ceramic media maintain consistent particle size distribution, leading to improved product uniformity and extended lifespan during milling processes.
Alumina Grinding Media: Properties and Uses
Alumina grinding media exhibit exceptional hardness, high wear resistance, and excellent chemical stability, making them ideal for fine and ultra-fine grinding applications. These properties ensure prolonged service life in abrasive environments such as mineral processing, paint manufacturing, and pharmaceuticals. Their superior density and thermal resistance compared to nano-ceramic media result in efficient energy transfer and consistent grinding performance.
Comparative Hardness and Wear Resistance
Nano-ceramic grinding media exhibits significantly higher hardness and superior wear resistance compared to alumina, making it ideal for high-performance milling applications. The enhanced nano-structure provides increased density and toughness, reducing breakage and abrasion during grinding processes. Alumina, while cost-effective and widely used, generally shows lower hardness and faster wear rates under similar operating conditions.
Performance Efficiency in Milling Processes
Nano-ceramic grinding media exhibits superior wear resistance and higher hardness compared to alumina, resulting in extended media life and reduced contamination during milling. Alumina offers cost-effectiveness and chemical inertness but typically presents lower grinding efficiency due to its coarser particle size and less consistent hardness. The enhanced toughness and fine grain structure of nano-ceramic media leads to improved energy transfer and finer particle size distribution, optimizing milling performance and throughput.
Chemical Stability and Contamination Risks
Nano-ceramic grinding media exhibit superior chemical stability due to their uniform structure and resistance to acidic and alkaline environments, minimizing contamination risks in sensitive milling processes. Alumina grinding media, while chemically stable in neutral to mildly acidic conditions, can release trace ions under extreme pH or high-temperature operations, increasing potential contamination. Selecting nano-ceramic media reduces impurity levels in the final product, making it ideal for applications requiring high purity and minimal chemical interaction.
Cost-Effectiveness and Longevity
Nano-ceramic grinding media outperform alumina in terms of longevity due to their enhanced wear resistance and toughness, leading to reduced replacement frequency and downtime. Although the initial cost of nano-ceramic media is higher than alumina, the total cost of operation becomes more economical over time because of lower media consumption and improved grinding efficiency. Cost-effectiveness is further amplified by nano-ceramic's superior performance in high-intensity grinding applications, resulting in better energy utilization and higher throughput.
Applications in Various Industries
Nano-ceramic grinding media offer superior wear resistance and higher grinding efficiency compared to alumina, making them ideal for high-precision applications in electronics, pharmaceuticals, and advanced materials industries. Alumina grinding media, known for their hardness and chemical stability, are widely used in mineral processing, cement production, and paint manufacturing where cost-effectiveness and durability are critical. The choice between nano-ceramic and alumina media depends on industry-specific requirements like particle size reduction, contamination sensitivity, and operational lifespan.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Nano-ceramic grinding media exhibit enhanced wear resistance and reduced contamination compared to alumina, leading to less frequent replacement and lower waste generation. Alumina, while cost-effective, often results in higher abrasive dust and energy consumption during production, increasing its environmental footprint. The superior durability and recyclability of nano-ceramic materials contribute to improved sustainability in industrial grinding applications.
Choosing the Right Grinding Media: Key Considerations
Choosing the right grinding media between nano-ceramic and alumina hinges on factors such as material hardness, abrasion resistance, and cost efficiency. Nano-ceramic grinding media offer superior hardness and wear resistance, ideal for high-precision and prolonged milling processes, while alumina provides a cost-effective solution with good performance for less demanding applications. Evaluating the specific milling environment, including particle size distribution, contamination tolerance, and milling speed, is crucial to optimize media selection for enhanced grinding efficiency and product quality.
Infographic: Nano-ceramic vs Alumina for Grinding Media
 azmater.com
azmater.com