Tiles offer lightweight, water-resistant surfaces ideal for interior and decorative applications, while bricks provide superior structural strength and thermal insulation for building foundations and exterior walls. Choosing between tile and brick depends on factors like load-bearing requirements, moisture exposure, and aesthetic preferences.
Table of Comparison
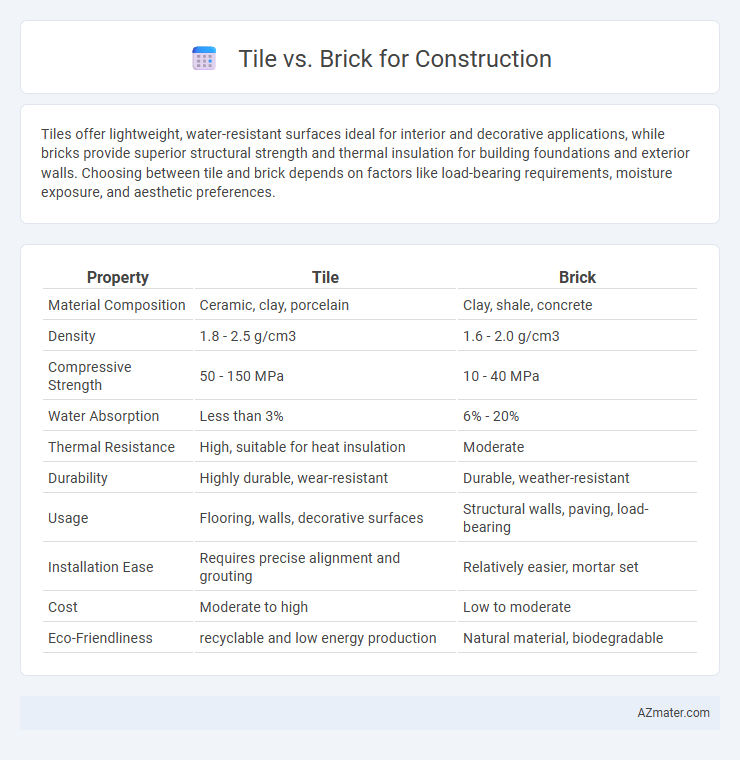
| Property | Tile | Brick |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Ceramic, clay, porcelain | Clay, shale, concrete |
| Density | 1.8 - 2.5 g/cm3 | 1.6 - 2.0 g/cm3 |
| Compressive Strength | 50 - 150 MPa | 10 - 40 MPa |
| Water Absorption | Less than 3% | 6% - 20% |
| Thermal Resistance | High, suitable for heat insulation | Moderate |
| Durability | Highly durable, wear-resistant | Durable, weather-resistant |
| Usage | Flooring, walls, decorative surfaces | Structural walls, paving, load-bearing |
| Installation Ease | Requires precise alignment and grouting | Relatively easier, mortar set |
| Cost | Moderate to high | Low to moderate |
| Eco-Friendliness | recyclable and low energy production | Natural material, biodegradable |
Introduction to Tile and Brick in Construction
Tile and brick are fundamental materials in construction, each offering distinct structural and aesthetic properties. Tiles, made from ceramic, porcelain, or natural stone, provide versatile surfaces primarily for flooring and wall coverings due to their durability and water resistance. Bricks, typically composed of clay or concrete, serve as robust load-bearing units that ensure stability and thermal insulation in building frameworks.
Material Composition and Properties
Tile is typically made from ceramic, porcelain, or natural stone, offering a smooth, dense surface with low porosity and high resistance to water and stains. Brick, composed mainly of clay or shale fired at high temperatures, features a porous and textured structure providing strong compressive strength and excellent thermal mass. The material composition directly influences durability, insulation properties, and suitability for interior versus exterior applications in construction.
Strength and Durability Comparison
Brick offers superior strength and durability compared to tile, with compressive strength often exceeding 3000 psi, making it ideal for load-bearing walls and structural applications. Tiles, typically ceramic or porcelain, provide surface durability and resistance to wear but lack the structural integrity required for foundational support. Long-term performance favors bricks in harsh weather and heavy-use environments due to their density and moisture resistance.
Aesthetic Appeal and Design Versatility
Tile offers a sleek and polished aesthetic with a wide range of colors, patterns, and finishes that enhance design versatility in modern construction. Brick provides a timeless, rustic charm with natural textures and earthy tones, often used to convey warmth and durability in architectural designs. Both materials can be combined creatively to achieve unique visual effects, balancing contemporary elegance with traditional character.
Installation Process and Complexity
Tile installation requires precise surface preparation, including waterproofing and leveling, followed by careful placement with adhesive and grout application, making it moderately complex but manageable with proper tools. Brick installation involves setting each unit in mortar with consistent spacing and alignment, demanding more labor-intensive skills and time due to its heavier material and curing process. Overall, brick installation presents greater complexity and physical effort compared to the quicker, more detailed-oriented tile installation.
Cost Analysis: Tile vs Brick
Tile and brick vary significantly in cost, with tile generally offering a lower initial expense due to affordable materials and simpler installation processes, making it ideal for budget-conscious projects. Brick, while more expensive upfront because of higher material costs and labor-intensive installation, provides superior durability and long-term value through reduced maintenance and enhanced structural integrity. Evaluating total cost of ownership, including installation, maintenance, and lifespan, is critical for accurate cost analysis between tile and brick in construction.
Thermal and Acoustic Insulation
Tile offers moderate thermal insulation but generally underperforms compared to brick due to its lower thermal mass, making brick a superior choice for maintaining stable indoor temperatures. Brick's dense composition provides excellent acoustic insulation by effectively absorbing and blocking sound waves, whereas tile surfaces tend to reflect noise, resulting in less sound dampening. For construction projects prioritizing energy efficiency and noise reduction, brick is the optimal material over tile in both thermal and acoustic insulation aspects.
Maintenance and Longevity
Tiles offer lower maintenance requirements compared to bricks due to their resistance to moisture, stains, and mold, making them ideal for environments prone to humidity. Brick construction is known for its exceptional durability and longevity, often lasting centuries with minimal deterioration, but it may require periodic sealing and mortar repairs to maintain structural integrity. The choice between tile and brick depends on the balance between desired maintenance effort and expected lifespan, with brick favored for long-term resilience and tile preferred for ease of upkeep.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Tile production typically consumes less raw material and energy compared to brick manufacturing, resulting in a smaller carbon footprint. Bricks require high-temperature kilns that emit significant CO2 and deplete natural clay resources, whereas many tiles incorporate recycled materials, enhancing sustainability. Choosing eco-friendly tiles or sustainably fired bricks reduces environmental impact in construction projects.
Choosing the Right Material for Your Project
Selecting between tile and brick for construction hinges on factors such as durability, aesthetic appeal, and project requirements. Brick offers robust structural integrity and excellent thermal insulation, making it ideal for load-bearing walls and exterior facades. Tile provides versatile design options and moisture resistance, suitable for interior applications like flooring and backsplashes, emphasizing the importance of matching material properties to project needs.
Infographic: Tile vs Brick for Construction
 azmater.com
azmater.com