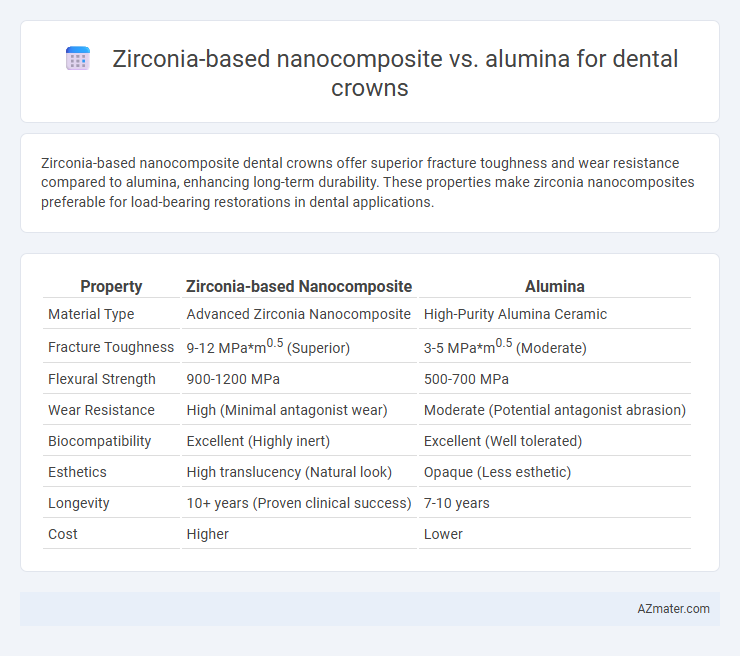
Zirconia-based nanocomposite dental crowns offer superior fracture toughness and wear resistance compared to alumina, enhancing long-term durability. These properties make zirconia nanocomposites preferable for load-bearing restorations in dental applications.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Zirconia-based Nanocomposite | Alumina |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Advanced Zirconia Nanocomposite | High-Purity Alumina Ceramic |
| Fracture Toughness | 9-12 MPa*m0.5 (Superior) | 3-5 MPa*m0.5 (Moderate) |
| Flexural Strength | 900-1200 MPa | 500-700 MPa |
| Wear Resistance | High (Minimal antagonist wear) | Moderate (Potential antagonist abrasion) |
| Biocompatibility | Excellent (Highly inert) | Excellent (Well tolerated) |
| Esthetics | High translucency (Natural look) | Opaque (Less esthetic) |
| Longevity | 10+ years (Proven clinical success) | 7-10 years |
| Cost | Higher | Lower |
Introduction to Dental Crown Materials
Zirconia-based nanocomposites offer superior mechanical strength, fracture toughness, and esthetic properties compared to traditional alumina used in dental crowns. Their nanoscale reinforcement enhances wear resistance and biocompatibility, making them highly suitable for long-lasting restorations in posterior and anterior teeth. Alumina crowns, while biocompatible and durable, generally exhibit lower translucency and mechanical performance than zirconia nanocomposites, limiting their applications in esthetically demanding cases.
Overview of Zirconia-Based Nanocomposites
Zirconia-based nanocomposites offer enhanced mechanical properties and superior aesthetic qualities compared to traditional alumina, making them highly suitable for dental crowns. These nanocomposites exhibit increased fracture toughness and wear resistance due to the integration of nanoscale zirconia particles within a biocompatible matrix. Their improved translucency and color stability also provide a more natural appearance, addressing limitations of alumina-based materials in restorative dentistry.
Properties of Alumina in Dentistry
Alumina exhibits exceptional hardness, excellent wear resistance, and high biocompatibility, making it a reliable material for dental crowns. Its chemical stability ensures resistance to corrosion and low solubility in oral environments, promoting longevity and maintaining structural integrity over time. The material's natural white color and translucency contribute to superior esthetic outcomes in restorative dentistry.
Mechanical Strength Comparison
Zirconia-based nanocomposites exhibit superior mechanical strength compared to alumina in dental crowns, with fracture toughness values reaching 9-10 MPa*m^0.5 versus alumina's typical 3-4 MPa*m^0.5. The enhanced flexural strength of zirconia, often exceeding 900 MPa, outperforms alumina's 400-600 MPa range, providing greater resistance to occlusal forces during mastication. Moreover, the transformation toughening mechanism in zirconia nanocomposites contributes to improved crack propagation resistance, making them a more durable choice for long-term dental restorations.
Aesthetic Outcomes: Zirconia vs Alumina
Zirconia-based nanocomposites exhibit superior aesthetic outcomes compared to alumina for dental crowns due to their enhanced translucency and ability to mimic natural tooth color more closely. The nanostructured zirconia allows for improved light transmission and a lifelike appearance, whereas alumina tends to be more opaque and less visually appealing. This makes zirconia the preferred choice for anterior restorations where aesthetics are critical.
Wear Resistance and Longevity
Zirconia-based nanocomposites exhibit superior wear resistance compared to alumina, making them more durable for dental crowns under occlusal stress. Their enhanced fracture toughness and resistance to micro-cracking contribute to longer clinical longevity, reducing the need for replacements. Alumina crowns, while biocompatible and wear-resistant, generally show lower toughness and higher brittleness, potentially limiting lifespan in high-load areas.
Biocompatibility and Patient Response
Zirconia-based nanocomposites exhibit superior biocompatibility compared to alumina, demonstrating lower cytotoxicity and enhanced tissue integration in dental crown applications. Studies reveal zirconia's ability to minimize inflammatory responses and promote gingival cell adhesion, leading to improved patient comfort and reduced risk of allergic reactions. While alumina provides adequate mechanical strength, zirconia nanocomposites offer a more favorable biological response, contributing to higher patient satisfaction and long-term clinical success.
Clinical Performance and Applications
Zirconia-based nanocomposites exhibit superior fracture toughness and wear resistance compared to alumina, making them highly suitable for dental crowns subjected to high occlusal forces. Clinical studies demonstrate that zirconia crowns provide enhanced aesthetics and long-term durability, with lower chipping rates and better biocompatibility than alumina-based restorations. These properties enable zirconia nanocomposites to be preferred in posterior crown applications and implant-supported prostheses where mechanical reliability and esthetic outcomes are critical.
Cost Considerations and Accessibility
Zirconia-based nanocomposite dental crowns typically incur higher costs due to advanced material processing and superior mechanical properties compared to alumina crowns, which offer a more cost-effective alternative with acceptable durability. Accessibility to zirconia crowns may be limited by geographic and economic factors, as specialized manufacturing and dental lab capabilities are required, whereas alumina crowns are widely available and easier to produce. The selection between zirconia and alumina crowns often balances budget constraints with desired longevity and aesthetic outcomes in dental restorations.
Future Trends in Dental Crown Materials
Zirconia-based nanocomposites exhibit superior mechanical properties and enhanced translucency compared to alumina, making them increasingly favorable for dental crown applications. Innovations in nanotechnology are driving the development of hybrid materials that combine the toughness of zirconia with the wear resistance of alumina. Future trends indicate a shift towards bioactive and multifunctional crowns that promote tissue integration and long-term durability, leveraging the unique properties of zirconia-based nanocomposites.
Infographic: Zirconia-based nanocomposite vs Alumina for Dental crown
 azmater.com
azmater.com