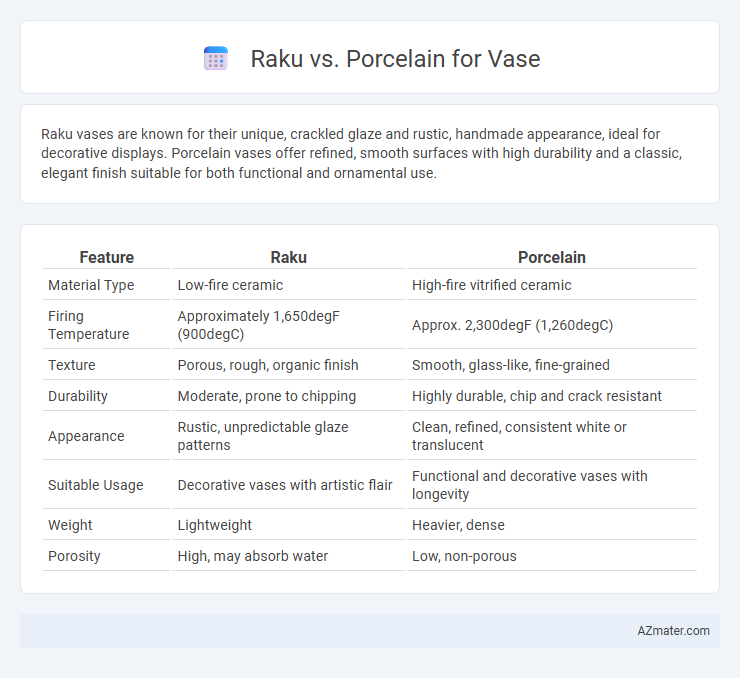
Raku vases are known for their unique, crackled glaze and rustic, handmade appearance, ideal for decorative displays. Porcelain vases offer refined, smooth surfaces with high durability and a classic, elegant finish suitable for both functional and ornamental use.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Raku | Porcelain |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Low-fire ceramic | High-fire vitrified ceramic |
| Firing Temperature | Approximately 1,650degF (900degC) | Approx. 2,300degF (1,260degC) |
| Texture | Porous, rough, organic finish | Smooth, glass-like, fine-grained |
| Durability | Moderate, prone to chipping | Highly durable, chip and crack resistant |
| Appearance | Rustic, unpredictable glaze patterns | Clean, refined, consistent white or translucent |
| Suitable Usage | Decorative vases with artistic flair | Functional and decorative vases with longevity |
| Weight | Lightweight | Heavier, dense |
| Porosity | High, may absorb water | Low, non-porous |
Introduction to Raku and Porcelain Vases
Raku vases are distinguished by their unique firing process that creates crackled textures and smoky effects, resulting in one-of-a-kind pieces with an organic, rustic appeal. Porcelain vases, known for their smooth, translucent quality and high firing temperature, offer a refined, delicate aesthetic with exceptional strength and durability. Both materials reflect distinct artistic traditions, with Raku emphasizing spontaneity and earthy textures, while Porcelain highlights precision and elegance.
Historical Background of Raku and Porcelain
Raku pottery originated in 16th-century Japan, closely associated with the tea ceremony and prized for its hand-shaped forms and unique firing process that creates unpredictable, organic textures and colors. Porcelain, developed in China during the Tang Dynasty and perfected by the Ming Dynasty, is renowned for its high strength, translucency, and smooth, white surface achieved through high-temperature kiln firing of refined clay. The historical significance of Raku lies in its connection to Zen aesthetics and wabi-sabi philosophy, while porcelain reflects centuries of technological innovation and global export as a luxury ceramic material.
Material Composition: Raku vs Porcelain
Raku vases are crafted from porous clay fired at low temperatures, resulting in a rough texture with natural cracks and a smoky finish, which enhances their unique handmade aesthetic. Porcelain vases use highly refined kaolin clay fired at higher temperatures, producing a dense, non-porous material characterized by smoothness, translucency, and exceptional durability. The material composition difference significantly affects functionality, with porcelain offering better resistance to water and staining compared to the more fragile and absorbent raku ceramic.
Firing Techniques and Processes
Raku firing involves rapid heating and cooling, where the vase is removed from the kiln while glowing hot and placed in a combustible material to create unique crackled surfaces and smoky effects. Porcelain firing requires high-temperature, slow firing in a controlled kiln environment to achieve its characteristic smooth, translucent, and durable finish without surface cracks. The Raku process emphasizes artistic volatility and texture, while porcelain firing prioritizes precision and strength through vitrification at temperatures around 1300degC (2372degF).
Aesthetic Differences in Vase Appearance
Raku vases exhibit a distinctive, rustic aesthetic characterized by crackled glaze patterns and smoky, earth-toned surfaces resulting from their unique firing process. Porcelain vases offer a smooth, refined appearance with a translucent quality and a wide range of vibrant, glossy finishes due to their high-fired, fine-grained composition. The organic, unpredictable textures of Raku contrast sharply with the polished, delicate elegance found in porcelain, making each material ideal for different decorative styles.
Durability and Functional Qualities
Raku vases, created through a low-firing process and rapid cooling, exhibit unique crackled textures but are more porous and fragile, making them less durable for everyday use. Porcelain vases, fired at higher temperatures, possess a dense, vitrified structure that ensures superior strength, resistance to chipping, and optimal water retention. Functional qualities favor porcelain for long-lasting practicality and ease of cleaning, whereas raku is often chosen for decorative purposes due to its delicate nature.
Texture and Surface Finish Comparisons
Raku vases exhibit a unique, crackled texture with a rustic, matte surface finish resulting from rapid cooling and reduction firing techniques, enhancing their organic, tactile appeal. Porcelain vases feature a smooth, glossy surface with a refined texture due to high-temperature firing and the fine, dense clay body, providing a sleek and elegant appearance. The choice between Raku and porcelain emphasizes the contrast between Raku's raw, unpredictable surface qualities and porcelain's polished, consistent finish.
Artistic Flexibility and Design Potential
Raku pottery offers unparalleled artistic flexibility due to its unpredictable firing process, enabling unique textures and crackle effects that enhance each vase's individuality. Porcelain provides superior design potential with its smooth, fine-grained surface and translucency, allowing for intricate detailing and refined elegance in vase creation. Both materials cater to distinct artistic visions, with Raku excelling in organic, rustic aesthetics and porcelain suited for delicate, precise designs.
Cost and Accessibility of Materials
Raku vases typically involve specialized clay and firing techniques that require a kiln capable of rapid temperature changes, making the materials moderately expensive and less accessible for beginners. Porcelain vases use highly refined white clay that is often costlier but widely available through commercial suppliers, offering easier access for hobbyists and professionals alike. The choice between Raku and porcelain often hinges on budget constraints and material availability, with Raku posing higher initial costs due to equipment and kiln operation requirements.
Choosing Between Raku and Porcelain for Your Vase
Choosing between Raku and porcelain for your vase depends on the desired aesthetic and durability; Raku offers unique, crackled textures with smoky, organic finishes due to its rapid cooling process, while porcelain provides a smooth, refined, and highly durable surface ideal for elegant, classic designs. Raku vases are often favored for their artisanal, rustic appearance and unpredictability, whereas porcelain vases appeal to those seeking a timeless, pristine look with resistance to chipping and staining. Consider the environment where the vase will be placed since porcelain excels in both indoor and outdoor durability, while Raku is best suited for decorative indoor settings due to its fragility.
Infographic: Raku vs Porcelain for Vase
 azmater.com
azmater.com