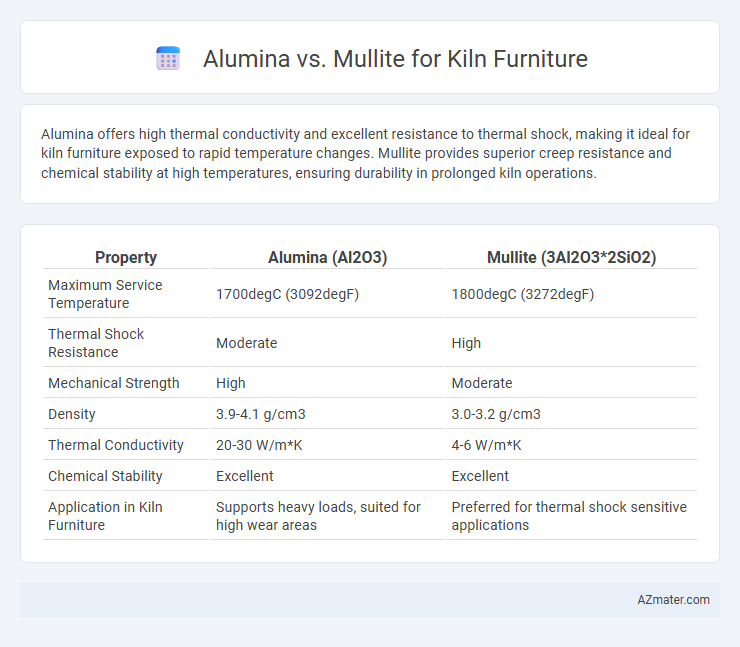
Alumina offers high thermal conductivity and excellent resistance to thermal shock, making it ideal for kiln furniture exposed to rapid temperature changes. Mullite provides superior creep resistance and chemical stability at high temperatures, ensuring durability in prolonged kiln operations.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Alumina (Al2O3) | Mullite (3Al2O3*2SiO2) |
|---|---|---|
| Maximum Service Temperature | 1700degC (3092degF) | 1800degC (3272degF) |
| Thermal Shock Resistance | Moderate | High |
| Mechanical Strength | High | Moderate |
| Density | 3.9-4.1 g/cm3 | 3.0-3.2 g/cm3 |
| Thermal Conductivity | 20-30 W/m*K | 4-6 W/m*K |
| Chemical Stability | Excellent | Excellent |
| Application in Kiln Furniture | Supports heavy loads, suited for high wear areas | Preferred for thermal shock sensitive applications |
Introduction to Kiln Furniture Materials
Alumina and mullite are essential materials used in kiln furniture due to their high-temperature resistance and mechanical strength. Alumina offers superior thermal conductivity and density, making it ideal for applications requiring rapid heat transfer and durability. Mullite, known for its excellent thermal shock resistance and lower thermal expansion, is preferred in environments where dimensional stability and thermal cycling are critical.
Overview of Alumina in Kiln Furniture
Alumina, a high-purity ceramic material, offers exceptional thermal stability, mechanical strength, and resistance to thermal shock, making it ideal for kiln furniture applications. Its high melting point above 2000degC and low thermal conductivity ensure durability under intense kiln conditions. Alumina's chemical inertness and corrosion resistance also protect kiln components from molten glass and metal slags, enhancing furnace lifespan and performance.
Mullite: Composition and Characteristics
Mullite, primarily composed of 3Al2O3*2SiO2, exhibits superior thermal shock resistance and low thermal expansion, making it ideal for kiln furniture in high-temperature applications. Its unique interlocking crystal structure enhances mechanical strength and thermal stability compared to alumina, which is predominantly Al2O3 but tends to have higher thermal expansion. This balance of chemical composition and physical properties ensures Mullite provides durability and longevity in repetitive heating cycles within industrial kilns.
Thermal Stability: Alumina vs Mullite
Alumina exhibits higher thermal stability than mullite, maintaining structural integrity at temperatures exceeding 1700degC, making it ideal for high-temperature kiln furniture applications. Mullite, while less thermally stable, offers excellent resistance to thermal shock and lower thermal expansion, which reduces cracking risks during rapid temperature changes. The choice between alumina and mullite depends on specific kiln operating temperatures and the need for thermal shock resistance versus maximum temperature endurance.
Mechanical Strength Comparison
Alumina kiln furniture exhibits higher mechanical strength due to its superior density and enhanced thermal shock resistance, making it ideal for high-stress kiln environments. Mullite offers moderate mechanical strength combined with excellent thermal stability and lower thermal expansion, which reduces the risk of cracking under thermal cycling. The choice between alumina and mullite depends on the specific mechanical load requirements and thermal conditions within the kiln.
Resistance to Chemical Attack
Alumina offers superior resistance to chemical attack due to its high purity and stable crystalline structure, making it highly effective in corrosive kiln environments. Mullite, while also chemically resistant, contains silica, which can lead to gradual degradation in highly acidic or alkaline atmospheres. The high alumina content in Alumina kiln furniture ensures prolonged service life and minimal contamination during high-temperature industrial processes.
Weight and Durability Considerations
Alumina offers higher density and weight compared to mullite, providing superior thermal mass for kiln furniture applications. Mullite, being lighter, reduces overall kiln load and improves energy efficiency while maintaining excellent thermal shock resistance. Durability-wise, alumina excels in high-wear conditions due to its hardness, whereas mullite provides better resistance to thermal cycling and chemical corrosion.
Cost Efficiency and Availability
Alumina kiln furniture offers high cost efficiency due to its widespread availability and lower raw material costs compared to mullite. Mullite, while more expensive, provides enhanced thermal stability and longer lifespan in high-temperature environments, which can reduce replacement frequency and maintenance expenses. The choice between alumina and mullite depends on balancing upfront material costs against long-term durability and performance requirements in kiln operations.
Application Suitability in Kiln Environments
Alumina offers exceptional thermal conductivity and high resistance to chemical corrosion, making it ideal for high-temperature kiln furniture where rapid heat transfer and durability are critical. Mullite provides superior thermal shock resistance and mechanical strength, well-suited for kiln environments requiring cycling stability and reduced thermal stress. Selection between alumina and mullite depends on specific kiln conditions, including temperature ranges, atmosphere, and the mechanical load of the firing process.
Conclusion: Choosing Between Alumina and Mullite
Selecting between alumina and mullite for kiln furniture depends primarily on the specific thermal and mechanical demands of the firing process; alumina excels in high-temperature resistance above 1700degC with superior hardness, while mullite offers better thermal shock resistance and lower thermal expansion. Alumina's high purity and density provide enhanced durability in aggressive kiln atmospheres, whereas mullite's composition reduces warping and elongation during rapid heating. Optimal kiln furniture choice balances alumina's robustness for extreme conditions against mullite's adaptability for quicker temperature cycles.
Infographic: Alumina vs Mullite for Kiln Furniture
 azmater.com
azmater.com