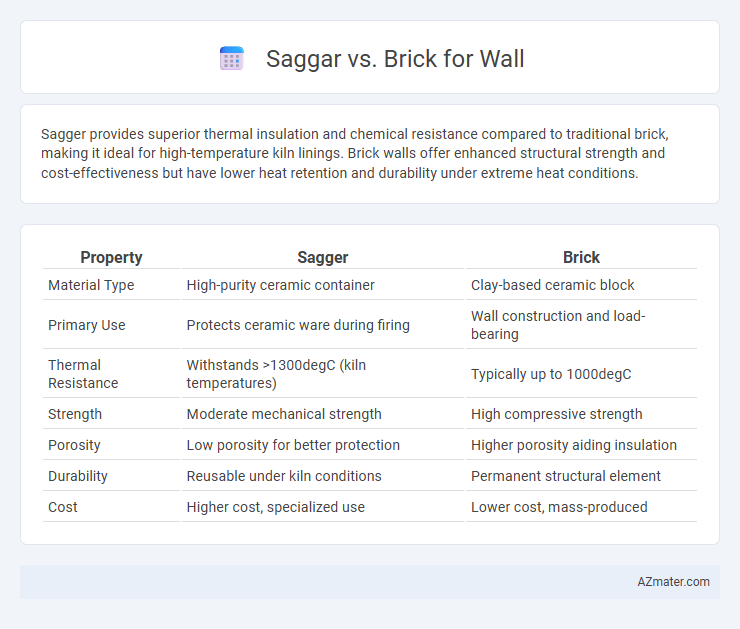
Sagger provides superior thermal insulation and chemical resistance compared to traditional brick, making it ideal for high-temperature kiln linings. Brick walls offer enhanced structural strength and cost-effectiveness but have lower heat retention and durability under extreme heat conditions.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Sagger | Brick |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | High-purity ceramic container | Clay-based ceramic block |
| Primary Use | Protects ceramic ware during firing | Wall construction and load-bearing |
| Thermal Resistance | Withstands >1300degC (kiln temperatures) | Typically up to 1000degC |
| Strength | Moderate mechanical strength | High compressive strength |
| Porosity | Low porosity for better protection | Higher porosity aiding insulation |
| Durability | Reusable under kiln conditions | Permanent structural element |
| Cost | Higher cost, specialized use | Lower cost, mass-produced |
Introduction to Sagger and Brick Walls
Sagger walls and brick walls are foundational elements in construction, each offering distinct structural benefits. Sagger walls, made from refractory materials, specialize in withstanding high temperatures, making them ideal for industrial furnaces and kilns. Brick walls, composed of fired clay bricks, provide versatile, durable, and thermally insulating solutions suitable for residential and commercial buildings.
What is a Sagger Wall?
A sagger wall is constructed using saggers, which are fire-resistant containers that protect bricks or ceramics during kiln firing by preventing direct flame exposure. Unlike traditional brick walls that rely on stacked bricks bound with mortar, sagger walls encapsulate the materials within these protective saggers, ensuring even heat distribution and minimizing damage. This method enhances the durability and quality of fired products by optimizing thermal insulation and reducing deformation.
What is a Brick Wall?
A brick wall is constructed using individual units of fired clay or concrete called bricks, which are laid in horizontal courses and bonded together with mortar. Brick walls provide durability, fire resistance, and aesthetic appeal, making them a popular choice for both structural and decorative purposes. Unlike sagger walls, brick walls typically focus on load-bearing capabilities and long-term stability in building construction.
Material Composition: Sagger vs Brick
Sagger is typically made from refractory materials like clay, alumina, and silica designed to withstand high temperatures during kiln firing. In contrast, bricks are primarily composed of clay, shale, and sand, molded and baked to form durable construction units. The material composition of sagger emphasizes thermal resistance and chemical inertness, while bricks prioritize structural strength and load-bearing capabilities.
Construction Process Comparison
Sagger walls require firing clay bricks inside a protective container, ensuring uniform heat exposure and reducing warping or cracking during the kiln process. In contrast, traditional brick walls involve laying individual bricks with mortar in a sequential manner, allowing for immediate structural assembly but requiring skilled masonry work to ensure stability and alignment. The sagger construction process is more focused on quality control during firing, whereas brick wall construction prioritizes precise installation and bonding for long-term durability.
Durability and Strength Analysis
Sagger walls exhibit greater durability due to their high resistance to thermal stress and minimal moisture absorption, making them ideal for industrial applications. Brick walls offer superior compressive strength and load-bearing capacity, suitable for structural and residential construction. Evaluating long-term performance, saggers withstand higher thermal shock, while bricks provide better mechanical stability under static loads.
Thermal and Acoustic Insulation Properties
Sagger and brick differ significantly in thermal and acoustic insulation properties, with brick providing superior heat retention and soundproofing due to its dense, porous structure that traps air and reduces thermal conductivity. Saggers, typically used for heat protection in kilns, offer limited insulation when applied to walls because they are thinner and less dense, resulting in higher thermal transfer and inadequate noise reduction. Selecting brick for wall construction enhances energy efficiency and acoustic comfort, making it a preferred choice for both residential and commercial buildings.
Cost and Budget Considerations
Sagger offers a cost-effective alternative to traditional bricks, often reducing overall wall construction expenses due to its lower material and manufacturing costs. Bricks, while generally more expensive, provide greater durability and long-term maintenance savings, which can influence the total budget over time. Choosing between Sagger and brick depends on balancing upfront cost savings with potential long-term structural investment.
Aesthetic and Design Flexibility
Sagger bricks offer a smoother surface and uniform color, enhancing aesthetic appeal with a refined, consistent look ideal for modern architectural designs. In contrast, traditional bricks provide varied textures and tones that add rustic charm and character, supporting more eclectic and natural design styles. Design flexibility benefits from sagger's precision, allowing intricate patterns and sharp lines, while brick's organic imperfections contribute to warmth and visual interest in walls.
Best Applications: When to Use Sagger or Brick
Sagger containers are ideal for high-temperature kiln firing and protecting fragile ceramics from direct flame exposure, ensuring even heat distribution and preventing damage during the firing process. Bricks are best suited for building kiln walls due to their durability, thermal insulation properties, and ability to withstand structural loads under intense heat. Use sagger for delicate ceramic ware protection and bricks for constructing or repairing kiln walls where strength and heat resistance are critical.
Infographic: Sagger vs Brick for Wall
 azmater.com
azmater.com