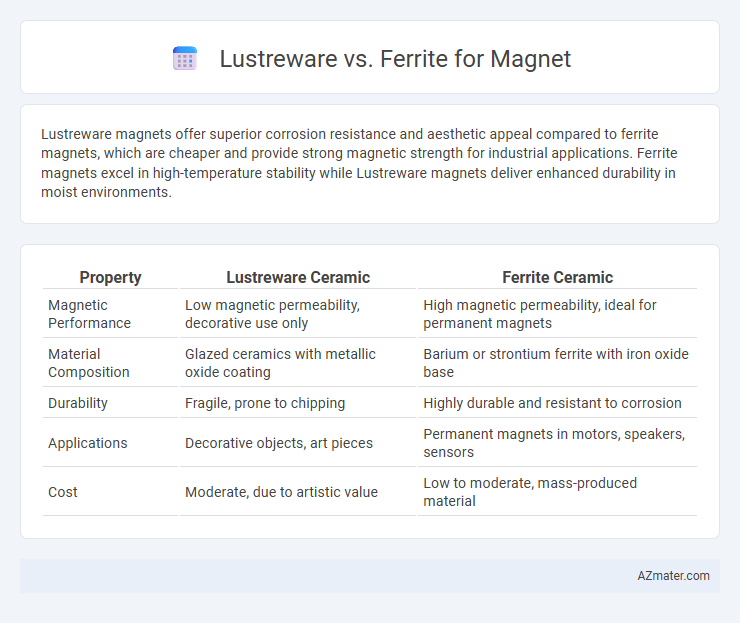
Lustreware magnets offer superior corrosion resistance and aesthetic appeal compared to ferrite magnets, which are cheaper and provide strong magnetic strength for industrial applications. Ferrite magnets excel in high-temperature stability while Lustreware magnets deliver enhanced durability in moist environments.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Lustreware Ceramic | Ferrite Ceramic |
|---|---|---|
| Magnetic Performance | Low magnetic permeability, decorative use only | High magnetic permeability, ideal for permanent magnets |
| Material Composition | Glazed ceramics with metallic oxide coating | Barium or strontium ferrite with iron oxide base |
| Durability | Fragile, prone to chipping | Highly durable and resistant to corrosion |
| Applications | Decorative objects, art pieces | Permanent magnets in motors, speakers, sensors |
| Cost | Moderate, due to artistic value | Low to moderate, mass-produced material |
Introduction to Lustreware and Ferrite
Lustreware magnets utilize a glossy, reflective coating that enhances magnetic strength and durability, making them ideal for decorative applications requiring both magnetism and aesthetic appeal. Ferrite magnets, composed of ceramic iron oxide, offer strong magnetic properties at low cost and high resistance to demagnetization, commonly used in industrial and electronic applications. Each material's unique composition influences its magnetic performance, temperature stability, and corrosion resistance in various environments.
Historical Background of Lustreware and Ferrite Magnets
Lustreware magnets emerged during the 18th and 19th centuries, originally crafted using ceramic materials with metallic glazes to produce decorative and functional magnetic pieces. Ferrite magnets, developed in the mid-20th century, utilize iron oxide combined with barium or strontium carbonate, marking a significant advancement in magnetic materials due to their strong magnetic properties and resistance to demagnetization. Their historical development reflects a transition from artisanal lustrous ceramics to industrial mass-produced magnetic components essential in modern electronics.
Material Composition of Lustreware vs Ferrite
Lustreware magnets are primarily composed of rare-earth materials such as neodymium, iron, and boron, allowing for high magnetic strength and resistance to demagnetization. In contrast, ferrite magnets consist mainly of ceramic compounds including iron oxide mixed with barium or strontium carbonate, which provide lower magnetic performance but superior corrosion resistance and cost-effectiveness. The differing material compositions impact their applications, with lustreware magnets favored for high-performance uses and ferrite magnets chosen for budget-sensitive or harsh-environment conditions.
Magnetic Properties Comparison
Lustreware magnets exhibit higher coercivity and remanence compared to ferrite magnets, resulting in stronger magnetic strength and resistance to demagnetization. Ferrite magnets, composed mainly of iron oxide and ceramic materials, have lower magnetic energy products but offer excellent corrosion resistance and thermal stability. The magnetic permeability of Lustreware magnets surpasses that of ferrite, making them more suitable for applications requiring concentrated magnetic fields.
Durability and Lifespan
Lustreware magnets typically feature a durable coating that enhances resistance to wear and corrosion, providing a moderate lifespan suitable for everyday applications. Ferrite magnets are known for their exceptional hardness and chemical stability, resulting in superior durability and a longer operational lifespan, especially in high-temperature or harsh environments. Choosing between Lustreware and Ferrite depends on the specific application requirements, with Ferrite offering enhanced longevity for industrial uses.
Electrical Conductivity Differences
Lustreware magnets exhibit significantly lower electrical conductivity compared to ferrite magnets due to their ceramic-based composition, which restricts electron mobility. Ferrite magnets, composed primarily of iron oxide and barium or strontium carbonate, demonstrate higher resistivity and thus reduced eddy current losses in electrical applications. The distinct electrical conductivity characteristics of Lustreware and ferrite magnets influence their suitability for use in transformers, inductors, and electromagnetic devices where efficiency and heat dissipation are critical.
Cost-Effectiveness and Availability
Lustreware magnets typically offer higher cost-effectiveness due to their lower raw material expenses and simpler manufacturing processes compared to ferrite magnets. Ferrite magnets possess widespread availability and are produced at large scales globally, which ensures consistent supply and stable pricing. Businesses prioritize Lustreware when budget-sensitive applications demand affordability, while Ferrite magnets remain preferred for mass-produced products requiring significant volume and availability.
Applications in Industry and Everyday Use
Lustreware magnets excel in household applications such as fridge magnets and decorative items due to their vibrant finishes and moderate magnetic strength. Ferrite magnets find extensive industrial use in electric motors, loudspeakers, and magnetic separators due to their high resistance to demagnetization and cost-effectiveness. The durability and temperature tolerance of ferrite magnets make them preferable for heavy-duty industrial environments compared to the more fragile lustreware magnets.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Lustreware magnets, typically made from rare-earth elements, have a higher environmental impact due to intensive mining processes and energy consumption, leading to significant habitat disruption and carbon emissions. Ferrite magnets, composed mainly of iron oxide and barium or strontium carbonate, offer a more sustainable option with abundant raw materials and lower ecological footprints during production and disposal. Choosing ferrite magnets supports eco-friendly manufacturing and reduces reliance on scarce raw materials, promoting long-term sustainability in magnet applications.
Choosing Between Lustreware and Ferrite for Your Magnet Needs
Choosing between Lustreware and Ferrite magnets depends on specific application requirements such as magnetic strength, durability, and cost-effectiveness. Lustreware magnets offer superior aesthetic finishes and corrosion resistance, ideal for decorative or light-duty uses, while Ferrite magnets provide high magnetic strength and thermal stability suitable for industrial and heavy-duty applications. Assessing factors like magnetic performance, environmental conditions, and budget ensures the optimal magnet type selection for your project.
Infographic: Lustreware vs Ferrite for Magnet
 azmater.com
azmater.com