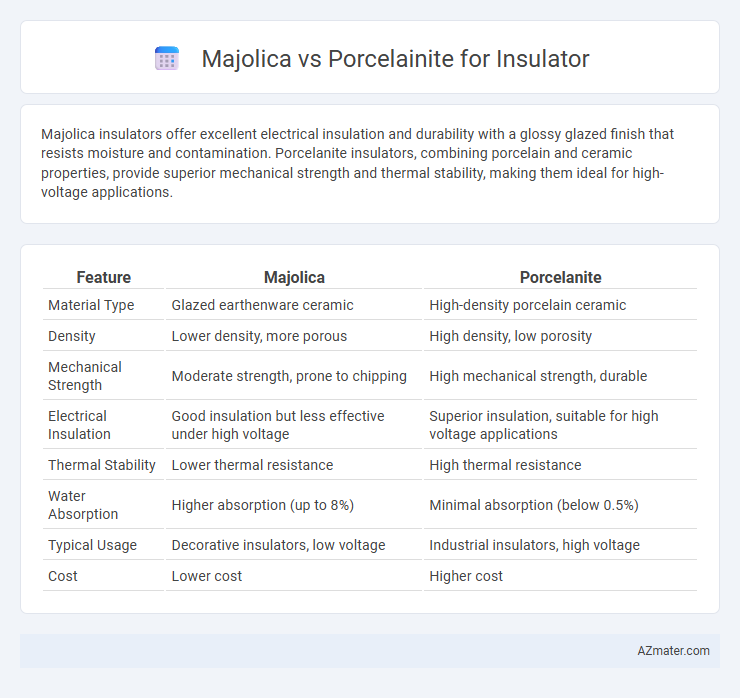
Majolica insulators offer excellent electrical insulation and durability with a glossy glazed finish that resists moisture and contamination. Porcelanite insulators, combining porcelain and ceramic properties, provide superior mechanical strength and thermal stability, making them ideal for high-voltage applications.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Majolica | Porcelanite |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Glazed earthenware ceramic | High-density porcelain ceramic |
| Density | Lower density, more porous | High density, low porosity |
| Mechanical Strength | Moderate strength, prone to chipping | High mechanical strength, durable |
| Electrical Insulation | Good insulation but less effective under high voltage | Superior insulation, suitable for high voltage applications |
| Thermal Stability | Lower thermal resistance | High thermal resistance |
| Water Absorption | Higher absorption (up to 8%) | Minimal absorption (below 0.5%) |
| Typical Usage | Decorative insulators, low voltage | Industrial insulators, high voltage |
| Cost | Lower cost | Higher cost |
Introduction to Insulator Materials
Majolica and Porcelanite are common materials used in electrical insulators, each offering unique properties suited for various applications. Majolica, a type of ceramic with a glazed surface, provides excellent electrical insulation and moisture resistance, making it ideal for outdoor and high-voltage uses. Porcelanite, a dense, vitrified ceramic, offers superior mechanical strength and thermal stability, ensuring durability and long-term performance in harsh environmental conditions.
What is Majolica?
Majolica is a type of glazed ceramic material often used for insulators due to its excellent electrical resistance and durability. Unlike Porcelanite, which is a dense, vitrified porcelain, Majolica features a distinctive glossy surface created by applying a tin-based glaze, enhancing its moisture resistance. This makes Majolica ideal for applications where insulation must withstand environmental exposure while maintaining high dielectric properties.
What is Porcelanite?
Porcelanite is a high-density ceramic material engineered for superior electrical insulation and mechanical strength, often used in insulators for power transmission and distribution networks. Its composition includes feldspar, quartz, and kaolin, which are fired at high temperatures to achieve low porosity and high dielectric strength, making it resistant to weathering and electrical stress. Compared to majolica, porcelanite offers enhanced durability and performance in high-voltage applications, ensuring long-term reliability in harsh environmental conditions.
Chemical Composition Comparison
Majolica insulators primarily consist of a clay-based ceramic with high silica and alumina content, offering excellent resistance to chemical corrosion and thermal stability. Porcelanite insulators are composed mainly of highly vitrified porcelain materials, characterized by a dense, glass-like structure with significant feldspar, kaolin, and quartz proportions, enhancing mechanical strength and chemical inertness. The chemical composition differences result in Majolica providing superior chemical resistance in acidic environments, while Porcelanite excels in mechanical durability and electrical insulation due to its higher vitrification level.
Mechanical Strength and Durability
Majolica insulators exhibit moderate mechanical strength and are prone to chipping under high-stress conditions due to their porous ceramic composition. Porcelanite insulators, composed of dense, high-quality porcelain, deliver superior mechanical strength and enhanced durability, making them highly resistant to impact, weathering, and electrical stress. The dense microstructure of Porcelanite also contributes to better long-term performance and reliability in demanding electrical insulation applications.
Electrical Insulation Properties
Majolica insulators offer moderate electrical insulation properties suitable for low to medium voltage applications, featuring natural clay composition with glazed surfaces that provide basic resistance to electrical conductivity. Porcelanite insulators, made from high-purity ceramic materials combined with advanced porcelain formulations, deliver superior dielectric strength, minimal porosity, and enhanced resistance to electrical tracking and corona discharge, making them ideal for high-voltage and high-stress electrical insulation environments. The dense, vitrified structure of Porcelanite significantly reduces leakage currents and improves long-term reliability compared to the more porous and less uniformly glazed Majolica insulators.
Thermal Performance and Stability
Majolica insulators exhibit moderate thermal performance with reasonable heat resistance but tend to experience slight dimensional changes under prolonged high-temperature exposure. Porcelanite insulators demonstrate superior thermal stability, maintaining structural integrity and electrical insulation properties even at elevated temperatures up to 1200degC. The enhanced crystalline structure of Porcelanite provides higher thermal shock resistance and reduced thermal conductivity compared to Majolica, making it more reliable for high-temperature electrical insulation applications.
Applications in Electrical Systems
Majolica insulators excel in medium-voltage electrical systems due to their high dielectric strength and thermal resistance, making them ideal for power distribution and substation equipment. Porcelanite insulators offer superior mechanical durability and moisture resistance, which suits them for high-voltage transmission lines exposed to harsh environmental conditions. Both materials ensure electrical insulation reliability, but the choice depends on specific voltage requirements and environmental factors in electrical infrastructure.
Cost and Availability
Majolica insulators are generally more cost-effective due to their traditional manufacturing process and widespread availability in many regions. Porcelanite offers superior durability but tends to be more expensive and less readily available, especially in markets focused on high-performance applications. Choosing between Majolica and Porcelanite depends on balancing budget constraints with the specific durability requirements of the insulator.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Insulator
Majolica insulators offer excellent thermal resistance and durability, making them suitable for high-voltage applications, while Porcelanite insulators provide superior mechanical strength and moisture resistance, ideal for harsh environmental conditions. Selecting the right insulator depends on specific operational requirements such as voltage levels, exposure to weather elements, and mechanical stress. Prioritizing these factors ensures optimal performance and longevity of the insulator in electrical infrastructure.
Infographic: Majolica vs Porcelanite for Insulator
 azmater.com
azmater.com