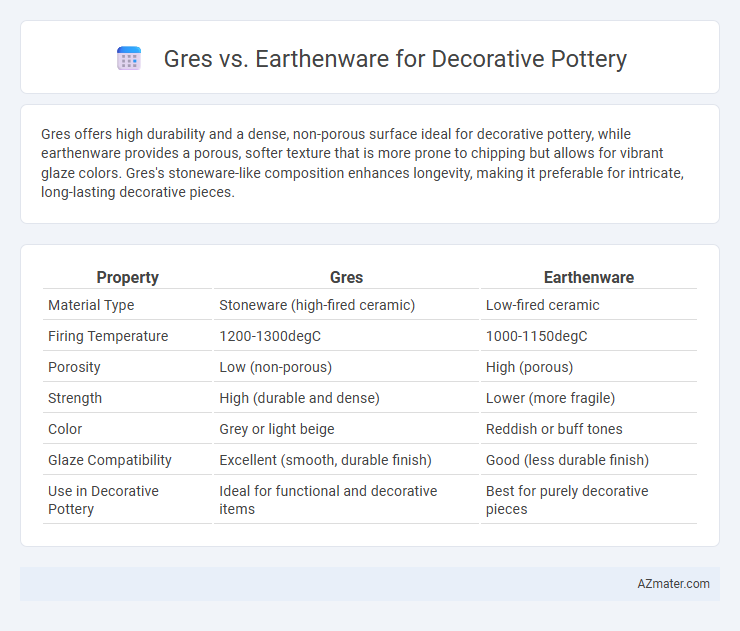
Gres offers high durability and a dense, non-porous surface ideal for decorative pottery, while earthenware provides a porous, softer texture that is more prone to chipping but allows for vibrant glaze colors. Gres's stoneware-like composition enhances longevity, making it preferable for intricate, long-lasting decorative pieces.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Gres | Earthenware |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Stoneware (high-fired ceramic) | Low-fired ceramic |
| Firing Temperature | 1200-1300degC | 1000-1150degC |
| Porosity | Low (non-porous) | High (porous) |
| Strength | High (durable and dense) | Lower (more fragile) |
| Color | Grey or light beige | Reddish or buff tones |
| Glaze Compatibility | Excellent (smooth, durable finish) | Good (less durable finish) |
| Use in Decorative Pottery | Ideal for functional and decorative items | Best for purely decorative pieces |
Introduction to Decorative Pottery Materials
Gres and earthenware are two popular materials in decorative pottery, each offering distinct properties and aesthetic possibilities. Gres, also known as stoneware, is a dense, durable material fired at high temperatures, resulting in a non-porous and sturdy finish ideal for both functional and ornamental pieces. Earthenware, typically fired at lower temperatures, presents a more porous texture that can be enriched with vibrant glazes and intricate designs, making it favored for colorful and detailed decorative pottery.
What is Gres? Properties and Characteristics
Gres, a highly durable stoneware clay, is known for its dense, non-porous composition and resistance to high temperatures during firing, making it ideal for decorative pottery that requires strength and longevity. Its fine-grained texture allows for smooth finishes and intricate detailing, distinguishing it from the more porous and fragile earthenware. Gres pottery typically features natural earthy tones and offers excellent resistance to chipping and thermal shock, ensuring both aesthetic appeal and functional durability in decorative applications.
Understanding Earthenware: Definition and Features
Earthenware is a type of pottery made from natural clay fired at lower temperatures, typically between 1,000degC and 1,150degC, resulting in a porous and coarse texture. It is known for its warm, earthy tones and rustic appearance, often requiring a glaze to make it waterproof and suitable for decorative uses. Unlike gres, earthenware is more porous, less durable, and generally more affordable, making it a popular choice for artistic and ornamental pottery.
Appearance and Aesthetics: Gres vs Earthenware
Gres pottery exhibits a smooth, dense, and often matte surface with subtle earthy tones, enhancing a modern minimalist aesthetic. Earthenware offers a warmer, rustic appearance with porous texture and vibrant glazes, emphasizing traditional and artisanal charm. The choice between Gres and Earthenware impacts decorative pottery's visual appeal, with Gres suited for sleek, contemporary designs and Earthenware favored for rich, colorful, and textural expressions.
Durability and Strength Comparison
Gres pottery, made from stoneware clay fired at high temperatures, offers superior durability and strength compared to earthenware, which is fired at lower temperatures, resulting in a more porous and fragile material. The dense, vitrified structure of gres makes it resistant to chipping, cracking, and water absorption, ideal for long-lasting decorative pottery. Earthenware, while popular for its rustic appeal, requires glazing to improve its durability but remains more susceptible to damage under stress or impact.
Workability for Potters: Ease of Shaping and Firing
Gres clay offers superior workability for potters due to its fine texture and high plasticity, allowing for easier shaping and detailed forms in decorative pottery. Its higher firing temperature also results in a durable, vitrified finish that withstands cracking or warping. In contrast, earthenware is more porous and fires at lower temperatures, making it less durable but often easier to work with for beginners due to its softer consistency.
Color and Glazing Options
Gres pottery offers a wide range of color options due to its composition, allowing for both muted earth tones and vibrant hues that maintain durability during high-temperature firing. Earthenware, characterized by its porous nature, typically features rich, warm colors and benefits from a variety of glazing techniques that enhance glossiness and surface texture. The glazing on gres is often thinner and more refined, providing a sleek finish, while earthenware glazing tends to be thicker, adding depth and a tactile quality to decorative pottery.
Suitability for Indoor and Outdoor Decorative Use
Gres pottery, known for its high density and low porosity, offers excellent durability and weather resistance, making it ideal for outdoor decorative use where exposure to moisture and temperature changes occurs. Earthenware, being more porous and less dense, is better suited for indoor decorative pottery, as it requires glazing to prevent water absorption and is more vulnerable to outdoor elements. The superior strength and frost resistance of gres enhance its suitability for exterior environments, while earthenware's aesthetic versatility often favors controlled indoor settings.
Cost and Accessibility of Gres and Earthenware
Gres pottery, made from high-fired stoneware clay, tends to be more expensive due to its durability and complexity in firing, which limits accessibility for casual or beginner potters. Earthenware is generally more affordable and widely accessible, with lower firing temperatures making it an ideal choice for decorative pottery beginners and hobbyists. The cost difference reflects gres's enhanced strength and water resistance, whereas earthenware remains popular for its versatility and ease of use in decorative projects.
Choosing the Right Material for Your Decorative Pottery
Gres, or stoneware, offers greater durability and resistance to chipping compared to earthenware, making it ideal for long-lasting decorative pottery with a robust finish. Earthenware, being more porous and fragile, allows for vibrant glazes and intricate designs but requires careful handling and sealing to prevent damage. Choosing between gres and earthenware depends on the desired balance of durability, aesthetic detail, and the intended display environment of the decorative piece.
Infographic: Gres vs Earthenware for Decorative Pottery
 azmater.com
azmater.com