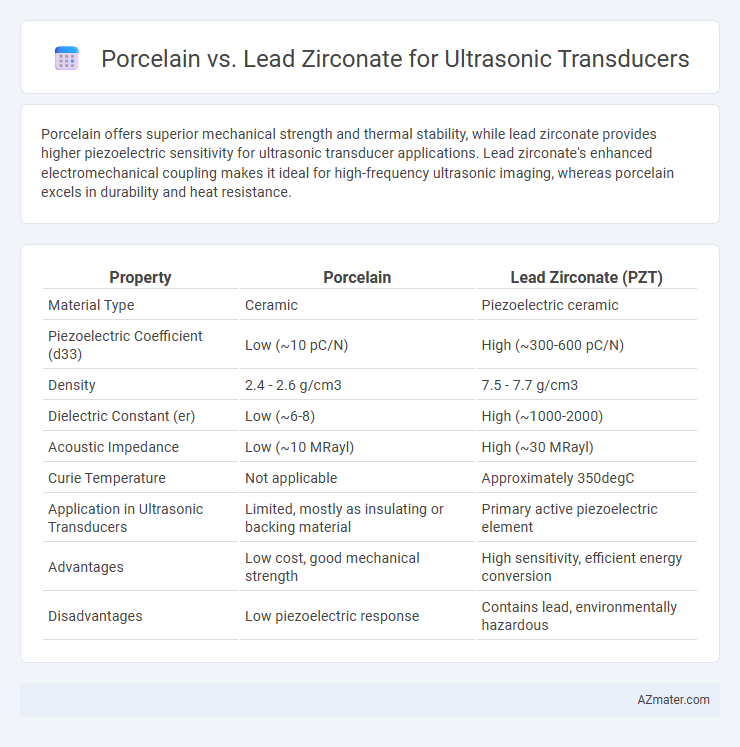
Porcelain offers superior mechanical strength and thermal stability, while lead zirconate provides higher piezoelectric sensitivity for ultrasonic transducer applications. Lead zirconate's enhanced electromechanical coupling makes it ideal for high-frequency ultrasonic imaging, whereas porcelain excels in durability and heat resistance.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Porcelain | Lead Zirconate (PZT) |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Ceramic | Piezoelectric ceramic |
| Piezoelectric Coefficient (d33) | Low (~10 pC/N) | High (~300-600 pC/N) |
| Density | 2.4 - 2.6 g/cm3 | 7.5 - 7.7 g/cm3 |
| Dielectric Constant (er) | Low (~6-8) | High (~1000-2000) |
| Acoustic Impedance | Low (~10 MRayl) | High (~30 MRayl) |
| Curie Temperature | Not applicable | Approximately 350degC |
| Application in Ultrasonic Transducers | Limited, mostly as insulating or backing material | Primary active piezoelectric element |
| Advantages | Low cost, good mechanical strength | High sensitivity, efficient energy conversion |
| Disadvantages | Low piezoelectric response | Contains lead, environmentally hazardous |
Introduction to Ultrasonic Transducers
Ultrasonic transducers convert electrical energy into high-frequency sound waves used in medical imaging, industrial non-destructive testing, and underwater sonar systems. Porcelain ceramics exhibit high mechanical strength and thermal stability, making them suitable for durable ultrasonic transducer elements. Lead zirconate titanate (PZT) offers superior piezoelectric performance with higher sensitivity and electromechanical coupling, enhancing signal clarity and efficiency in ultrasonic devices.
Overview of Porcelain Materials in Ultrasonic Applications
Porcelain materials are widely used in ultrasonic transducers due to their excellent piezoelectric properties, high mechanical strength, and thermal stability. These ceramics offer a stable dielectric constant and low acoustic loss, which enhance signal clarity and transducer efficiency in medical imaging and industrial ultrasonic testing. Compared to lead zirconate, porcelain materials provide a cost-effective and environmentally friendly alternative with moderate piezoelectric sensitivity suitable for various ultrasonic applications.
