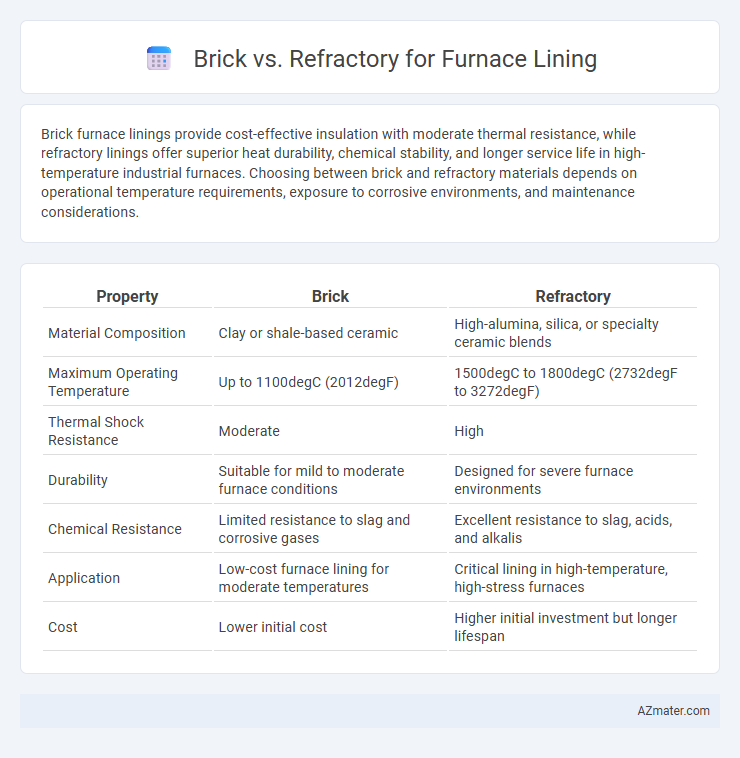
Brick furnace linings provide cost-effective insulation with moderate thermal resistance, while refractory linings offer superior heat durability, chemical stability, and longer service life in high-temperature industrial furnaces. Choosing between brick and refractory materials depends on operational temperature requirements, exposure to corrosive environments, and maintenance considerations.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Brick | Refractory |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Clay or shale-based ceramic | High-alumina, silica, or specialty ceramic blends |
| Maximum Operating Temperature | Up to 1100degC (2012degF) | 1500degC to 1800degC (2732degF to 3272degF) |
| Thermal Shock Resistance | Moderate | High |
| Durability | Suitable for mild to moderate furnace conditions | Designed for severe furnace environments |
| Chemical Resistance | Limited resistance to slag and corrosive gases | Excellent resistance to slag, acids, and alkalis |
| Application | Low-cost furnace lining for moderate temperatures | Critical lining in high-temperature, high-stress furnaces |
| Cost | Lower initial cost | Higher initial investment but longer lifespan |
Introduction to Furnace Lining Materials
Furnace lining materials are critical for thermal insulation and structural durability in high-temperature environments. Brick linings, typically composed of fireclay or silica, offer cost-effective solutions with moderate thermal resistance and ease of installation. Refractory linings, made from advanced ceramic composites or alumina-based materials, provide superior heat resistance, enhanced chemical stability, and extended service life for industrial furnaces.
Understanding Brick Linings
Brick linings in furnace construction provide excellent thermal insulation and durability due to their dense composition and high resistance to heat. These linings are often made from fireclay or silica bricks, which maintain structural integrity at temperatures exceeding 1500degC, making them ideal for various industrial furnaces. Their modular installation allows for easier maintenance and replacement compared to monolithic refractory materials, ensuring extended furnace lifespan and operational efficiency.
Overview of Refractory Materials
Refractory materials are engineered to withstand extreme temperatures, thermal shock, and chemical corrosion, making them essential for furnace linings. These materials include firebricks, castables, and ceramic fibers, each designed to provide high thermal insulation and mechanical strength in harsh operating conditions. Compared to traditional bricks, refractories offer superior resistance to heat degradation and structural integrity, ensuring longer service life and improved energy efficiency in industrial furnaces.
Thermal Performance: Brick vs Refractory
Refractory linings offer superior thermal insulation and withstand higher temperatures compared to standard bricks, making them ideal for furnace applications requiring consistent heat retention. Bricks, while cost-effective, have lower thermal resistance and tend to degrade faster under extreme heat conditions. Selecting refractory materials with specialized compositions ensures enhanced durability and efficient thermal performance in industrial furnaces.
Durability and Lifespan Comparison
Refractory linings outperform traditional brick linings in furnace durability due to their superior resistance to high temperatures, chemical corrosion, and thermal shock. While standard bricks may crack or degrade under continuous exposure to extreme heat, refractory materials can maintain structural integrity for significantly longer periods, often extending furnace lifespan by several years. This enhanced durability reduces maintenance frequency and operational downtime, making refractory linings a more cost-effective choice for high-temperature industrial furnace applications.
Cost Analysis: Initial and Maintenance Expenses
Refractory materials typically incur higher initial costs compared to standard bricks due to their superior heat resistance and durability in furnace lining applications. Maintenance expenses for refractory linings are generally lower over time as they withstand thermal stress better, reducing the frequency of repairs and replacements. Conversely, bricks may have lower upfront costs but can lead to increased maintenance expenses and shorter service life in high-temperature environments.
Installation Techniques and Challenges
Brick furnace linings require precise mortar application and careful joint alignment to ensure thermal stability, while refractory linings demand skilled casting or gunning techniques for uniform thickness and reduced porosity. Installation challenges of bricks include managing expansion gaps and avoiding efflorescence, whereas refractory linings must address curing schedules and potential shrinkage cracks. Both methods require strict temperature control during installation to prevent structural damage and ensure long-term durability under cyclic thermal loads.
Suitability for Different Furnace Types
Firebricks are highly suitable for high-temperature furnaces such as blast furnaces and cupolas due to their excellent thermal conductivity and resistance to slag and thermal shock. Refractory linings composed of castable refractories or ceramic fiber best fit steel-making induction furnaces and glass melting furnaces where rapid heat cycling and chemical corrosion resistance are crucial. The choice between firebrick and refractory materials depends primarily on furnace operating temperature, atmosphere, and specific chemical exposure conditions.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Refractory linings for furnaces typically exhibit higher durability and thermal efficiency compared to standard brick linings, resulting in reduced energy consumption and lower carbon emissions during operation. Sustainable refractory materials often incorporate recycled content and promote longer service life, minimizing landfill waste and resource extraction. Brick linings, while generally more affordable, tend to require more frequent replacement, increasing environmental impact through higher material usage and disposal concerns.
Choosing the Right Material for Your Furnace
Selecting the right furnace lining material hinges on understanding the thermal resistance and durability of bricks versus refractories. Fire bricks offer excellent insulation and are cost-effective for moderate temperatures, while refractory materials provide superior chemical stability and can withstand extreme heat and corrosive environments. For optimizing furnace performance and longevity, consider the operational temperature, mechanical stress, and chemical exposure to choose between fire bricks and advanced refractory linings.
Infographic: Brick vs Refractory for Furnace Lining
 azmater.com
azmater.com