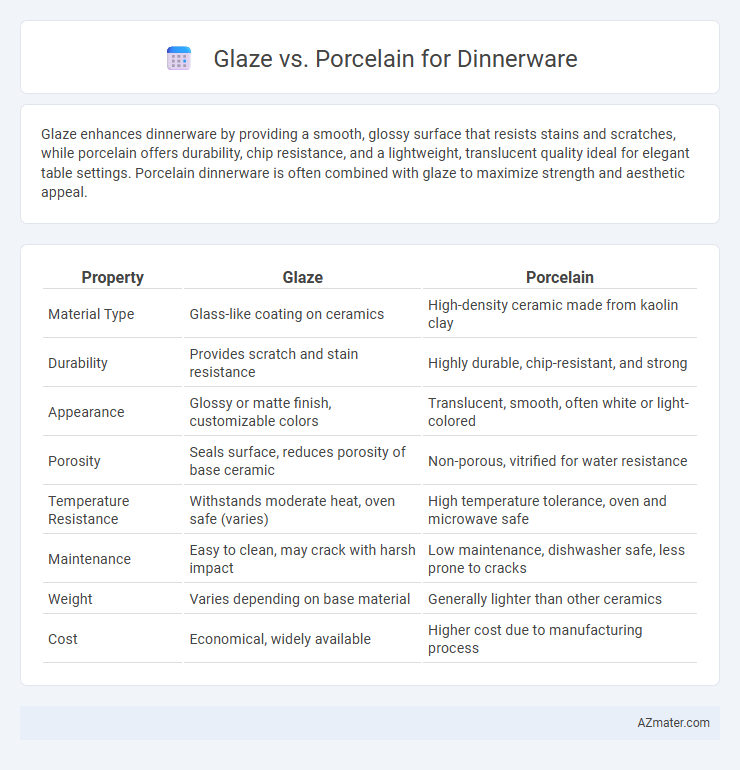
Glaze enhances dinnerware by providing a smooth, glossy surface that resists stains and scratches, while porcelain offers durability, chip resistance, and a lightweight, translucent quality ideal for elegant table settings. Porcelain dinnerware is often combined with glaze to maximize strength and aesthetic appeal.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Glaze | Porcelain |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Glass-like coating on ceramics | High-density ceramic made from kaolin clay |
| Durability | Provides scratch and stain resistance | Highly durable, chip-resistant, and strong |
| Appearance | Glossy or matte finish, customizable colors | Translucent, smooth, often white or light-colored |
| Porosity | Seals surface, reduces porosity of base ceramic | Non-porous, vitrified for water resistance |
| Temperature Resistance | Withstands moderate heat, oven safe (varies) | High temperature tolerance, oven and microwave safe |
| Maintenance | Easy to clean, may crack with harsh impact | Low maintenance, dishwasher safe, less prone to cracks |
| Weight | Varies depending on base material | Generally lighter than other ceramics |
| Cost | Economical, widely available | Higher cost due to manufacturing process |
Introduction to Dinnerware Materials
Dinnerware materials primarily consist of glazed ceramic and porcelain, each offering unique characteristics. Glaze provides a protective, often colorful, glass-like coating that enhances durability and aesthetics, while porcelain is a refined, high-fired ceramic known for its strength, translucency, and resistance to chipping. Understanding these materials helps in selecting dinnerware that balances functionality, elegance, and maintenance requirements.
What is Glaze in Dinnerware?
Glaze in dinnerware is a glass-like coating applied to the surface of ceramic or porcelain pieces, providing a smooth, glossy finish that enhances durability and stain resistance. This protective layer seals the porous material beneath, preventing moisture absorption and making the dinnerware easier to clean. Glazes can vary in color, texture, and composition, influencing the aesthetic appeal and functional qualities of the dinnerware.
Understanding Porcelain Dinnerware
Porcelain dinnerware is prized for its durability, non-porous surface, and resistance to chipping, making it ideal for everyday use and special occasions. The glaze on porcelain enhances its smooth finish and adds a protective layer that prevents stain absorption and maintains the dinnerware's pristine appearance over time. Compared to other ceramics, porcelain's fine, dense composition and high firing temperature result in a lightweight yet strong product that retains heat well and resists scratching.
Key Differences: Glaze vs Porcelain
Glaze is a glassy coating applied to porcelain dinnerware that enhances durability, provides a smooth surface, and adds color or texture, while porcelain is a type of ceramic material known for its strength, whiteness, and translucency. Porcelain dinnerware is fired at high temperatures, creating a dense, non-porous base that is resistant to chipping, whereas the glaze acts as a protective layer that prevents stains and moisture absorption. The primary key difference lies in the composition and function: porcelain forms the structural body of the dinnerware, and glaze serves as the finishing surface that improves aesthetics and usability.
Durability and Longevity Comparison
Porcelain dinnerware is known for its exceptional durability due to its dense, vitrified structure that resists chipping and cracking over time. Glazed dinnerware, while offering a smooth, protective coating that enhances resistance to stains and scratches, may be more prone to surface wear or crazing with prolonged use. Porcelain generally outperforms glazed ceramics in longevity, maintaining structural integrity and appearance through frequent use and dishwasher cycles.
Aesthetic Appeal and Design Options
Glaze on dinnerware offers a wide range of aesthetic appeal with its glossy, matte, or textured finishes, allowing for vibrant colors and intricate patterns that enhance table settings. Porcelain, known for its smooth, translucent surface and refined elegance, provides timeless design options often favored for formal dining due to its delicate yet durable nature. Both materials support diverse artistic expressions, but porcelain's versatility in shape and fine detailing tends to elevate sophisticated design preferences.
Safety and Food Compatibility
Porcelain dinnerware is known for its non-porous surface that prevents bacteria absorption, making it highly safe and food-compatible. Glaze applied on porcelain enhances durability and creates a smooth, non-toxic barrier resistant to scratches and stains. Both materials are FDA-approved for food use, but high-quality glazed porcelain offers superior protection against contaminants and leaching.
Maintenance and Cleaning Tips
Glaze on dinnerware provides a smooth, non-porous surface that resists stains and makes cleaning easier, often compatible with dishwasher use. Porcelain dinnerware, known for its dense, vitrified composition, requires careful handling to avoid chips but is generally stain-resistant and simple to clean with mild detergents. Avoid abrasive cleaners or harsh scrubbing on both glazed and porcelain pieces to maintain their glossy finish and prolong durability.
Cost and Value Considerations
Glaze coatings on dinnerware are generally more affordable, offering a wide range of styles and colors but may chip or wear over time, affecting longevity and value. Porcelain dinnerware commands a higher initial cost due to its durability, non-porous nature, and elegant appearance, which often translates into better long-term value and resistance to staining and heat. Selecting between glaze and porcelain dinnerware balances budget constraints with desired durability and aesthetic appeal, impacting overall satisfaction and cost-effectiveness.
Choosing the Best Option for Your Needs
Glaze enhances porcelain dinnerware by providing a smooth, protective coating that increases durability and resistance to stains, making it ideal for everyday use. Porcelain itself is valued for its strength, translucency, and elegant finish, often preferred for formal dining due to its refined appearance and chip resistance. Selecting between glazed and unglazed porcelain depends on whether you prioritize ease of maintenance and sturdiness or a minimalist, delicate look for special occasions.
Infographic: Glaze vs Porcelain for Dinnerware
 azmater.com
azmater.com