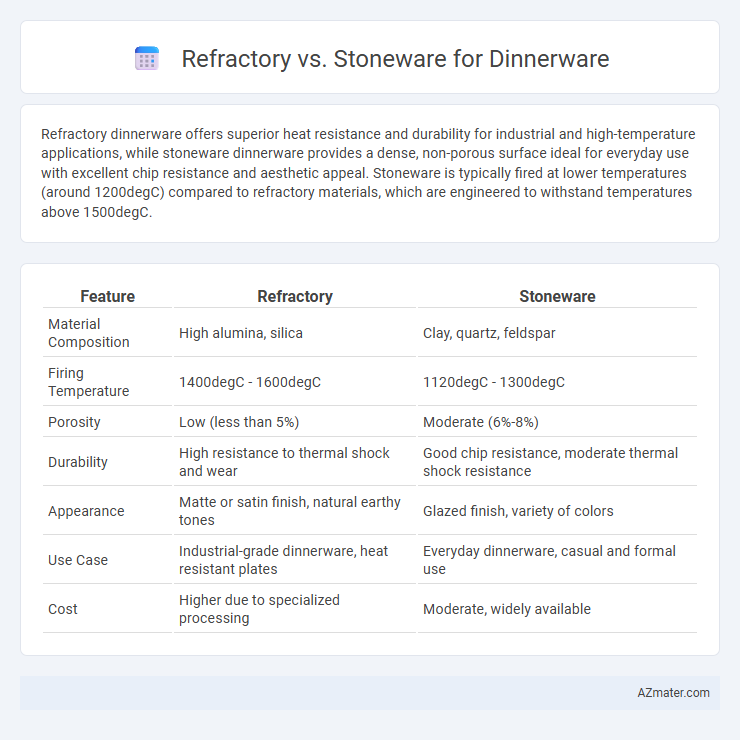
Refractory dinnerware offers superior heat resistance and durability for industrial and high-temperature applications, while stoneware dinnerware provides a dense, non-porous surface ideal for everyday use with excellent chip resistance and aesthetic appeal. Stoneware is typically fired at lower temperatures (around 1200degC) compared to refractory materials, which are engineered to withstand temperatures above 1500degC.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Refractory | Stoneware |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | High alumina, silica | Clay, quartz, feldspar |
| Firing Temperature | 1400degC - 1600degC | 1120degC - 1300degC |
| Porosity | Low (less than 5%) | Moderate (6%-8%) |
| Durability | High resistance to thermal shock and wear | Good chip resistance, moderate thermal shock resistance |
| Appearance | Matte or satin finish, natural earthy tones | Glazed finish, variety of colors |
| Use Case | Industrial-grade dinnerware, heat resistant plates | Everyday dinnerware, casual and formal use |
| Cost | Higher due to specialized processing | Moderate, widely available |
Introduction to Dinnerware Materials
Refractory and stoneware are prominent materials used in dinnerware, each offering unique durability and thermal properties. Refractory dinnerware excels in heat resistance, making it ideal for high-temperature applications, while stoneware provides robust strength combined with a slightly porous texture that enhances its rustic appeal. Understanding the distinctions between these materials helps in selecting dinnerware that balances functionality and aesthetic preferences for everyday use.
What is Refractory Dinnerware?
Refractory dinnerware is made from specially formulated clay mixtures designed to withstand extreme temperatures and thermal shock without cracking or breaking. This type of dinnerware is highly durable, often used in professional kitchens and for oven-to-table service due to its exceptional heat resistance. Compared to stoneware, refractory dinnerware offers superior strength and is less porous, making it more resistant to staining and chipping.
What is Stoneware Dinnerware?
Stoneware dinnerware is a type of ceramic made from refined clay fired at high temperatures, typically between 1,100degC and 1,200degC, resulting in a dense, durable, and non-porous material. It offers excellent chip resistance and a natural, earthy appearance, often glazed to enhance its strength and aesthetics. Unlike refractory materials, stoneware is designed specifically for everyday use, combining functionality with rustic elegance.
Key Differences Between Refractory and Stoneware
Refractory dinnerware is engineered for extreme heat resistance and durability, making it ideal for professional kitchens and high-temperature applications, while stoneware offers a more artisanal aesthetic with moderate heat tolerance suitable for everyday use. Refractory materials typically have higher thermal shock resistance and can withstand temperatures up to 2700degF, whereas stoneware generally endures up to 2300degF but provides a wider range of colors and finishes. The porosity of refractory is low, ensuring non-absorbency and stain resistance, compared to stoneware, which may require glazing to achieve similar properties.
Durability and Strength Comparison
Refractory dinnerware is engineered to withstand extreme temperatures and resist thermal shock, making it exceptionally durable for frequent use and high-heat applications. Stoneware offers strong resistance to chipping and cracking due to its dense, non-porous composition, providing long-lasting strength suitable for everyday dining. Comparing both, refractory materials excel in heat endurance and mechanical strength, while stoneware balances toughness with aesthetic versatility and moderate durability.
Heat Resistance and Cooking Applications
Refractory dinnerware offers superior heat resistance, withstanding temperatures over 2,500degF, making it ideal for direct cooking and high-temperature oven use. Stoneware typically endures up to 2,200degF and excels in heat retention, perfect for baking and serving but less suited for open flame or broiler settings. Both materials provide durability, but refractory is preferred for extreme heat cooking, while stoneware balances heat resistance with aesthetic appeal for everyday use.
Aesthetic Qualities and Design Options
Refractory dinnerware offers a sleek, modern aesthetic with smooth surfaces and subtle matte finishes, making it ideal for minimalist or contemporary table settings. Stoneware features rich textures and earthy tones, providing a rustic, handcrafted appearance that enhances cozy, traditional dining experiences. Both materials allow various glazing techniques, but stoneware's organic patterns and color variations deliver more artisanal, visually dynamic design options.
Care, Cleaning, and Maintenance
Refractory dinnerware, made from high-temperature resistant materials, requires gentle cleaning with mild detergents to preserve its thermal properties and avoid cracking. Stoneware, known for its durability and chip resistance, can tolerate dishwasher use but benefits from hand washing to maintain its glaze and prevent surface scratches. Both types should avoid harsh abrasives and sudden temperature changes to ensure long-lasting performance and aesthetic appeal.
Cost and Value Considerations
Refractory dinnerware typically costs more upfront because of its high durability and resistance to thermal shock, making it suitable for frequent use and harsh conditions. Stoneware offers a more affordable option with moderate durability and aesthetic appeal, providing good value for everyday dining without the premium price. Investing in refractory pieces can reduce long-term replacement costs, while stoneware balances cost and functional value for budget-conscious consumers.
Choosing the Right Material for Your Dinner Table
Refractory dinnerware offers exceptional heat resistance and durability, making it ideal for high-temperature cooking and serving, while stoneware provides a naturally rustic look with good chip resistance and heat retention suitable for everyday use. Stoneware's non-porous glaze ensures easy cleaning and stain resistance, whereas refractory ceramics excel in thermal shock resistance, preventing cracks when transitioning from oven to table. Selecting between refractory and stoneware depends on balancing the need for thermal performance with aesthetic preferences and everyday practicality on your dinner table.
Infographic: Refractory vs Stoneware for Dinnerware
 azmater.com
azmater.com