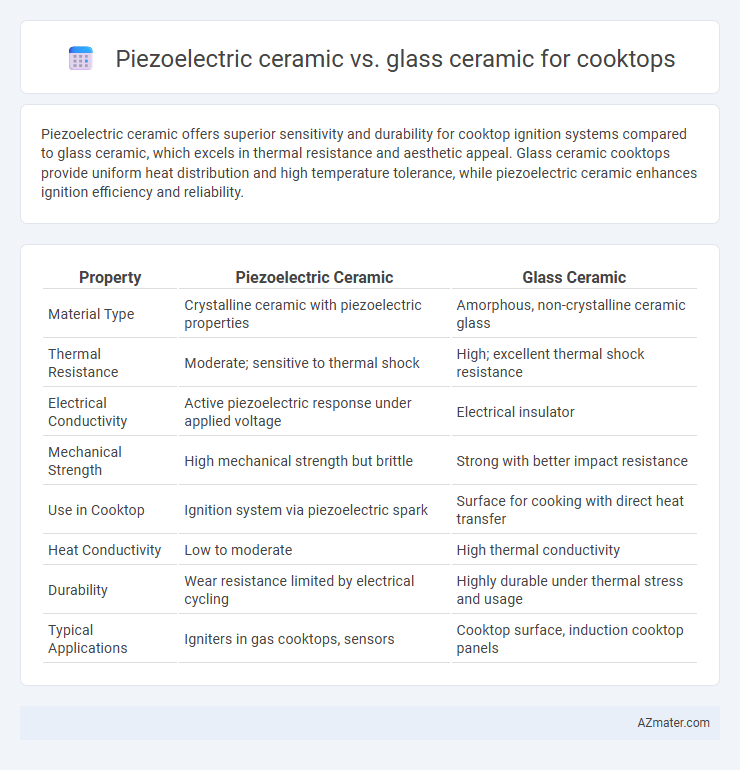
Piezoelectric ceramic offers superior sensitivity and durability for cooktop ignition systems compared to glass ceramic, which excels in thermal resistance and aesthetic appeal. Glass ceramic cooktops provide uniform heat distribution and high temperature tolerance, while piezoelectric ceramic enhances ignition efficiency and reliability.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Piezoelectric Ceramic | Glass Ceramic |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Crystalline ceramic with piezoelectric properties | Amorphous, non-crystalline ceramic glass |
| Thermal Resistance | Moderate; sensitive to thermal shock | High; excellent thermal shock resistance |
| Electrical Conductivity | Active piezoelectric response under applied voltage | Electrical insulator |
| Mechanical Strength | High mechanical strength but brittle | Strong with better impact resistance |
| Use in Cooktop | Ignition system via piezoelectric spark | Surface for cooking with direct heat transfer |
| Heat Conductivity | Low to moderate | High thermal conductivity |
| Durability | Wear resistance limited by electrical cycling | Highly durable under thermal stress and usage |
| Typical Applications | Igniters in gas cooktops, sensors | Cooktop surface, induction cooktop panels |
Introduction to Cooktop Technologies
Piezoelectric ceramic cooktops utilize materials that generate an electric charge when mechanically stressed, enabling precise ignition and temperature control. Glass ceramic cooktops feature a smooth, heat-resistant surface made from a blend of glass and crystalline ceramics, providing even heat distribution and easy cleaning. Both technologies enhance cooking efficiency, with piezoelectric systems offering reliable ignition and glass ceramics delivering superior thermal performance and durability.
Understanding Piezoelectric Ceramics
Piezoelectric ceramics generate an electric charge in response to mechanical stress, making them ideal for reliable ignition systems in cooktops, ensuring rapid and precise spark production. These materials exhibit high durability and consistent performance under repeated use, outperforming glass ceramics, which primarily serve as heat-resistant surfaces rather than active ignition components. Understanding the piezoelectric effect in ceramics highlights their critical role in enhancing cooktop safety and functionality compared to glass ceramics.
