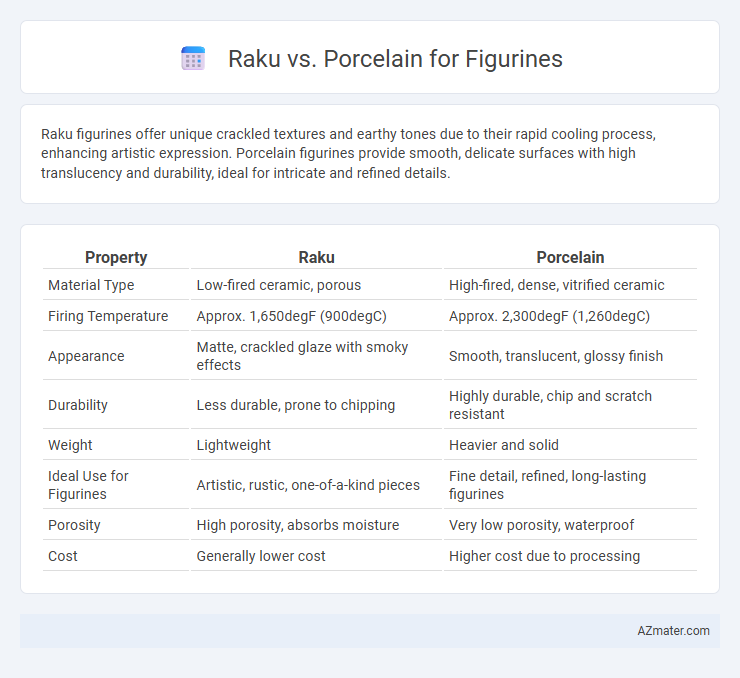
Raku figurines offer unique crackled textures and earthy tones due to their rapid cooling process, enhancing artistic expression. Porcelain figurines provide smooth, delicate surfaces with high translucency and durability, ideal for intricate and refined details.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Raku | Porcelain |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Low-fired ceramic, porous | High-fired, dense, vitrified ceramic |
| Firing Temperature | Approx. 1,650degF (900degC) | Approx. 2,300degF (1,260degC) |
| Appearance | Matte, crackled glaze with smoky effects | Smooth, translucent, glossy finish |
| Durability | Less durable, prone to chipping | Highly durable, chip and scratch resistant |
| Weight | Lightweight | Heavier and solid |
| Ideal Use for Figurines | Artistic, rustic, one-of-a-kind pieces | Fine detail, refined, long-lasting figurines |
| Porosity | High porosity, absorbs moisture | Very low porosity, waterproof |
| Cost | Generally lower cost | Higher cost due to processing |
Introduction to Raku and Porcelain Figurines
Raku figurines are prized for their unique, unpredictable glaze patterns created through a rapid cooling process that produces a distinctive crackled surface, often associated with traditional Japanese pottery techniques. Porcelain figurines, made from refined kaolin clay fired at high temperatures, offer a smooth, translucent finish prized for its delicate detail and durability. Both materials serve distinct artistic purposes, with Raku emphasizing organic texture and Porcelain highlighting refined elegance in collectible and decorative figurines.
Historical Origins and Traditions
Raku pottery, originating in 16th-century Japan, is characterized by its unpredictable glaze effects and low-firing technique tied to the traditional Japanese tea ceremony. Porcelain figurines trace back to 7th-century China, renowned for their fine, translucent quality achieved through high-temperature kiln firing and intricate craftsmanship. These distinct materials represent contrasting cultural heritages: Raku emphasizes spontaneity and Zen aesthetics, while porcelain embodies precision and luxury in historical ceramic art.
Material Composition and Properties
Raku figurines are crafted from low-firing clay coated with a porous glaze that allows rapid cooling, resulting in unique crackling and smoky patterns with a rough texture. Porcelain figurines, made from fine kaolin clay fired at high temperatures, exhibit a smooth, translucent surface with exceptional strength and delicate details. Raku's thermal shock resistance contrasts with porcelain's rigidity and brittleness, making material composition and firing methods key in determining durability and aesthetic qualities.
Artistic Techniques and Crafting Processes
Raku figurines are crafted using a rapid firing technique involving removal from a hot kiln and reduction in combustible materials, resulting in unique crackled glazes and smoky textures that emphasize spontaneity and organic aesthetics. Porcelain figurines involve meticulous molding and firing at high temperatures to achieve a smooth, translucent finish, enabling fine detail and delicate features with a polished, refined appearance. The contrasting techniques highlight Raku's earthy, unpredictable surface effects versus Porcelain's precise, elegant craftsmanship.
Durability and Longevity Comparison
Raku figurines, known for their unique firing process, often exhibit surface crackles which may reduce their durability and make them more susceptible to chipping over time. Porcelain figurines, crafted from fine white clay and fired at higher temperatures, offer superior strength, resistance to cracking, and long-lasting durability. The inherent density and vitrification of porcelain contribute to its longevity, making it a preferred choice for collectors seeking durable and enduring figurines.
Surface Texture and Visual Appeal
Raku figurines feature a distinctive, crackled surface texture achieved through rapid cooling and reduction firing, giving each piece a unique, organic visual appeal marked by earthy tones and irregular patterns. Porcelain figurines, in contrast, exhibit a smooth, glossy finish with fine detail and a luminous, translucent quality that enhances delicate features and vibrant colors. The tactile richness of raku contrasts with porcelain's refined elegance, making surface texture and overall visual impact key factors in selecting between these ceramic art forms.
Color, Glaze, and Finish Differences
Raku figurines exhibit a distinctive metallic or crackled glaze created through rapid cooling and atmospheric exposure during firing, resulting in unpredictable color variations and textured finishes. Porcelain figurines offer smooth, translucent surfaces with consistent, vibrant glazes achieved through high-temperature kiln firing, emphasizing fine detail and durability. The color palette in porcelain remains stable and glossy, while Raku's finish is more rustic and varied, highlighting the firing process's spontaneous effects.
Cost, Accessibility, and Market Value
Raku figurines, fired at lower temperatures with unique crackle glazing, generally cost less due to their artisanal, small-batch nature and lower material expenses, making them accessible to collectors on a budget. Porcelain figurines, crafted from fine kaolin clay and high-temperature firing, command higher prices reflecting durability, smooth finish, and centuries-old prestige, often enhancing resale market value. Accessibility favors Raku in local studios and niche markets, while porcelain enjoys widespread availability through established manufacturers and auction houses, attracting different collector profiles.
Popular Uses and Collector Preferences
Raku figurines, known for their unique crackled glaze and smoky finishes, are highly favored for their artistic unpredictability and rustic charm, making them popular among collectors who appreciate traditional Japanese pottery techniques. Porcelain figurines, celebrated for their smooth, delicate texture and fine detailing, are preferred by collectors seeking elegance and refined craftsmanship, often associated with European artistry. Collectors often choose Raku for its distinctive, one-of-a-kind aesthetic, while porcelain appeals to those valuing precision and glossy surfaces in collectible figurines.
Choosing the Right Material for Figurines
Raku offers a distinctive, crackled texture with earthy tones, ideal for artistic and decorative figurines that emphasize rustic aesthetics. Porcelain provides a smooth, translucent finish with fine detail and durability, making it suitable for collector's pieces requiring precision and elegance. Selecting between Raku and porcelain depends on the desired appearance, durability, and artistic expression of the figurine.
Infographic: Raku vs Porcelain for Figurine
 azmater.com
azmater.com