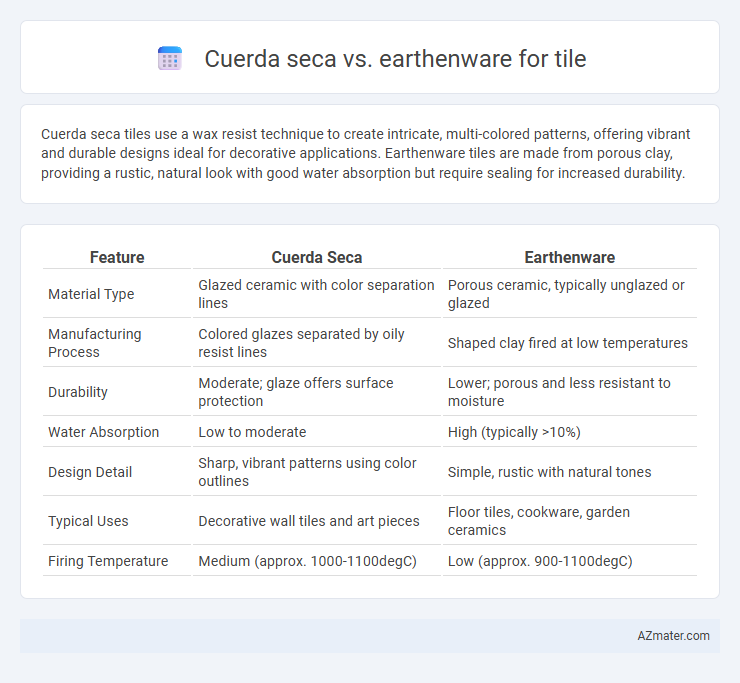
Cuerda seca tiles use a wax resist technique to create intricate, multi-colored patterns, offering vibrant and durable designs ideal for decorative applications. Earthenware tiles are made from porous clay, providing a rustic, natural look with good water absorption but require sealing for increased durability.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Cuerda Seca | Earthenware |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Glazed ceramic with color separation lines | Porous ceramic, typically unglazed or glazed |
| Manufacturing Process | Colored glazes separated by oily resist lines | Shaped clay fired at low temperatures |
| Durability | Moderate; glaze offers surface protection | Lower; porous and less resistant to moisture |
| Water Absorption | Low to moderate | High (typically >10%) |
| Design Detail | Sharp, vibrant patterns using color outlines | Simple, rustic with natural tones |
| Typical Uses | Decorative wall tiles and art pieces | Floor tiles, cookware, garden ceramics |
| Firing Temperature | Medium (approx. 1000-1100degC) | Low (approx. 900-1100degC) |
Introduction to Cuerda Seca and Earthenware Tiles
Cuerda seca is a traditional Spanish-Moorish tile technique characterized by its bold, intricate patterns created using a greasy resist line to separate colored glazes, resulting in vibrant and durable designs. Earthenware tiles, made from porous clay fired at lower temperatures, offer a versatile and affordable option with a naturally rustic appearance but require sealing for water resistance. Both methods provide unique aesthetic and functional qualities, with cuerda seca favored for decorative, high-detail surfaces and earthenware prized for practical, everyday flooring and wall applications.
Historical Origins and Cultural Significance
Cuerda seca, originating in 10th-century Moorish Spain, employs a technique of using greasy lines to separate colored glazes, creating intricate geometric and floral patterns significant in Islamic art. Earthenware, dating back to prehistoric times across various cultures, involves shaping and firing porous clay enriched with mineral pigments, commonly used in everyday pottery and architectural tiles. Both methods carry rich cultural heritage, with cuerda seca symbolizing intricate artistic expression in Islamic architecture, while earthenware reflects practical craftsmanship with diverse stylistic influences worldwide.
