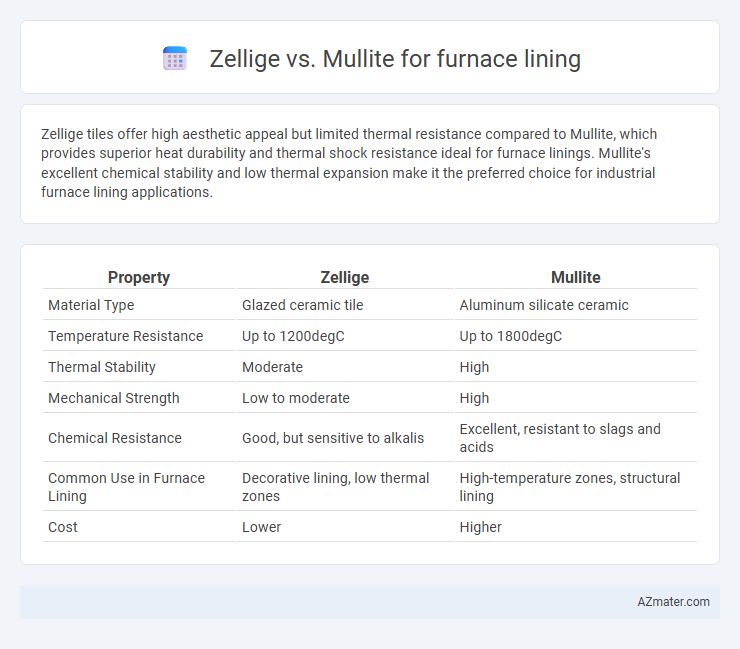
Zellige tiles offer high aesthetic appeal but limited thermal resistance compared to Mullite, which provides superior heat durability and thermal shock resistance ideal for furnace linings. Mullite's excellent chemical stability and low thermal expansion make it the preferred choice for industrial furnace lining applications.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Zellige | Mullite |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Glazed ceramic tile | Aluminum silicate ceramic |
| Temperature Resistance | Up to 1200degC | Up to 1800degC |
| Thermal Stability | Moderate | High |
| Mechanical Strength | Low to moderate | High |
| Chemical Resistance | Good, but sensitive to alkalis | Excellent, resistant to slags and acids |
| Common Use in Furnace Lining | Decorative lining, low thermal zones | High-temperature zones, structural lining |
| Cost | Lower | Higher |
Introduction to Furnace Lining Materials
Furnace lining materials like Zellige and Mullite offer distinct thermal and structural properties critical for high-temperature industrial applications. Zellige, a handcrafted Moroccan tile made from natural clay, excels in aesthetic appeal and moderate heat resistance but lacks the high thermal shock resistance and mechanical strength of Mullite. Mullite, an alumino-silicate ceramic, provides superior thermal stability, corrosion resistance, and insulation performance, making it the preferred material for demanding furnace linings in metallurgy and ceramics industries.
Overview of Zellige: Composition & Properties
Zellige is a handcrafted, glazed terracotta tile made primarily from natural clay, known for its high alumina content and fired at temperatures around 1000-1100degC, resulting in a distinctive, irregular surface texture. Its composition provides moderate thermal resistance and excellent aesthetic appeal, making it suitable for decorative furnace linings that require both durability and heat tolerance. While Zellige offers good thermal insulation and chemical stability, it generally exhibits lower thermal shock resistance compared to mullite-based refractory materials.
Understanding Mullite: Structure & Advantages
Mullite, an aluminum silicate mineral with the chemical formula 3Al2O3*2SiO2, exhibits a unique orthorhombic crystal structure that provides superior thermal stability and mechanical strength for furnace linings. Its low thermal expansion coefficient and excellent resistance to thermal shock make mullite highly durable under extreme temperature fluctuations commonly encountered in industrial furnaces. Compared to Zellige, mullite offers enhanced chemical inertness and wear resistance, ensuring prolonged service life and consistent performance in high-temperature refractory applications.
Thermal Resistance: Zellige vs Mullite
Zellige offers moderate thermal resistance, suitable for decorative and low-temperature furnace linings, but it lacks the high-temperature stability needed for industrial applications. Mullite exhibits exceptional thermal resistance, with a melting point above 1840degC and superior resistance to thermal shock, making it ideal for high-temperature furnace linings. The choice between Zellige and Mullite depends on the operating temperature and durability requirements of the furnace environment.
Mechanical Strength and Durability Comparison
Zellige offers excellent mechanical strength and durability due to its dense, tightly bonded crystalline structure, making it resistant to thermal shock and abrasion in furnace linings. Mullite exhibits superior high-temperature stability and creep resistance, maintaining mechanical integrity even at temperatures above 1700degC, which enhances its lifespan in extreme furnace environments. Comparing both, mullite provides better long-term durability under prolonged thermal exposure, while zellige excels in impact resistance and mechanical toughness in moderately high temperatures.
Chemical Stability in High-Temperature Environments
Zellige exhibits excellent chemical stability in high-temperature environments due to its natural clay composition and dense crystalline structure, making it resistant to thermal shock and corrosion. Mullite surpasses Zellige in chemical durability, offering superior resistance to alkaline and acidic slags commonly found in industrial furnaces, thanks to its high alumina and silica content. The enhanced chemical stability of mullite under extreme thermal cycles makes it a preferred choice for long-lasting, high-performance furnace linings.
Installation and Maintenance Requirements
Zellige tiles require meticulous installation due to their irregular shapes and delicate nature, demanding skilled craftsmanship and precise grout application to ensure durability in furnace linings. Mullite refractories, by contrast, offer easier installation with standardized shapes and higher thermal shock resistance, reducing downtime during furnace maintenance. Maintenance for Zellige involves regular inspections for cracks caused by thermal cycling, while Mullite's robust chemical stability minimizes the frequency of repairs, enhancing furnace lifespan and operational efficiency.
Cost Analysis: Zellige vs Mullite
Zellige tiles, made from natural clay, generally offer a lower initial cost compared to mullite, a synthetic ceramic known for high refractory properties and durability in furnace linings. Mullite's higher temperature resistance and longer lifespan can reduce maintenance and replacement expenses over time, compensating for its higher upfront price. Cost analysis should consider total lifecycle expenses, where zellige suits budget-sensitive applications and mullite is preferred for industrial furnaces requiring superior thermal stability.
Industrial Applications and Suitability
Zellige tiles, made from glazed terracotta, offer moderate thermal resistance and aesthetic appeal but lack the high-temperature durability required for industrial furnace linings. Mullite, an alumino-silicate ceramic material with excellent thermal stability up to 1800degC, is highly suitable for furnace linings due to its superior mechanical strength, corrosion resistance, and thermal shock resistance. Industrial applications demanding prolonged exposure to extreme heat and chemical attacks rely on mullite for enhanced longevity and operational efficiency.
Conclusion: Best Choice for Furnace Lining
Zellige offers exceptional thermal shock resistance and aesthetic appeal, but its lower mechanical strength compared to Mullite limits its use in high-stress furnace linings. Mullite provides superior thermal stability, chemical resistance, and mechanical durability, making it the preferred choice for high-temperature industrial furnace linings. For optimal performance and longevity in harsh thermal environments, Mullite remains the best choice for furnace lining applications.
Infographic: Zellige vs Mullite for Furnace lining
 azmater.com
azmater.com