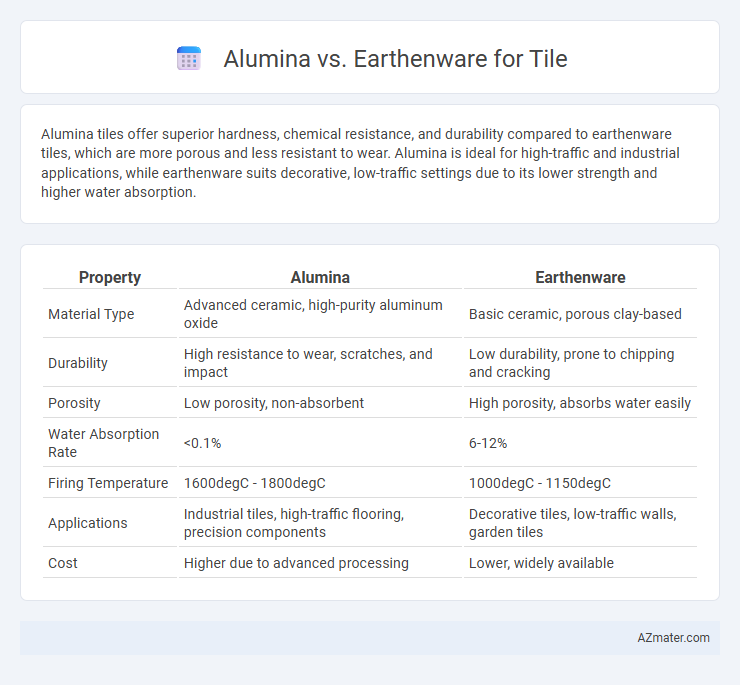
Alumina tiles offer superior hardness, chemical resistance, and durability compared to earthenware tiles, which are more porous and less resistant to wear. Alumina is ideal for high-traffic and industrial applications, while earthenware suits decorative, low-traffic settings due to its lower strength and higher water absorption.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Alumina | Earthenware |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Advanced ceramic, high-purity aluminum oxide | Basic ceramic, porous clay-based |
| Durability | High resistance to wear, scratches, and impact | Low durability, prone to chipping and cracking |
| Porosity | Low porosity, non-absorbent | High porosity, absorbs water easily |
| Water Absorption Rate | <0.1% | 6-12% |
| Firing Temperature | 1600degC - 1800degC | 1000degC - 1150degC |
| Applications | Industrial tiles, high-traffic flooring, precision components | Decorative tiles, low-traffic walls, garden tiles |
| Cost | Higher due to advanced processing | Lower, widely available |
Introduction to Alumina and Earthenware Tiles
Alumina tiles, composed primarily of aluminum oxide, offer exceptional hardness and chemical resistance, making them ideal for high-traffic and industrial applications. Earthenware tiles, crafted from natural clay fired at lower temperatures, provide a porous, lightweight, and cost-effective option suited for decorative and low-impact surfaces. The distinct material compositions influence their durability, water absorption rates, and suitability for various indoor and outdoor environments.
Composition and Material Properties
Alumina tiles are composed primarily of aluminum oxide, offering high hardness, excellent wear resistance, and thermal stability, making them suitable for heavy-duty applications. Earthenware tiles consist mainly of clay fired at lower temperatures, resulting in a porous, softer material with lower durability and reduced resistance to moisture and abrasion. The significant difference in alumina's dense, crystalline structure versus earthenware's porous ceramic matrix directly influences their mechanical strength and suitability for demanding environments.
Manufacturing Processes Compared
Alumina tiles are produced through a high-temperature sintering process that involves compacting aluminum oxide powder and firing it at temperatures exceeding 1600degC, resulting in a dense, durable ceramic with superior wear resistance. Earthenware tiles are manufactured by shaping natural clay mixtures followed by low-temperature firing around 1000degC, yielding a more porous, less dense material that is often glazed to enhance strength and water resistance. The manufacturing contrast between alumina's advanced powder metallurgy and earthenware's traditional clay molding dictates significant differences in their mechanical properties and durability.
Durability and Strength Differences
Alumina tiles exhibit superior durability and strength compared to earthenware tiles, with alumina's high hardness rating of 9 on the Mohs scale providing exceptional resistance to scratches and wear. Earthenware tiles, being more porous and softer, typically rate around 4-5 on the Mohs scale, making them more prone to chipping and damage under heavy use. These properties make alumina ideal for high-traffic areas requiring long-lasting performance, while earthenware suits decorative applications with less mechanical stress.
Water Absorption and Porosity
Alumina tiles exhibit significantly lower water absorption rates, typically below 0.5%, due to their dense, non-porous ceramic structure, making them highly resistant to moisture and ideal for wet environments. In contrast, earthenware tiles have higher porosity, with water absorption often exceeding 5%, which can lead to increased susceptibility to water damage and staining if not properly sealed. The low porosity of alumina enhances durability and stain resistance, while the porous nature of earthenware requires additional maintenance to prevent moisture infiltration.
Thermal and Chemical Resistance
Alumina tiles exhibit superior thermal stability, withstanding high temperatures above 1700degC, making them ideal for environments requiring exceptional heat resistance. Their chemical inertness resists corrosion from acids, alkalis, and solvents, ensuring durability in harsh industrial applications. Earthenware tiles, however, offer lower thermal resistance up to approximately 1200degC and are more susceptible to chemical etching and degradation when exposed to aggressive substances.
Aesthetic Appeal and Design Options
Alumina tiles offer a sleek, modern aesthetic with smooth surfaces and a wide range of vibrant colors and finishes, making them ideal for contemporary designs. Earthenware tiles feature warm, rustic tones and natural textures that provide a handcrafted, authentic appeal suited for traditional and Mediterranean-style interiors. The versatility of alumina supports complex patterns and high gloss finishes, while earthenware excels in matte glazes and artisanal decorative motifs.
Cost Analysis: Alumina vs Earthenware
Alumina tiles generally cost more than earthenware due to higher manufacturing expenses and superior durability. The initial investment in alumina is offset by its longer lifespan and resistance to wear, reducing replacement and maintenance costs over time. Earthenware tiles offer a lower upfront price but may incur additional expenses related to frequent repairs or replacements in high-traffic areas.
Ideal Applications for Each Material
Alumina tiles excel in industrial applications requiring high durability, chemical resistance, and thermal stability, making them ideal for environments like laboratories, manufacturing plants, and heavy-traffic flooring. Earthenware tiles, with their porous nature and aesthetic versatility, are best suited for decorative indoor settings such as kitchen backsplashes, bathrooms, and low-traffic residential areas. The choice between alumina and earthenware hinges on balancing mechanical performance with design preferences and environmental demands.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Tile
Alumina tiles offer superior hardness and durability, making them ideal for high-traffic areas requiring long-lasting performance. Earthenware tiles provide a more affordable and aesthetically versatile option, suitable for low-traffic interior spaces with moderate wear. Selecting the appropriate tile depends on balancing durability requirements and design preferences for the specific application.
Infographic: Alumina vs Earthenware for Tile
 azmater.com
azmater.com