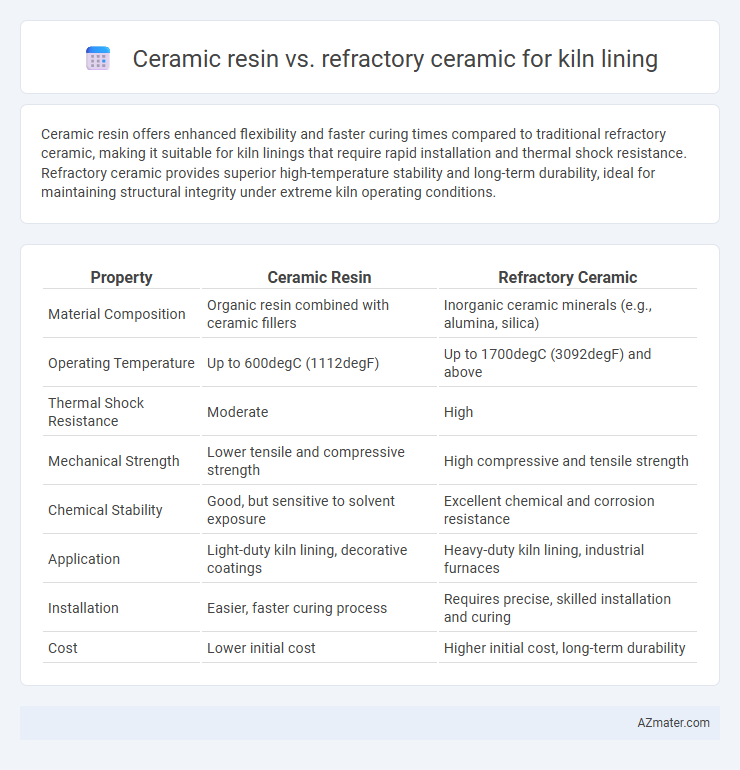
Ceramic resin offers enhanced flexibility and faster curing times compared to traditional refractory ceramic, making it suitable for kiln linings that require rapid installation and thermal shock resistance. Refractory ceramic provides superior high-temperature stability and long-term durability, ideal for maintaining structural integrity under extreme kiln operating conditions.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Ceramic Resin | Refractory Ceramic |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Organic resin combined with ceramic fillers | Inorganic ceramic minerals (e.g., alumina, silica) |
| Operating Temperature | Up to 600degC (1112degF) | Up to 1700degC (3092degF) and above |
| Thermal Shock Resistance | Moderate | High |
| Mechanical Strength | Lower tensile and compressive strength | High compressive and tensile strength |
| Chemical Stability | Good, but sensitive to solvent exposure | Excellent chemical and corrosion resistance |
| Application | Light-duty kiln lining, decorative coatings | Heavy-duty kiln lining, industrial furnaces |
| Installation | Easier, faster curing process | Requires precise, skilled installation and curing |
| Cost | Lower initial cost | Higher initial cost, long-term durability |
Introduction to Kiln Lining Materials
Kiln lining materials are critical for maintaining thermal efficiency and structural integrity in high-temperature environments. Ceramic resin offers superior chemical resistance and flexibility, making it suitable for dynamic thermal cycles, while refractory ceramics provide exceptional heat resistance and durability at extreme temperatures, ensuring long-term stability. Understanding the differences in thermal conductivity, expansion rates, and mechanical strength between ceramic resin and refractory ceramic is essential for optimizing kiln performance and lifespan.
Overview of Ceramic Resin
Ceramic resin is a high-performance material composed of inorganic binders and ceramic fillers, providing excellent thermal stability and mechanical strength for kiln lining applications. Unlike traditional refractory ceramics, ceramic resin offers enhanced adhesion and flexibility, reducing crack formation during thermal cycling. Its ability to form dense, seamless coatings makes it ideal for protecting kiln structures from extreme temperatures and chemical corrosion.
