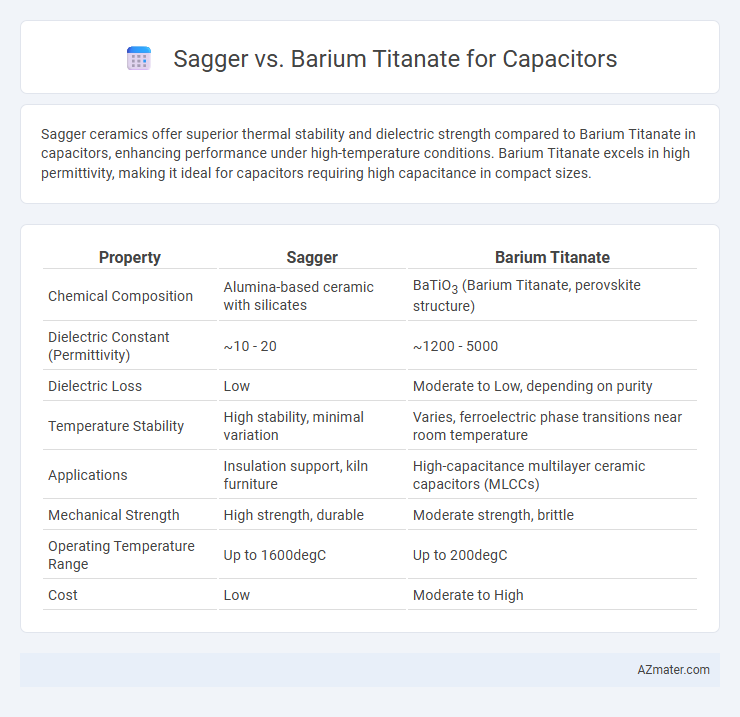
Sagger ceramics offer superior thermal stability and dielectric strength compared to Barium Titanate in capacitors, enhancing performance under high-temperature conditions. Barium Titanate excels in high permittivity, making it ideal for capacitors requiring high capacitance in compact sizes.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Sagger | Barium Titanate |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Composition | Alumina-based ceramic with silicates | BaTiO3 (Barium Titanate, perovskite structure) |
| Dielectric Constant (Permittivity) | ~10 - 20 | ~1200 - 5000 |
| Dielectric Loss | Low | Moderate to Low, depending on purity |
| Temperature Stability | High stability, minimal variation | Varies, ferroelectric phase transitions near room temperature |
| Applications | Insulation support, kiln furniture | High-capacitance multilayer ceramic capacitors (MLCCs) |
| Mechanical Strength | High strength, durable | Moderate strength, brittle |
| Operating Temperature Range | Up to 1600degC | Up to 200degC |
| Cost | Low | Moderate to High |
Introduction to Sagger and Barium Titanate in Capacitors
Sagger and Barium Titanate are critical materials in capacitor technology, each offering unique dielectric properties that influence capacitor performance. Sagger, known for its high thermal stability and robust mechanical strength, enhances the durability and reliability of capacitors in high-temperature environments. Barium Titanate, a ferroelectric ceramic with exceptional dielectric constant and polarization characteristics, significantly improves the energy storage capacity and efficiency of capacitors, making it ideal for advanced electronic applications.
Material Composition and Properties Overview
Sagger and Barium Titanate differ significantly in material composition; Sagger typically consists of a ceramic blend designed for high-temperature stability, while Barium Titanate is a perovskite structured ferroelectric oxide known for its high dielectric constant. Barium Titanate exhibits excellent dielectric permittivity, making it ideal for capacitors requiring high capacitance and energy storage, whereas Sagger's composition prioritizes thermal stability and mechanical robustness. The intrinsic properties of Barium Titanate include strong polarization and tunable dielectric behavior, contrasting with Sagger's focus on durability and consistent performance under thermal stress.