Key Differences in Production Techniques
Cuerda seca tiles use a resist technique involving a greasy substance to separate colored glazes during firing, creating intricate, multi-colored patterns without blending. Earthenware tiles are crafted from porous clay fired at lower temperatures, often glazed afterward for durability and color but without the resist method. The cuerda seca method enables sharper, more complex designs, whereas earthenware's simpler glazing allows for varied textures but less precise color separation.
Material Composition and Durability
Cuerda seca tiles are made using a technique that applies a greasy resist line which separates colored glazes, typically produced on a fired clay base, resulting in vibrant, intricate designs with high glaze stability. Earthenware tiles consist of porous clay fired at lower temperatures, making them less dense and more susceptible to wear and moisture damage compared to cuerda seca tiles. The cuerda seca method offers superior durability due to its firmer clay body and protective glazes, while earthenware provides a more porous and less durable surface prone to chipping and staining.
Visual Styles and Artistic Variations
Cuerda seca tiles feature intricate, raised outlines created by a greasy substance mixed with manganese oxide, producing sharp contrasts and vibrant colors ideal for detailed, geometric, and floral designs. Earthenware tiles offer a broader palette with softer, more muted tones due to their porous clay base and glaze application, allowing for diverse artistic variations including rustic, hand-painted, and textured finishes. Visual styles in cuerda seca emphasize precision and vivid, segmented patterns, while earthenware embraces organic, fluid aesthetics with greater tactile variety.
Color Retention and Glazing Methods
Cuerda seca tiles maintain color vibrancy through a resist line technique that prevents glaze colors from mixing during firing, resulting in sharp, well-defined patterns and long-lasting color retention. Earthenware tiles absorb glaze more readily due to their porous nature, which can lead to softer color edges but require specific glazing methods like tin or lead glazes to enhance surface finish and durability. The glazing process for cuerda seca emphasizes precision and separation of hues using oil-based resist, whereas earthenware glazing focuses on achieving smooth, even coverage through dipping or brushing methods.
Suitability for Indoor and Outdoor Applications
Cuerda seca tiles feature a resistive glaze that enhances durability and moisture resistance, making them ideal for both indoor and outdoor applications, especially in areas exposed to weather and heavy foot traffic. Earthenware tiles, being more porous and less resistant to freezing conditions, are better suited for indoor environments where exposure to moisture and temperature fluctuations is minimal. Selecting cuerda seca tiles ensures long-lasting performance in patios and exterior walls, while earthenware remains a cost-effective choice for decorative indoor flooring and wall accents.
Maintenance and Longevity Comparison
Cuerda seca tiles require careful maintenance due to their intricate glaze lines, which can trap dirt and necessitate gentle cleaning with non-abrasive materials to preserve the vivid colors and prevent glaze wear. Earthenware tiles, while more porous and susceptible to staining, can achieve long-lasting durability with regular sealing and prompt cleaning to avoid moisture damage and surface deterioration. The longevity of cuerda seca tiles typically surpasses that of earthenware when properly maintained, thanks to their hard, glazed surface that resists chipping and fading over time.
Cost Analysis and Accessibility
Cuerda seca tiles, known for intricate, multicolored designs, typically incur higher costs due to the labor-intensive glazing process and specialized craftsmanship required, limiting accessibility to niche markets and artisans. Earthenware tiles offer a more affordable option with widespread availability, benefiting from simpler manufacturing techniques and mass production, making them accessible for budget-conscious projects and large-scale installations. The cost differential largely stems from production complexity and regional availability, influencing project budgets and design choices.
Choosing the Right Tile for Your Project
Cuerda seca tiles feature intricate, colorful designs created by using a wax-resist technique that prevents colors from merging, making them ideal for decorative or artistic projects requiring vibrant patterns. Earthenware tiles offer durability and affordability with a more uniform and natural clay texture, suitable for high-traffic areas and outdoor use where resilience is critical. Choosing the right tile depends on balancing aesthetic appeal with functional requirements such as location, wear resistance, and maintenance needs.
Infographic: Cuerda seca vs Earthenware for Tile
 azmater.com
azmater.com