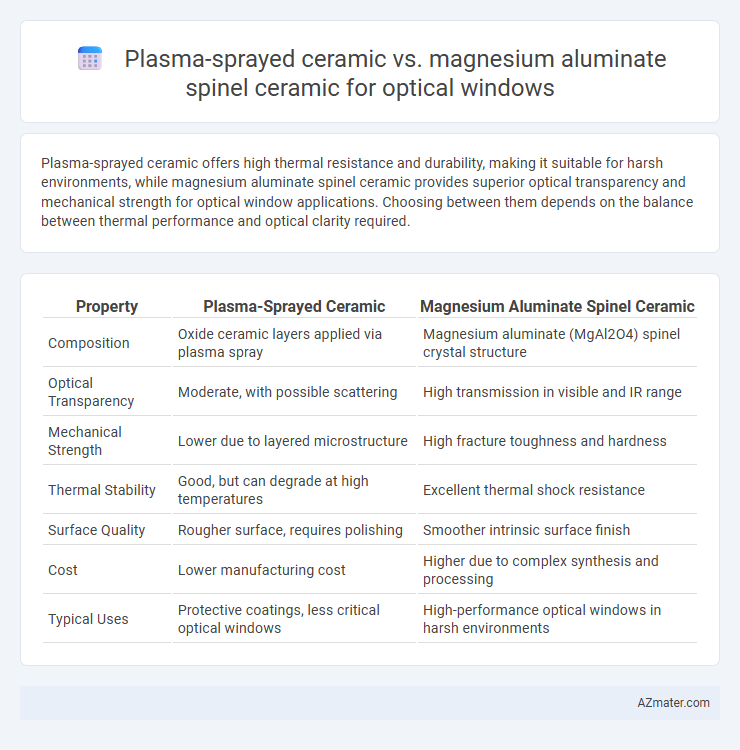
Plasma-sprayed ceramic offers high thermal resistance and durability, making it suitable for harsh environments, while magnesium aluminate spinel ceramic provides superior optical transparency and mechanical strength for optical window applications. Choosing between them depends on the balance between thermal performance and optical clarity required.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Plasma-Sprayed Ceramic | Magnesium Aluminate Spinel Ceramic |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Oxide ceramic layers applied via plasma spray | Magnesium aluminate (MgAl2O4) spinel crystal structure |
| Optical Transparency | Moderate, with possible scattering | High transmission in visible and IR range |
| Mechanical Strength | Lower due to layered microstructure | High fracture toughness and hardness |
| Thermal Stability | Good, but can degrade at high temperatures | Excellent thermal shock resistance |
| Surface Quality | Rougher surface, requires polishing | Smoother intrinsic surface finish |
| Cost | Lower manufacturing cost | Higher due to complex synthesis and processing |
| Typical Uses | Protective coatings, less critical optical windows | High-performance optical windows in harsh environments |
Introduction to Optical Window Materials
Plasma-sprayed ceramics offer high thermal stability and wear resistance, making them suitable for harsh environmental conditions in optical windows. Magnesium aluminate spinel ceramic provides exceptional optical transparency in a broad wavelength range from ultraviolet to infrared, combined with excellent mechanical strength. The choice between plasma-sprayed ceramics and magnesium aluminate spinel depends on the required optical clarity, thermal tolerance, and environmental durability for specific optical window applications.
Overview of Plasma-Sprayed Ceramic Technology
Plasma-sprayed ceramic technology leverages high-temperature plasma jets to deposit ceramic powders, creating dense, durable coatings with excellent thermal and mechanical properties ideal for optical windows. Compared to magnesium aluminate spinel ceramic, plasma-sprayed ceramics offer tailored microstructures and thickness control, enhancing optical clarity and resistance to thermal shock. This technology enables the fabrication of complex shapes with minimal defects, improving transparency and durability in harsh environmental conditions.
Properties of Magnesium Aluminate Spinel Ceramic
Magnesium aluminate spinel ceramic offers exceptional optical transparency across a wide spectral range from ultraviolet to infrared, making it ideal for advanced optical window applications. Its high mechanical strength, excellent thermal stability, and superior chemical resistance outperform plasma-sprayed ceramic coatings, ensuring durability in harsh environments. The intrinsic cubic crystal structure of magnesium aluminate spinel also provides isotropic optical properties and low birefringence, critical for maintaining image quality and minimizing distortion.
