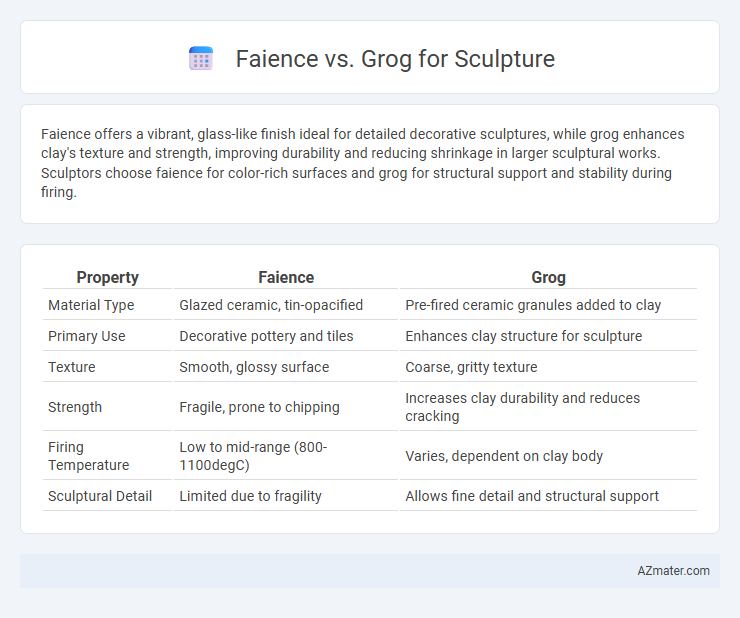
Faience offers a vibrant, glass-like finish ideal for detailed decorative sculptures, while grog enhances clay's texture and strength, improving durability and reducing shrinkage in larger sculptural works. Sculptors choose faience for color-rich surfaces and grog for structural support and stability during firing.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Faience | Grog |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Glazed ceramic, tin-opacified | Pre-fired ceramic granules added to clay |
| Primary Use | Decorative pottery and tiles | Enhances clay structure for sculpture |
| Texture | Smooth, glossy surface | Coarse, gritty texture |
| Strength | Fragile, prone to chipping | Increases clay durability and reduces cracking |
| Firing Temperature | Low to mid-range (800-1100degC) | Varies, dependent on clay body |
| Sculptural Detail | Limited due to fragility | Allows fine detail and structural support |
Introduction to Faience and Grog in Sculpture
Faience is a glazed ceramic material known for its bright colors and smooth surface, often used in sculpture for decorative purposes and fine details. Grog consists of pre-fired clay particles incorporated into raw clay to improve strength, reduce shrinkage, and enhance texture during firing, making it ideal for sculptural construction and durability. Both materials play distinct roles in sculpture, with faience emphasizing aesthetic finish and grog providing structural integrity.
Defining Faience: Composition and Properties
Faience is a non-clay ceramic material primarily composed of finely ground quartz or silica, combined with small amounts of feldspar and a fluxing agent to create a glassy, porous body after firing. Its distinct properties include a bright, often turquoise or blue glaze, achieved through the incorporation of metallic oxides, which provide vibrant coloration and a glossy finish ideal for decorative sculpture. Unlike grog, which is pre-fired clay added to improve workability and reduce shrinkage, faience's silica-rich composition results in a harder, more fragile surface but allows for intricate detailing and luminous aesthetic effects.
What is Grog? Key Features and Benefits
Grog is a granular, pre-fired ceramic material added to clay to improve its structural integrity, reduce shrinkage, and enhance thermal shock resistance during firing. Key features include its ability to increase clay body strength, provide texture for better workability, and prevent cracking in sculptural pieces. Benefits of using grog in sculpture involve improved durability, enhanced surface detail retention, and minimized warping, making it essential for large or intricate ceramic artworks.
Historical Uses: Faience vs Grog
Faience, a glazed non-clay ceramic material, was historically prominent in ancient Egyptian sculpture for its vibrant colors and glossy finish, often used in small statues, amulets, and decorative tiles. Grog, composed of crushed fired clay, was traditionally incorporated into sculptural clay bodies by ancient potters and artisans across cultures to enhance thermal shock resistance and improve structural strength, especially for larger and more complex forms. The contrasting historical uses highlight faience's role in ornamental art and grog's function as a practical additive in ceramic sculpture production.
Texture and Workability Differences
Faience offers a smooth, glass-like texture with a glossy surface after firing, ideal for detailed, delicate sculptural work requiring fine finishes. Grog adds a gritty, coarse texture to clay, enhancing workability by reducing shrinkage and improving structural strength, making it suitable for larger, more robust sculptures. The choice between faience and grog fundamentally depends on the desired surface finish and the mechanical demands of the sculpture.
Firing Temperatures and Techniques
Faience, a glazed ceramic material, typically requires firing temperatures between 800degC and 1000degC to achieve its characteristic glossy finish, often involving a two-step firing process with an initial bisque firing followed by a glaze firing. Grog, composed of pre-fired clay particles added to sculpture clay, enhances structural integrity and thermal shock resistance, allowing for higher firing temperatures up to 1200degC or more without cracking. Sculptors use faience for detailed, decorative surfaces requiring controlled firing schedules, whereas grog is favored for large or thick forms needing durability during high-temperature reductions.
Surface Finishes: Glaze Compatibility and Effects
Faience offers a smoother surface finish ideal for glazing, producing vibrant and glossy effects due to its high silica content and fine particle size. Grog, containing pre-fired, coarse clay particles, creates a rougher texture that enhances surface grip but results in more matte and rustic glazes with reduced glossy impact. Selecting between faience and grog depends on desired glaze compatibility, with faience optimizing bright, reflective finishes and grog supporting textured, earthy glaze aesthetics.
Durability and Structural Strength Compared
Faience, a glazed ceramic material, offers delicate surface detail but lacks the structural strength and durability of grog, which contains pre-fired ceramic particles that reinforce the clay body. Grog enhances the sculpture's resistance to cracking and warping during firing, making it more suitable for large or heavy pieces that require substantial support. Sculptors favor grog for its improved thermal shock resistance and mechanical stability, especially in functional or outdoor artworks where longevity is critical.
Best Applications: Choosing Faience or Grog for Projects
Faience, a glazed non-clay ceramic material, excels in projects requiring vibrant color and decorative finishes, ideal for intricate sculptures and ornamental pieces. Grog, composed of ground-up fired clay, enhances structural strength and reduces shrinkage, making it best suited for large-scale or functional sculptures demanding durability and reduced cracking. Selecting between Faience and Grog depends on whether the priority is aesthetic detail and glaze compatibility or robustness and workability in heavy or frequently handled forms.
Conclusion: Which Material Suits Your Sculpture Needs?
Faience offers vibrant, glass-like finishes ideal for decorative sculptures requiring fine detail and color intensity, whereas grog enhances structural strength and thermal resistance, making it suitable for larger, functional, or outdoor pieces. Sculptors prioritizing aesthetic appeal and smooth textures favor faience, while those focusing on durability and workability benefit from grog-enhanced clay bodies. Selecting between faience and grog depends on the desired balance of visual effect, mechanical performance, and specific sculptural application.
Infographic: Faience vs Grog for Sculpture
 azmater.com
azmater.com