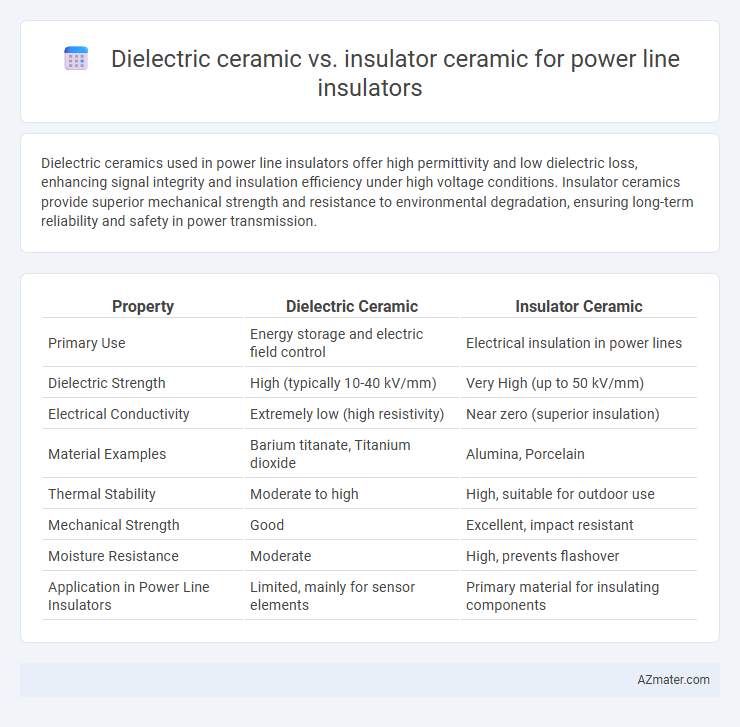
Dielectric ceramics used in power line insulators offer high permittivity and low dielectric loss, enhancing signal integrity and insulation efficiency under high voltage conditions. Insulator ceramics provide superior mechanical strength and resistance to environmental degradation, ensuring long-term reliability and safety in power transmission.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Dielectric Ceramic | Insulator Ceramic |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Use | Energy storage and electric field control | Electrical insulation in power lines |
| Dielectric Strength | High (typically 10-40 kV/mm) | Very High (up to 50 kV/mm) |
| Electrical Conductivity | Extremely low (high resistivity) | Near zero (superior insulation) |
| Material Examples | Barium titanate, Titanium dioxide | Alumina, Porcelain |
| Thermal Stability | Moderate to high | High, suitable for outdoor use |
| Mechanical Strength | Good | Excellent, impact resistant |
| Moisture Resistance | Moderate | High, prevents flashover |
| Application in Power Line Insulators | Limited, mainly for sensor elements | Primary material for insulating components |
Introduction to Power Line Insulators
Power line insulators are critical components designed to support and electrically isolate high-voltage conductors from transmission towers. Dielectric ceramics, characterized by high permittivity and excellent voltage withstand capability, are often preferred for their superior insulating properties and mechanical strength. Insulator ceramics, typically alumina or porcelain-based, provide reliable thermal stability and mechanical durability essential for long-term outdoor performance in power transmission systems.
What Are Dielectric Ceramics?
Dielectric ceramics are advanced materials with high electrical resistivity and low dielectric loss, making them ideal for power line insulators that require efficient electrical insulation and minimal energy dissipation. These ceramics exhibit exceptional dielectric strength and thermal stability, ensuring reliable performance under high voltage conditions found in power transmission. Insulator ceramics, while also providing electrical insulation, often lack the optimized dielectric properties of dielectric ceramics, which are specifically engineered to enhance capacitive performance in power line applications.
What Are Insulator Ceramics?
Insulator ceramics for power line insulators are specialized materials designed to prevent electrical conduction while withstanding high voltage and environmental stress. These ceramics, typically made from alumina, porcelain, or glass, exhibit high dielectric strength, mechanical robustness, and resistance to moisture and contaminants. Dielectric ceramics prioritize energy storage and electrical insulation but may differ in composition and properties, making insulator ceramics specifically optimized for durability and insulating performance in power transmission applications.
Key Material Properties Comparison
Dielectric ceramics for power line insulators exhibit high dielectric strength, low dielectric loss, and excellent thermal stability, making them suitable for efficient electric insulation under high voltage conditions. Insulator ceramics prioritize mechanical strength, moisture resistance, and surface hydrophobicity to prevent flashover and withstand environmental stresses. Comparing key properties, dielectric ceramics emphasize electrical performance metrics like permittivity and resistivity, while insulator ceramics focus more on toughness and environmental durability to ensure reliable long-term operation in power transmission.
Performance in High-Voltage Applications
Dielectric ceramics exhibit superior electrical insulating properties with high dielectric strength and low loss tangent, making them ideal for high-voltage power line insulators. Insulator ceramics offer excellent mechanical robustness and weather resistance but may have lower dielectric performance compared to specialized dielectric ceramics. In high-voltage applications, dielectric ceramics ensure enhanced insulation reliability and reduced leakage currents, critical for long-term operational stability and safety.
Mechanical Strength and Durability
Dielectric ceramic materials used for power line insulators exhibit higher mechanical strength and enhanced durability compared to traditional insulator ceramics, ensuring better performance under mechanical stress and environmental conditions. Their superior fracture toughness and resistance to thermal cycling improve lifespan and reliability in high-voltage applications. Insulator ceramics, while effective in electrical insulation, often have lower mechanical robustness, making dielectric ceramics the preferred choice for critical power line insulator components.
Electrical Breakdown and Safety Considerations
Dielectric ceramics for power line insulators exhibit higher electrical breakdown strength compared to conventional insulator ceramics, enabling better resistance to high voltages and minimizing flashover incidents. Their superior dielectric properties reduce leakage currents and improve overall insulation efficiency, enhancing system reliability and safety under extreme electrical stress. Safety considerations prioritize dielectric ceramics due to their enhanced thermal stability and mechanical robustness, which prevent abrupt failures and maintain insulation integrity during transient overvoltages.
Cost and Manufacturing Differences
Dielectric ceramics for power line insulators typically feature higher purity materials and require precise sintering processes, resulting in increased manufacturing costs compared to insulator ceramics, which use more common clay and alumina blends. Cost differences stem from dielectric ceramics' enhanced electrical properties and mechanical strength, justifying their premium price in high-voltage applications. Manufacturing differences also include tighter quality control and advanced fabrication techniques needed for dielectric ceramics, while insulator ceramics have simpler production lines and lower material expenses.
Suitability for Outdoor Environments
Dielectric ceramics exhibit superior electrical insulation and thermal stability, making them highly suitable for outdoor power line insulators exposed to varying weather conditions. Insulator ceramics, while effective in preventing current leakage, often have lower mechanical strength and weather resistance compared to dielectric ceramics in harsh environments. The enhanced durability and resistance to moisture and UV radiation make dielectric ceramics the preferred choice for outdoor power line insulation applications.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Ceramic for Power Line Insulators
Dielectric ceramics excel in high permittivity and breakdown voltage, making them ideal for efficient electrical insulation under varying load conditions in power lines. Insulator ceramics offer superior mechanical strength and environmental resistance, crucial for durability against weather and pollution in outdoor installations. Selecting the right ceramic depends on balancing electrical performance requirements with mechanical and environmental durability to ensure long-term reliability and safety of power line insulators.
Infographic: Dielectric ceramic vs Insulator ceramic for Power line insulator
 azmater.com
azmater.com