Bone china offers superior heat resistance and durability compared to glass ceramic, making it ideal for long-lasting cooktop surfaces. Glass ceramic provides excellent thermal shock resistance and easy cleaning but is more prone to scratches and cracks under heavy impact.
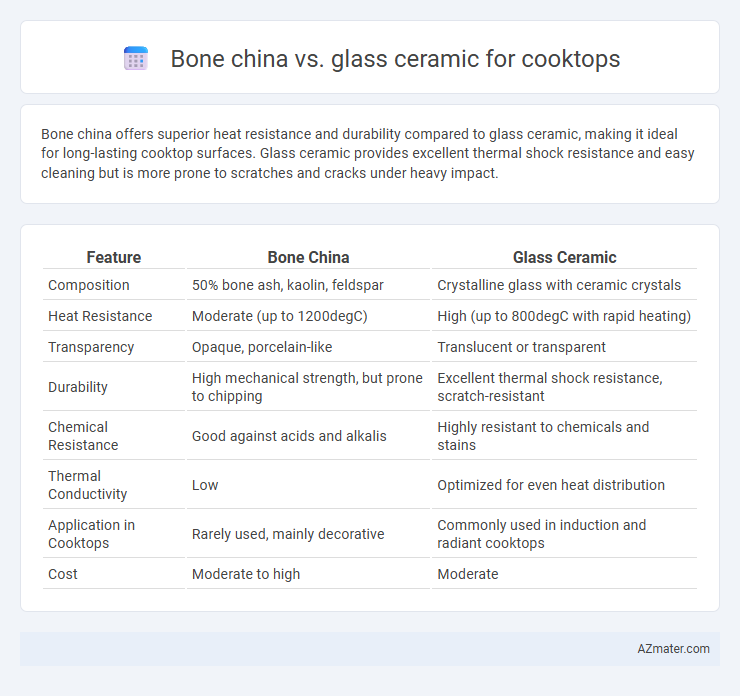
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Bone China | Glass Ceramic |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | 50% bone ash, kaolin, feldspar | Crystalline glass with ceramic crystals |
| Heat Resistance | Moderate (up to 1200degC) | High (up to 800degC with rapid heating) |
| Transparency | Opaque, porcelain-like | Translucent or transparent |
| Durability | High mechanical strength, but prone to chipping | Excellent thermal shock resistance, scratch-resistant |
| Chemical Resistance | Good against acids and alkalis | Highly resistant to chemicals and stains |
| Thermal Conductivity | Low | Optimized for even heat distribution |
| Application in Cooktops | Rarely used, mainly decorative | Commonly used in induction and radiant cooktops |
| Cost | Moderate to high | Moderate |
Introduction to Bone China and Glass Ceramic
Bone china is a type of porcelain known for its high strength, translucency, and durability, made from a mixture of bone ash, feldspar, and kaolin. Glass ceramic, used in cooktops, is a non-porous material composed of crystalline glass that offers excellent thermal shock resistance and rapid heat conduction. Both materials serve distinct purposes: bone china excels in fine dining ware due to its elegant appearance and robustness, while glass ceramic is engineered for efficient and safe heat transfer in cooking appliances.
Composition and Manufacturing Processes
Bone china is composed mainly of bone ash, kaolin, and feldspar, resulting in a lightweight and translucent material created through high-temperature firing and glazing processes. Glass ceramic cooktops are made from a mix of glass and crystalline materials, developed through controlled crystallization heat treatment to achieve high thermal resistance and durability. The manufacturing of bone china involves shaping and firing at temperatures around 1200-1300degC, whereas glass ceramic undergoes rapid cooling and reheating to produce a strong, smooth surface suitable for cooktops.
Heat Resistance and Thermal Stability
Bone china offers moderate heat resistance but is more prone to thermal shock compared to glass ceramic, making it less suitable for direct cooktop use. Glass ceramic cooktops feature superior thermal stability, withstanding rapid temperature changes up to 1000degC without cracking. Their capacity to evenly distribute heat and resist thermal stress ensures longevity and optimal performance in cooking applications.
Durability and Scratch Resistance
Bone china offers moderate durability but is prone to chipping and cracking under high heat or heavy impact, making it less ideal for cooktop surfaces. Glass ceramic cooktops, such as those made from Schott Ceran, deliver superior scratch resistance and thermal shock durability, ensuring long-lasting performance even with frequent cookware use. The heat-resistant properties and smooth surface of glass ceramic enhance its resilience compared to bone china, making it the preferred choice for modern cooktops.
Aesthetic Appeal and Design Options
Bone china offers a refined elegance with its smooth, translucent surface and classic white or delicate patterned finishes, making it ideal for traditional and sophisticated kitchen aesthetics. Glass ceramic cooktops showcase a sleek, modern look with a glossy, often black or neutral surface that complements minimalist and contemporary designs. Both materials provide diverse design options, but bone china emphasizes timeless beauty while glass ceramic highlights cutting-edge style and versatility.
Suitability for Different Cooktop Types
Bone china is unsuitable for induction cooktops due to its poor magnetic properties but performs well on electric and gas cooktops because of its heat resistance and aesthetic appeal. Glass ceramic, engineered for cooktops, excels in compatibility with induction, electric, and gas stoves, offering even heat distribution and thermal shock resistance. The choice depends on cooktop type, with glass ceramic providing superior versatility and durability for various cooking surfaces.
Ease of Cleaning and Maintenance
Bone china's smooth, non-porous surface resists stains and grime, making it easy to clean with mild detergents and reducing the risk of scratches. Glass ceramic cooktops also offer a sleek, smooth surface but require careful maintenance to avoid abrasive damage and mineral deposits from spills. Both materials demand regular wiping to maintain appearance, but bone china tends to be more resilient against stubborn residues, simplifying daily upkeep.
Safety Considerations
Bone china, known for its durability and heat resistance, offers a safer option for cooktops by minimizing the risk of cracking under rapid temperature changes. Glass ceramics, designed specifically for cooktop use, provide excellent thermal shock resistance and maintain structural integrity at high temperatures, enhancing safety during cooking. Both materials require careful handling to avoid damage, but glass ceramic's specialized engineering typically ensures superior performance and safety in everyday kitchen scenarios.
Cost Comparison
Bone china cooktops generally have a higher price point due to the intricate manufacturing process and premium materials, making them less common in budget kitchens. Glass ceramic cooktops offer a more cost-effective solution, with prices typically ranging from $300 to $1,500, depending on features and brand. The durability and heat resistance of glass ceramic often provide a better value-to-cost ratio compared to the luxury appeal but higher expense of bone china surfaces.
Conclusion: Choosing the Best Material for Your Cooktop
Bone china offers elegant aesthetics and moderate heat resistance but lacks the high durability and scratch resistance found in glass ceramic cooktops. Glass ceramic surfaces provide superior thermal shock resistance, faster heat conductivity, and easier maintenance, making them ideal for frequent cooking and high-temperature use. For long-term performance and safety, glass ceramic is generally the best material choice for modern cooktops.
Infographic: Bone china vs Glass ceramic for Cooktop
 azmater.com
azmater.com