Understanding Lead Zirconate in Ultrasonic Technology
Lead zirconate, a key piezoelectric ceramic in ultrasonic transducers, offers superior electromechanical coupling compared to standard porcelain materials, enabling higher sensitivity and efficiency in ultrasonic wave generation and detection. Its perovskite crystal structure enhances polarization stability and frequency response, crucial for precision ultrasonic applications such as medical imaging and non-destructive testing. Optimized lead zirconate formulations deliver improved acoustic impedance matching and durability, making it a preferred choice for advanced ultrasonic transducer design over traditional porcelain ceramics.
Material Properties: Porcelain vs Lead Zirconate
Porcelain exhibits excellent mechanical strength and chemical stability but has lower piezoelectric sensitivity compared to lead zirconate, which offers superior electromechanical coupling due to its perovskite crystal structure. Lead zirconate's high dielectric constant and strong piezoelectric coefficients enhance ultrasonic transducer efficiency, making it ideal for high-precision applications. However, porcelain's thermal stability and lower density provide advantages in specific environments requiring durability and lower acoustic impedance.
Performance Comparison: Sensitivity and Efficiency
Porcelain ultrasonic transducers exhibit moderate sensitivity with reliable efficiency, making them suitable for general-purpose applications. Lead zirconate transducers demonstrate superior sensitivity and higher electromechanical coupling coefficients, resulting in enhanced signal strength and energy conversion efficiency. The piezoelectric properties of lead zirconate enable more precise ultrasonic wave generation compared to the relatively lower performance characteristics of porcelain ceramics.
Durability and Reliability in Various Environments
Porcelain exhibits excellent chemical stability and high resistance to thermal shock, making it highly durable in harsh environments for ultrasonic transducers. Lead zirconate offers superior piezoelectric properties but can degrade faster under prolonged exposure to moisture and temperature fluctuations. Choosing between porcelain and lead zirconate hinges on balancing environmental resilience with optimal piezoelectric performance for reliable ultrasonic transducer operation.
Manufacturing Processes and Cost Analysis
Porcelain ultrasonic transducers typically involve sintering ceramic powders at high temperatures, offering uniform density and excellent dielectric properties, while lead zirconate transducers rely on complex solid-state synthesis and poling processes to achieve piezoelectricity. Manufacturing porcelain transducers generally results in lower raw material costs but higher energy consumption during firing, whereas lead zirconate demands expensive raw materials and precise control to ensure performance consistency. Cost analysis reveals that porcelain is more economical for large-scale production, whereas lead zirconate offers superior sensitivity and stability justifying its higher price in specialized applications.
Environmental and Health Considerations
Porcelain used in ultrasonic transducers offers a non-toxic and environmentally friendly alternative to lead zirconate titanate (PZT), which contains lead, posing significant health and environmental risks during manufacturing, disposal, and accidental breakage. Lead zirconate, despite its superior piezoelectric properties, raises concerns due to lead leaching, contributing to soil and water contamination and requiring strict regulatory controls under hazardous substance guidelines. Porcelain-based materials provide safer disposal processes and lower ecological footprints, making them preferable for applications prioritizing sustainability and human safety in ultrasonic transducer technology.
Application Suitability: Choosing the Right Material
Porcelain offers excellent electrical insulation and mechanical stability, making it suitable for low-frequency ultrasonic transducers in industrial cleaning and medical imaging. Lead zirconate exhibits high piezoelectric sensitivity and efficiency, ideal for high-frequency applications such as precision ultrasound diagnostics and nondestructive testing. Selecting between porcelain and lead zirconate depends on the operating frequency, sensitivity requirements, and environmental conditions of the ultrasonic transducer application.
Conclusion: Selecting the Optimal Material for Ultrasonic Transducers
Porcelain offers excellent mechanical strength and thermal stability, making it suitable for low-frequency, high-power ultrasonic transducers, while lead zirconate (PZT) exhibits superior piezoelectric properties and higher electromechanical coupling efficiency ideal for high-frequency, high-sensitivity applications. The optimal material selection depends on application-specific requirements such as frequency range, power handling, and sensitivity, with PZT preferred for precision imaging and sensing and porcelain favored for durability in harsh environments. Cost, fabrication complexity, and environmental considerations also influence the final choice between porcelain and lead zirconate in ultrasonic transducer design.
Infographic: Porcelain vs Lead Zirconate for Ultrasonic Transducer
 azmater.com
azmater.com