Comparison of Optical Transparency
Plasma-sprayed ceramic coatings typically exhibit lower optical transparency due to inherent surface roughness and microstructural porosity, which scatter and absorb light. Magnesium aluminate spinel ceramics demonstrate superior optical clarity with high transmittance in the visible and infrared spectra, attributed to their dense polycrystalline structure and minimal defects. For optical window applications requiring high transparency and durability, magnesium aluminate spinel offers a significant advantage over plasma-sprayed ceramic coatings.
Mechanical Strength and Hardness Analysis
Plasma-sprayed ceramic coatings exhibit enhanced mechanical strength due to their dense microstructure and strong adhesion, making them resistant to impact and wear in optical windows. Magnesium aluminate spinel ceramic offers superior hardness and excellent fracture toughness, providing excellent resistance to surface abrasion and mechanical deformation. Comparative analysis shows that while plasma-sprayed ceramics possess good toughness, magnesium aluminate spinel ceramic outperforms in hardness, making it ideal for high-durability optical window applications.
Thermal Stability and Resistance to Shock
Plasma-sprayed ceramic coatings offer excellent thermal stability withstanding temperatures up to 1200degC, but magnesium aluminate spinel ceramics demonstrate superior resistance to thermal shock due to their high fracture toughness and low thermal expansion coefficient. Spinel ceramics maintain optical transparency and structural integrity under rapid temperature fluctuations, making them more reliable for high-stress optical window applications. Their inherent chemical stability and resistance to cracking under thermal cycling surpass plasma-sprayed ceramics, ensuring longer service life in harsh thermal environments.
Environmental Durability in Harsh Conditions
Plasma-sprayed ceramic optical windows offer excellent thermal resistance and mechanical strength but may exhibit lower environmental durability due to microstructural porosity and susceptibility to moisture-induced degradation under harsh conditions. Magnesium aluminate spinel ceramic provides superior environmental durability with high resistance to thermal shock, chemical corrosion, and moisture infiltration, making it ideal for extreme environments requiring optical clarity and long-term stability. Its dense microstructure and intrinsic chemical stability enhance performance in abrasive, corrosive, and high-temperature applications compared to plasma-sprayed coatings.
Cost and Manufacturing Scalability
Plasma-sprayed ceramic coatings offer cost-effective manufacturing with scalability due to relatively simple deposition processes and lower material costs compared to magnesium aluminate spinel ceramics, which require high-purity raw materials and complex sintering techniques. Magnesium aluminate spinel provides superior optical clarity and durability but involves higher production expenses and limited scalability constrained by precise control of crystal growth and sintering conditions. Therefore, plasma-sprayed ceramics are preferred for large-scale, budget-sensitive optical window applications, while magnesium aluminate spinel suits specialized uses demanding top-tier optical performance despite higher costs.
Application Suitability for Optical Windows
Plasma-sprayed ceramic coatings offer excellent thermal resistance and durability but often exhibit higher surface roughness and lower optical clarity, limiting their application in high-precision optical windows. Magnesium aluminate spinel ceramic provides superior optical transparency, high mechanical strength, and excellent chemical stability, making it highly suitable for infrared and visible optical windows in harsh environments. Its low porosity and strong resistance to thermal shock enhance performance in aerospace, defense, and high-power laser applications where optical clarity and durability are critical.
Conclusion: Optimal Choice for Optical Window Performance
Plasma-sprayed ceramic offers superior thermal barrier properties and hardness, but magnesium aluminate spinel ceramic provides exceptional optical clarity, excellent mechanical strength, and high resistance to thermal shock, making it more suitable for optical windows. The magnesium aluminate spinel's superior transparency from infrared to visible wavelengths ensures minimal signal distortion and higher performance in harsh environments. Therefore, magnesium aluminate spinel ceramic stands as the optimal choice for optical window applications demanding durability and clarity.
Infographic: Plasma-sprayed ceramic vs Magnesium aluminate spinel ceramic for Optical window
 azmater.com
azmater.com