Overview of Glass Ceramics
Glass ceramics for cooktops offer excellent thermal shock resistance and durability, making them highly suitable for high-temperature cooking environments. Their unique crystalline structure provides superior heat distribution and stain resistance compared to piezoelectric ceramics, which primarily function in sensor applications rather than as the cooktop surface. Glass ceramics combine aesthetic appeal with practical performance, ensuring longevity and ease of maintenance in modern kitchen settings.
Thermal Performance Comparison
Piezoelectric ceramics exhibit superior thermal stability and rapid response under high heat conditions, maintaining consistent performance on cooktops with fluctuating temperatures. Glass ceramics offer excellent thermal shock resistance and uniform heat distribution, reducing the risk of cracking and ensuring even cooking surfaces. The choice depends on whether quick heat response or long-term durability against thermal stress is prioritized for cooktop applications.
Durability and Lifespan Factors
Piezoelectric ceramic cooktops exhibit exceptional durability due to their resistance to thermal shock and mechanical stress, extending their lifespan significantly compared to glass ceramic options. Glass ceramic cooktops, while aesthetically appealing and resistant to scratches, tend to be more prone to cracking under sudden temperature changes and heavy impacts, which can shorten their operational life. In terms of longevity, piezoelectric ceramic surfaces maintain consistent performance over time, making them a superior choice for high-use cooking environments.
Heat Distribution and Efficiency
Piezoelectric ceramic cooktops offer precise heat control but exhibit uneven heat distribution due to localized heating elements, potentially causing hotspots. Glass ceramic cooktops provide superior heat distribution with a smooth surface that evenly transfers heat across cookware, enhancing energy efficiency and cooking performance. The thermal conductivity of glass ceramic materials ensures quicker heat transfer and reduced heat loss, making them more efficient for consistent cooking results.
Safety Features and Considerations
Piezoelectric ceramic cooktops offer superior safety features through reliable electric spark ignition, minimizing the risk of gas leaks or accidental ignitions. Glass ceramic cooktops provide enhanced safety by featuring a smooth, heat-resistant surface with built-in sensors to prevent overheating and burns. Both materials prioritize user protection, but piezoelectric ceramics excel in ignition safety, while glass ceramics emphasize thermal safety and ease of cleaning.
Maintenance and Cleaning Requirements
Piezoelectric ceramic cooktops require minimal maintenance due to their robust, non-porous surface, which resists stains and allows easy cleaning with mild detergents and a soft cloth. Glass ceramic cooktops, while sleek and heat-resistant, demand careful cleaning to avoid scratches and damage from abrasive tools, and spills should be wiped promptly to prevent staining or residue buildup. Both materials benefit from routine gentle cleaning, but piezoelectric ceramics typically offer greater durability and ease in maintaining a pristine cooking surface over time.
Cost Analysis: Piezoelectric vs Glass Ceramic
Piezoelectric cooktops typically incur higher initial costs due to advanced sensor technology and durable materials, while glass ceramic cooktops offer a more budget-friendly upfront price with extensive availability. Maintenance expenses for piezoelectric models may be lower over time, as their precise controls reduce energy waste and wear on components compared to glass ceramic surfaces that can be prone to cracking or staining. The long-term cost-effectiveness of piezoelectric cooktops often surpasses glass ceramic alternatives when factoring in durability, energy efficiency, and minimal repair requirements.
Choosing the Right Cooktop Material
Piezoelectric ceramic cooktops offer rapid heat response and durability, making them ideal for precise cooking control, while glass ceramic cooktops provide a sleek surface with excellent heat distribution and easy cleaning. When choosing the right cooktop material, consider factors such as thermal conductivity, heat retention, and resistance to thermal shock; piezoelectric ceramics excel in responsiveness, whereas glass ceramics prioritize user-friendly maintenance and aesthetics. Selecting between piezoelectric ceramic and glass ceramic cooktops depends on whether you value responsive heating performance or surface elegance combined with durability.
Infographic: Piezoelectric ceramic vs Glass ceramic for Cooktop
 azmater.com
azmater.com