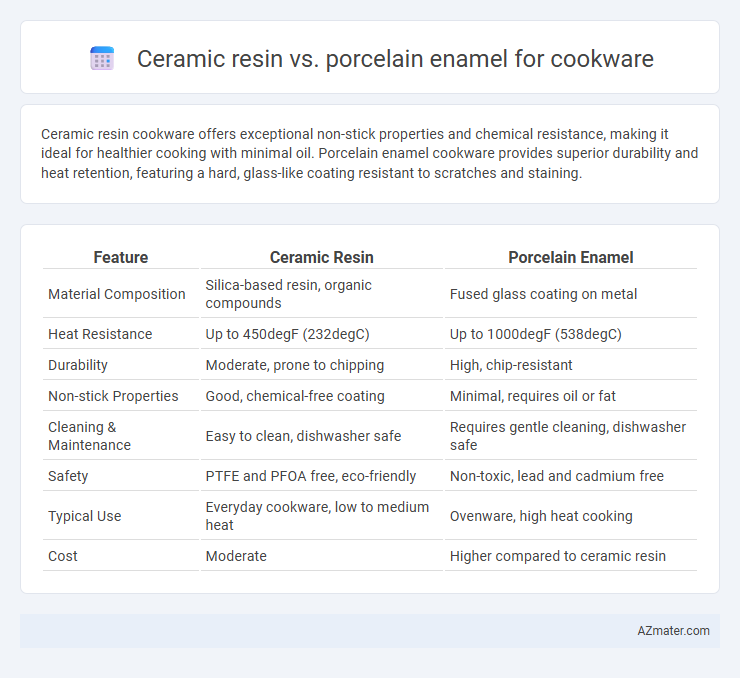
Ceramic resin cookware offers exceptional non-stick properties and chemical resistance, making it ideal for healthier cooking with minimal oil. Porcelain enamel cookware provides superior durability and heat retention, featuring a hard, glass-like coating resistant to scratches and staining.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Ceramic Resin | Porcelain Enamel |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Silica-based resin, organic compounds | Fused glass coating on metal |
| Heat Resistance | Up to 450degF (232degC) | Up to 1000degF (538degC) |
| Durability | Moderate, prone to chipping | High, chip-resistant |
| Non-stick Properties | Good, chemical-free coating | Minimal, requires oil or fat |
| Cleaning & Maintenance | Easy to clean, dishwasher safe | Requires gentle cleaning, dishwasher safe |
| Safety | PTFE and PFOA free, eco-friendly | Non-toxic, lead and cadmium free |
| Typical Use | Everyday cookware, low to medium heat | Ovenware, high heat cooking |
| Cost | Moderate | Higher compared to ceramic resin |
Introduction to Cookware Coatings
Ceramic resin and porcelain enamel are popular cookware coatings known for their durability and non-stick properties. Ceramic resin coatings are derived from silica and offer a chemical-free, heat-resistant surface that excels in even heat distribution. Porcelain enamel, made by fusing powdered glass to metal at high temperatures, provides a hard, smooth finish resistant to scratches and staining, ideal for longevity in cookware.
What Is Ceramic Resin?
Ceramic resin is a composite material used in cookware coatings, combining resin with ceramic particles to create a non-stick, heat-resistant surface. Unlike porcelain enamel, which is a glassy, vitreous coating fused onto metal at high temperatures, ceramic resin offers enhanced durability and scratch resistance while maintaining a lightweight feel. Its chemical inertness and ability to withstand high cooking temperatures make ceramic resin an increasingly popular choice for modern, eco-friendly cookware.
What Is Porcelain Enamel?
Porcelain enamel is a durable coating made by fusing powdered glass to a metal surface at high temperatures, creating a smooth, non-porous layer resistant to scratching and staining. It offers excellent heat retention and distribution, commonly used in cookware for its aesthetic appeal and ability to withstand high cooking temperatures without degrading. Compared to ceramic resin, porcelain enamel provides superior durability and a glass-like finish that resists chipping and retains color over time.
Durability Comparison: Ceramic Resin vs Porcelain Enamel
Ceramic resin cookware offers moderate durability with resistance to chipping but can degrade over time due to heat exposure and staining. Porcelain enamel excels in long-term durability, providing a hard, glass-like coating that resists scratches, heat, and chemical damage on cast iron and steel bases. Porcelain enamel's high resistance to thermal shock and corrosion makes it a superior choice for cookware intended for frequent, heavy use.
Heat Resistance and Cooking Performance
Ceramic resin cookware offers moderate heat resistance, typically withstanding temperatures up to 450degF, making it suitable for everyday cooking but less ideal for high-heat searing or broiling. Porcelain enamel cookware excels in heat resistance, often tolerating temperatures up to 500degF or higher, providing superior durability and even heat distribution that enhances cooking performance. The non-porous surface of porcelain enamel also prevents food sticking and staining better than ceramic resin, resulting in easier maintenance and optimal cooking results.
Nonstick Properties and Food Release
Ceramic resin cookware offers excellent nonstick properties with a smooth surface that facilitates easy food release, often free of PTFE and PFOA chemicals. Porcelain enamel, while durable and resistant to staining, tends to have less effective nonstick performance, requiring more oil or fat to prevent food from sticking. The superior food release of ceramic resin coatings makes them a popular choice for health-conscious cooks seeking easy cleanup and reduced need for added fats.
Health and Safety Considerations
Ceramic resin cookware offers a non-toxic, PTFE- and PFOA-free surface that heats evenly and resists chipping, making it a safer choice for health-conscious users. Porcelain enamel, made by fusing powdered glass to metal, is chemical-free and highly durable, but can chip or crack, potentially exposing the underlying metal and leading to contamination or rust. Both materials avoid harmful heavy metals like lead and cadmium, but ceramic resin typically provides better non-stick properties without risking toxic fume emissions at high temperatures.
Maintenance and Cleaning Requirements
Ceramic resin cookware typically requires gentle cleaning with non-abrasive sponges and mild detergents to preserve its non-stick surface and avoid scratches. Porcelain enamel cookware demands careful maintenance to prevent chipping and cracking; it is best cleaned with soft cloths and avoids harsh chemicals or metal scrubbers. Both materials benefit from hand washing and immediate drying to extend their lifespan and maintain cookware performance.
Cost and Value Analysis
Ceramic resin cookware typically costs less upfront than porcelain enamel, offering budget-friendly options for everyday use without compromising durability. Porcelain enamel cookware, while more expensive, provides superior heat retention and scratch resistance, delivering long-term value through enhanced cooking performance and longevity. Evaluating cost versus value depends on the frequency of use and desired durability, where ceramic resin suits casual cooks and porcelain enamel caters to those seeking premium, lasting cookware.
Which Cookware Coating Is Right for You?
Ceramic resin cookware offers a non-toxic, environmentally friendly coating that heats quickly and provides excellent non-stick properties, ideal for low to medium heat cooking and easy cleanup. Porcelain enamel cookware features a durable, glass-like surface bonded to metal, known for its resistance to high heat and chipping, making it suitable for baking, roasting, and stovetop use with little risk of warping. Choosing between them depends on your cooking style: ceramic resin is perfect for gentle, low-fat cooking, while porcelain enamel excels in heavy-duty, high-temperature applications.
Infographic: Ceramic resin vs Porcelain enamel for Cookware
 azmater.com
azmater.com