Overview of Refractory Ceramic
Refractory ceramic materials used for kiln lining provide exceptional thermal stability, resistance to chemical corrosion, and mechanical strength at high temperatures exceeding 1,500degC. These ceramics, typically composed of alumina, silica, and fireclay, maintain structural integrity during repeated thermal cycles, ensuring longevity and safety in industrial kilns. Their ability to withstand extreme heat and thermal shock makes refractory ceramics the preferred choice over ceramic resin for high-temperature kiln linings.
Key Properties: Ceramic Resin vs Refractory Ceramic
Ceramic resin offers superior chemical resistance and flexibility, making it ideal for kiln lining applications requiring adaptation to slight thermal expansions. Refractory ceramic excels in high-temperature stability, chemical inertness, and mechanical strength, providing excellent insulation and durability in industrial furnaces. Comparing thermal conductivity, refractory ceramics typically have lower values, enhancing energy efficiency, while ceramic resin's lower melting point limits its use in extreme heat environments.
Thermal Resistance and Performance
Ceramic resin linings provide moderate thermal resistance suitable for kilns operating under less extreme temperatures, benefiting from ease of installation and repair. Refractory ceramic materials exhibit superior thermal resistance, maintaining structural integrity and insulating properties at temperatures exceeding 1500degC, essential for high-performance industrial kilns. The choice directly impacts kiln efficiency, with refractory ceramics offering enhanced durability and energy conservation in high-temperature environments.
Installation Process and Flexibility
Ceramic resin kiln linings offer simplified installation with faster curing times and enhanced flexibility, allowing them to conform easily to complex kiln shapes and reducing labor costs. Refractory ceramic linings require more precise installation involving high-temperature preheating and careful setting to ensure structural integrity, making the process labor-intensive and less adaptable to irregular surfaces. The flexibility of ceramic resin materials enhances thermal shock resistance and accommodates kiln expansion better than the rigid, brittle refractory ceramics commonly used in traditional kiln linings.
Durability and Lifespan Comparison
Ceramic resin kiln linings offer moderate durability with resistance to thermal shock but typically have a shorter lifespan compared to refractory ceramic materials, which excel in prolonged exposure to extreme temperatures and chemical corrosion. Refractory ceramics, composed of high-purity alumina or silica, maintain structural integrity longer under cyclic heating and cooling, providing superior longevity for industrial kiln applications. The choice between ceramic resin and refractory ceramic hinges on operational temperature, chemical exposure, and maintenance frequency, with refractory ceramics favored for high-demand, long-term durability.
Cost Analysis: Ceramic Resin vs Refractory Ceramic
Ceramic resin kiln linings generally offer lower initial installation costs compared to refractory ceramics due to simpler application techniques and reduced labor requirements. Refractory ceramic linings, while more expensive upfront, provide superior durability and thermal resistance that can lower long-term maintenance and replacement expenses. Evaluating total cost of ownership reveals ceramic resin is cost-effective for short-term or moderate-temperature applications, whereas refractory ceramics deliver better value in high-temperature environments requiring extended service life.
Application Suitability for Various Kilns
Ceramic resin linings offer superior thermal shock resistance and are ideal for electric and gas kilns with frequent temperature fluctuations, enhancing longevity in rapid heat cycles. Refractory ceramics provide higher temperature tolerance and mechanical strength, making them suitable for industrial shaft and tunnel kilns operating at continuous high temperatures. Selecting between ceramic resin and refractory ceramic depends on kiln type, operating temperature, and thermal cycling demands to optimize kiln lining performance and durability.
Choosing the Right Lining Material for Your Kiln
Ceramic resin linings offer superior flexibility and chemical resistance, making them ideal for kilns exposed to fluctuating temperatures and corrosive environments. Refractory ceramics provide exceptional thermal insulation and high melting point durability, ensuring long-lasting performance in consistently high-temperature applications. Selecting the right kiln lining depends on operating temperature ranges, chemical exposure, and maintenance requirements, with refractory ceramics best suited for extreme heat and ceramic resin preferred for versatile protection.
Infographic: Ceramic resin vs Refractory ceramic for Kiln lining
 azmater.com
azmater.com