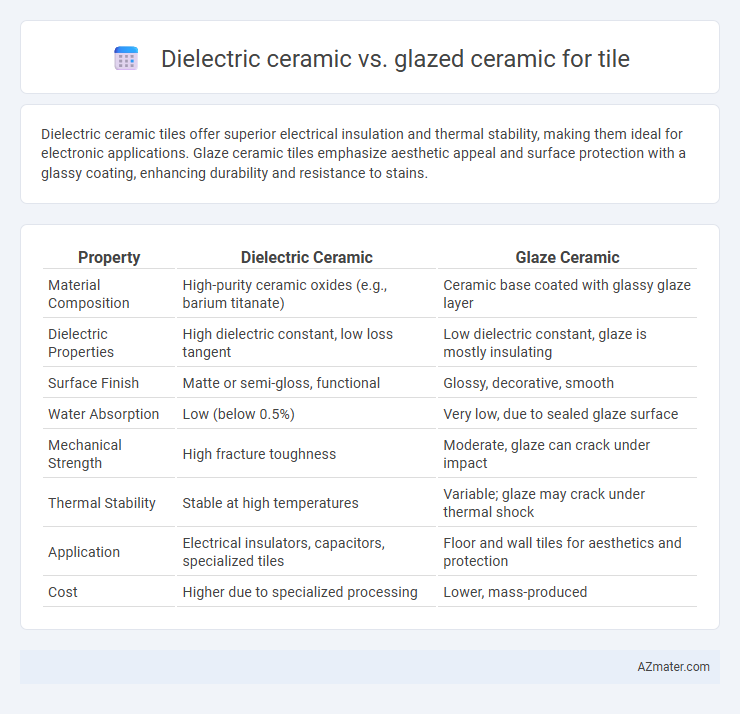
Dielectric ceramic tiles offer superior electrical insulation and thermal stability, making them ideal for electronic applications. Glaze ceramic tiles emphasize aesthetic appeal and surface protection with a glassy coating, enhancing durability and resistance to stains.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Dielectric Ceramic | Glaze Ceramic |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | High-purity ceramic oxides (e.g., barium titanate) | Ceramic base coated with glassy glaze layer |
| Dielectric Properties | High dielectric constant, low loss tangent | Low dielectric constant, glaze is mostly insulating |
| Surface Finish | Matte or semi-gloss, functional | Glossy, decorative, smooth |
| Water Absorption | Low (below 0.5%) | Very low, due to sealed glaze surface |
| Mechanical Strength | High fracture toughness | Moderate, glaze can crack under impact |
| Thermal Stability | Stable at high temperatures | Variable; glaze may crack under thermal shock |
| Application | Electrical insulators, capacitors, specialized tiles | Floor and wall tiles for aesthetics and protection |
| Cost | Higher due to specialized processing | Lower, mass-produced |
Introduction to Ceramic Materials in Tile Manufacturing
Dielectric ceramic and glaze ceramic in tile manufacturing differ fundamentally in composition and functionality; dielectric ceramics primarily serve electrical insulation purposes due to their high resistivity and low dielectric loss, while glaze ceramics provide a protective and decorative surface coating enhancing durability and aesthetic appeal. Dielectric ceramics are typically composed of oxides such as alumina and zirconia, which offer excellent thermal stability and electrical insulation critical for specialized tile applications. In contrast, glaze ceramics incorporate silica, fluxes, and colorants that melt during firing to form a glassy layer, sealing the tile surface against moisture and wear.
Understanding Dielectric Ceramic: Properties and Uses
Dielectric ceramic tiles exhibit high electrical insulation, low dielectric loss, and excellent thermal stability, making them ideal for electronic substrates and capacitors. These properties ensure minimal electrical conductivity, preventing current leakage and enhancing device performance in high-frequency applications. In contrast, glaze ceramic tiles prioritize aesthetic appeal and surface durability, often used in decorative and protective coatings rather than electrical functions.