Dielectric Constant Comparison
Barium Titanate exhibits a significantly higher dielectric constant, typically ranging from 1,000 to 10,000, compared to Sagger's dielectric constant, which is generally below 100. This stark difference in dielectric constants makes Barium Titanate highly suitable for high-capacitance, miniaturized capacitors in electronic devices. The superior dielectric constant of Barium Titanate enables enhanced energy storage and improved performance in capacitors versus the relatively lower dielectric properties of Sagger materials.
Manufacturing Processes
Sagger in capacitor manufacturing acts as a protective ceramic container that withstands high sintering temperatures, ensuring the precise shaping and structural integrity of barium titanate components during calcination. Barium titanate synthesis involves controlled solid-state reactions or sol-gel techniques followed by meticulous sintering, often utilizing saggers to prevent contamination and achieve optimal dielectric properties. The manufacturing process emphasizes temperature stability and atmospheric control within saggers, enhancing the microstructural uniformity and performance reliability of barium titanate-based capacitors.
Thermal Stability and Performance
Sagger exhibits superior thermal stability compared to Barium Titanate, maintaining consistent dielectric properties across a wider temperature range, which enhances capacitor performance under high-temperature conditions. Barium Titanate offers high dielectric permittivity and excellent ferroelectric characteristics but suffers from significant performance degradation at elevated temperatures. Capacitors utilizing Sagger-based dielectrics deliver better reliability and longevity in harsh thermal environments, making them preferable for applications requiring stable capacitance and minimal thermal drift.
Cost and Availability Analysis
Sagger ceramic components generally offer lower cost and higher availability compared to barium titanate, making them a preferred choice for large-scale capacitor production. Barium titanate, while providing superior dielectric properties and energy storage capabilities, tends to be more expensive and less readily available due to its complex manufacturing process and material sourcing constraints. Manufacturers balance cost-efficiency with performance requirements by selecting Sagger components when budget limitations and supply chain stability are critical factors.
Applications in Modern Electronics
Sagger and Barium Titanate are crucial dielectric materials used in capacitors for modern electronics, with Barium Titanate offering high permittivity and temperature stability, making it ideal for multilayer ceramic capacitors (MLCCs) in smartphones, automotive sensors, and energy storage devices. Sagger, typically used in traditional capacitor designs, provides reliable performance but lacks the enhanced dielectric properties of Barium Titanate, limiting its application in advanced miniaturized electronics. The superior dielectric constant and ferroelectric properties of Barium Titanate enable higher capacitance and integration density, essential for compact, high-performance electronic circuits in consumer electronics and industrial applications.
Environmental and Safety Considerations
Sagger materials generally exhibit lower environmental toxicity and are easier to recycle compared to barium titanate, which contains barium, a heavy metal known for its potential environmental hazards during disposal. Barium titanate capacitors may pose risks of soil and water contamination if not properly managed, whereas sagger-based capacitors reduce the reliance on hazardous substances. Safety protocols for manufacturing and disposal favor sagger materials due to their more benign chemical composition and lower environmental impact.
Longevity and Reliability Factors
Sagger capacitors exhibit exceptional longevity due to their robust ceramic composition, maintaining stable performance under high thermal and electrical stress, whereas Barium Titanate capacitors offer high permittivity but may degrade faster over time due to domain wall movements and aging effects. Reliability in Sagger capacitors is enhanced by their low dielectric loss and resistance to moisture, making them suitable for long-term industrial applications. Barium Titanate capacitors, while efficient in energy storage, require careful operational limits to mitigate breakdown risks and ensure prolonged lifespan.
Future Trends in Capacitor Materials
Sagger and Barium Titanate represent pivotal materials in the evolution of capacitor technology, with Barium Titanate dominating due to its high dielectric constant and excellent temperature stability, which are critical for next-generation energy storage solutions. Future trends highlight the integration of nano-engineered Barium Titanate composites to enhance capacitance and reduce leakage currents, driven by advancements in materials science and fabrication techniques. Research into hybrid Sagger-based dielectrics aims to leverage its unique electrical properties for flexible and high-frequency capacitors, signaling a shift towards multifunctional and miniaturized capacitive devices.
Infographic: Sagger vs Barium Titanate for Capacitor
 azmater.com
azmater.com