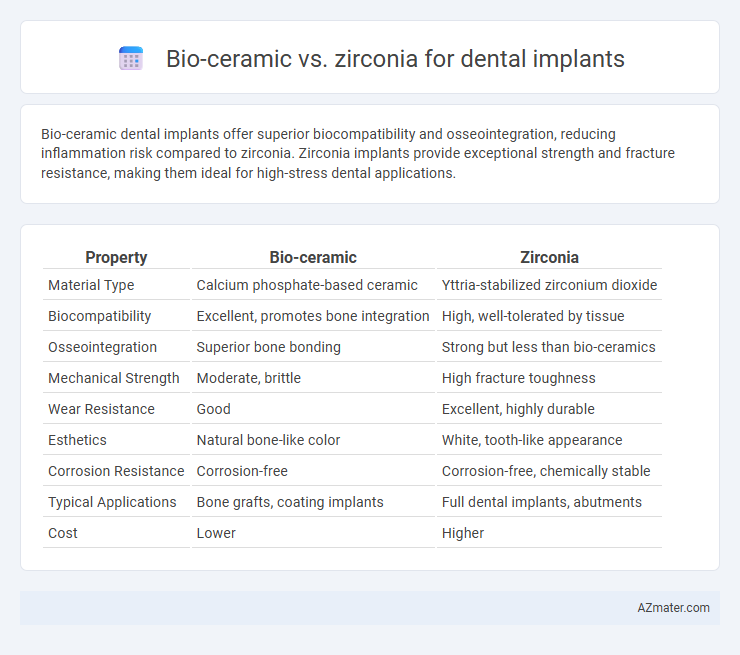
Bio-ceramic dental implants offer superior biocompatibility and osseointegration, reducing inflammation risk compared to zirconia. Zirconia implants provide exceptional strength and fracture resistance, making them ideal for high-stress dental applications.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Bio-ceramic | Zirconia |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Calcium phosphate-based ceramic | Yttria-stabilized zirconium dioxide |
| Biocompatibility | Excellent, promotes bone integration | High, well-tolerated by tissue |
| Osseointegration | Superior bone bonding | Strong but less than bio-ceramics |
| Mechanical Strength | Moderate, brittle | High fracture toughness |
| Wear Resistance | Good | Excellent, highly durable |
| Esthetics | Natural bone-like color | White, tooth-like appearance |
| Corrosion Resistance | Corrosion-free | Corrosion-free, chemically stable |
| Typical Applications | Bone grafts, coating implants | Full dental implants, abutments |
| Cost | Lower | Higher |
Introduction to Dental Implant Materials
Bio-ceramic and zirconia are prominent materials used in dental implants due to their excellent biocompatibility and mechanical strength. Zirconia implants offer high fracture resistance and aesthetic benefits with their tooth-like color, while bio-ceramics provide superior osseointegration and corrosion resistance. Both materials support long-term stability and function, making them ideal choices depending on patient-specific clinical needs and aesthetic demands.
What are Bio-ceramic Dental Implants?
Bio-ceramic dental implants are made from advanced materials such as alumina or zirconia-based ceramics, designed to integrate seamlessly with the jawbone while resisting corrosion and bacterial growth. These implants offer excellent biocompatibility, promoting natural osseointegration without triggering adverse tissue reactions. Compared to traditional titanium implants, bio-ceramic options provide superior aesthetics by matching tooth color and reducing the risk of metal sensitivity or allergic responses.
Understanding Zirconia Dental Implants
Zirconia dental implants offer superior biocompatibility and aesthetic advantages compared to traditional titanium, making them an ideal choice for patients with metal sensitivities or those seeking a natural tooth appearance. These implants exhibit high fracture toughness and corrosion resistance, ensuring long-term durability and integration within the jawbone. Bio-ceramic alternatives, while also biocompatible, typically do not match the mechanical strength and osseointegration properties of zirconia, positioning zirconia as the preferred material for modern dental implantology.
Bio-ceramic vs Zirconia: Material Composition
Bio-ceramic dental implants are primarily composed of calcium phosphate-based materials, such as hydroxyapatite, which closely resemble the mineral content of natural bone, promoting better osseointegration. Zirconia implants, made from zirconium dioxide, offer exceptional biocompatibility and high fracture toughness, exhibiting superior resistance to wear and corrosion. The material composition of bio-ceramics emphasizes bioactivity and bone integration, while zirconia focuses on mechanical strength and aesthetic advantages due to its tooth-like color.
Biocompatibility and Osseointegration Comparison
Bio-ceramic dental implants exhibit exceptional biocompatibility due to their inert composition, minimizing inflammatory responses and promoting better integration with surrounding tissues. Zirconia implants also demonstrate high biocompatibility with superior osseointegration properties, attributed to their stable zirconium oxide surface that encourages bone cell attachment and growth. Comparative studies reveal that while both materials are effective, zirconia may offer slightly faster osseointegration rates, whereas bio-ceramics provide enhanced antibacterial properties, supporting long-term implant stability.
Aesthetics: Appearance and Color Matching
Bio-ceramic dental implants offer superior aesthetics with a natural white color that closely resembles natural teeth, providing excellent color matching for patients with thin or translucent gums. Zirconia implants also provide appealing tooth-like whiteness but may exhibit slight color discrepancies under direct light due to their material density. Both materials enhance smile aesthetics, though bio-ceramics are often preferred for optimal translucency and lifelike appearance.
Durability and Mechanical Strength Analysis
Zirconia dental implants exhibit superior durability and mechanical strength compared to bio-ceramic alternatives, with tensile strength ranging from 900 to 1200 MPa and fracture toughness between 5 to 10 MPa*m^0.5, offering enhanced resistance to chipping and wear. Bio-ceramics, while biocompatible, typically demonstrate lower mechanical properties, with tensile strengths around 500 to 800 MPa and reduced fracture toughness, limiting their long-term performance under masticatory forces. The high crystalline content in zirconia contributes to its outstanding flexural strength and fatigue resistance, making it the preferred material for implants requiring prolonged functional stability.
Long-term Performance and Clinical Success Rates
Bio-ceramic dental implants demonstrate excellent biocompatibility and osseointegration, resulting in high long-term success rates comparable to traditional zirconia implants. Zirconia implants exhibit superior mechanical strength and resistance to fracture, contributing to their reliability in load-bearing situations over extended periods. Clinical studies report survival rates above 95% for both materials after five years, with bio-ceramics offering potential benefits in reducing peri-implant inflammation and promoting soft tissue integration.
Patient Safety and Allergic Reactions
Bio-ceramic dental implants offer high biocompatibility and lower risk of allergic reactions compared to zirconia, making them a safer option for patients with metal sensitivities. Zirconia implants, while also biocompatible, can occasionally cause hypersensitivity due to trace metal impurities or surface modifications. Choosing bio-ceramic materials reduces inflammation and promotes better osseointegration, enhancing overall patient safety in dental implant procedures.
Choosing the Right Implant: Factors to Consider
Bio-ceramic and zirconia dental implants differ in biocompatibility, strength, and aesthetic outcomes, making selection crucial based on patient-specific needs. Consider factors such as osseointegration efficiency, risk of allergic reactions, and the implant's ability to resist corrosion under oral conditions. Zirconia offers superior mechanical strength and esthetic appeal for visible areas, while bio-ceramics provide excellent biocompatibility and integration suited for patients with metal sensitivities.
Infographic: Bio-ceramic vs Zirconia for Dental Implant
 azmater.com
azmater.com