What Is Glaze Ceramic? Key Characteristics
Glaze ceramic tiles feature a glass-like coating fused to the tile surface during firing, enhancing durability, stain resistance, and aesthetic appeal with a wide range of colors and patterns. These tiles offer high moisture resistance and are ideal for both wall and floor applications, providing a smooth, glossy finish that improves cleanability and maintenance. Their key characteristics include enhanced wear resistance, vibrant surface design, and protection against scratching and fading.
Manufacturing Processes: Dielectric vs. Glaze Ceramic
Dielectric ceramic tiles undergo a manufacturing process involving the precise mixing of oxide powders such as barium titanate or titanium dioxide, followed by high-temperature sintering to enhance dielectric properties. Glaze ceramic tiles are produced by applying a glassy coating composed of silica, fluxes, and colorants onto a fired ceramic body, then re-firing to fuse the glaze and create a smooth, decorative surface. The dielectric ceramic process prioritizes electrical insulation and material density, whereas glaze ceramic manufacturing emphasizes surface aesthetics and protection against moisture and wear.
Mechanical Strength Comparison
Dielectric ceramics exhibit higher mechanical strength compared to glaze ceramics due to their dense microstructure and superior fracture toughness, making them more resistant to cracking and chipping under mechanical stress. Glaze ceramics often have a more brittle surface layer that can lead to surface microcracks and reduced impact resistance. In applications requiring enhanced durability and load-bearing capacity, dielectric ceramics are preferred for tile manufacturing due to their robust mechanical properties.
Electrical Insulation: Dielectric vs. Glaze Ceramic
Dielectric ceramics exhibit superior electrical insulation properties due to their high dielectric strength and low electrical conductivity, making them ideal for preventing current flow in electronic tile applications. Glaze ceramics, while offering a protective and decorative surface, generally possess lower dielectric constants and are primarily used for surface finishing rather than insulation. The inherent material composition of dielectric ceramics ensures better resistance to electrical breakdown compared to glaze ceramics commonly applied as a thin insulating layer.
Durability and Wear Resistance
Dielectric ceramic tiles exhibit superior durability due to their dense microstructure, which enhances resistance to mechanical stress and thermal shock. Glaze ceramic tiles feature a protective glassy surface that improves wear resistance but may be prone to chipping or cracking under heavy impact. For applications demanding long-term performance under high abrasion, dielectric ceramics provide enhanced toughness and lifespan compared to glazed ceramics.
Aesthetic Differences and Design Flexibility
Dielectric ceramic tiles offer a uniform, matte finish with subtle color variations ideal for minimalist and modern designs, while glaze ceramic tiles boast vibrant colors and glossy surfaces that enhance intricate patterns and decorative details. Glaze ceramic provides greater design flexibility through customizable textures and finishes, allowing for diverse stylistic expressions, whereas dielectric ceramic maintains a consistent look suited for sleek, understated aesthetics. The choice between dielectric and glaze ceramics significantly impacts the visual appeal and adaptability of tile applications in interior and exterior designs.
Application Suitability: Choosing the Right Ceramic for Tiles
Dielectric ceramics are ideal for tiles requiring electrical insulation and thermal stability, often used in electronic device housings or specialized industrial flooring. Glaze ceramics provide a durable, water-resistant surface suitable for residential and commercial floor and wall tiles, offering aesthetic versatility with various finishes and colors. Selecting the right ceramic depends on application requirements such as electrical insulation needs or decorative durability in tile installations.
Cost and Sustainability Considerations
Dielectric ceramic tiles typically incur higher manufacturing costs due to advanced material properties and specialized production processes compared to glaze ceramics, which are more economical and widely available. From a sustainability perspective, glaze ceramics often have a lower environmental impact since they can incorporate recycled materials and require less energy-intensive firing techniques. However, dielectric ceramics offer enhanced durability and longevity, potentially reducing replacement frequency and overall environmental footprint in long-term applications.
Infographic: Dielectric ceramic vs Glaze ceramic for Tile
 azmater.com
azmater.com