Tiles offer high heat resistance and durability for cooking pots, ensuring even heat distribution and longevity. Earthenware pots provide natural porosity and moisture retention, ideal for slow cooking and enhancing flavor.
Table of Comparison
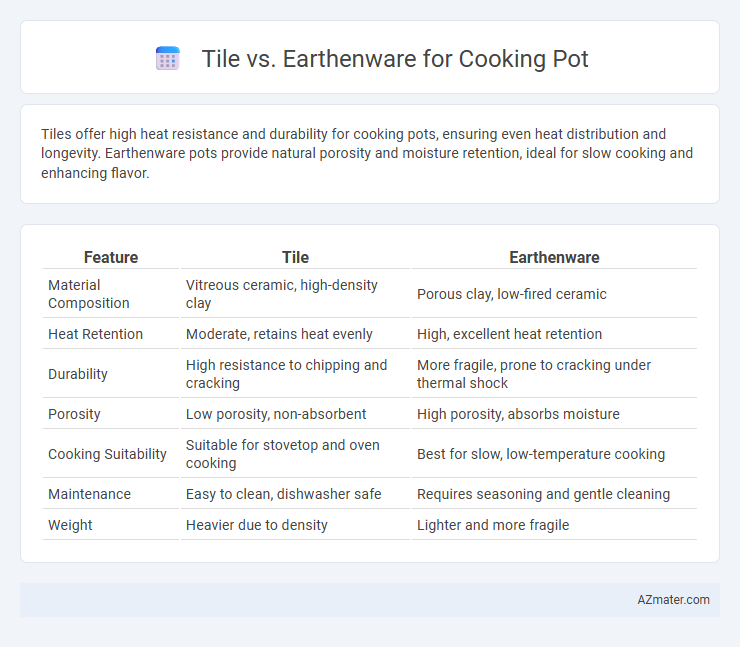
| Feature | Tile | Earthenware |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Vitreous ceramic, high-density clay | Porous clay, low-fired ceramic |
| Heat Retention | Moderate, retains heat evenly | High, excellent heat retention |
| Durability | High resistance to chipping and cracking | More fragile, prone to cracking under thermal shock |
| Porosity | Low porosity, non-absorbent | High porosity, absorbs moisture |
| Cooking Suitability | Suitable for stovetop and oven cooking | Best for slow, low-temperature cooking |
| Maintenance | Easy to clean, dishwasher safe | Requires seasoning and gentle cleaning |
| Weight | Heavier due to density | Lighter and more fragile |
Introduction: Tile vs Earthenware Cooking Pots
Tile cooking pots offer excellent heat retention and even distribution, making them ideal for slow-cooked dishes and stews. Earthenware pots, crafted from natural clay, provide porous properties that enhance moisture retention and impart a unique flavor to food. Choosing between tile and earthenware depends on cooking style, desired heat conductivity, and aesthetic preferences.
Material Composition and Origin
Tile cooking pots are typically made from natural clay mixed with minerals and fired at high temperatures, resulting in a dense, durable surface often glazed to prevent porosity. Earthenware pots originate from ancient pottery traditions using natural clay fired at lower temperatures, which creates a more porous and less dense material, usually requiring seasoning or glazing to improve durability. The distinct firing temperatures and clay composition influence their heat retention, durability, and suitability for different cooking methods.
Heat Distribution and Retention
Tile cooking pots offer superior heat retention due to their dense, non-porous surface, allowing for consistent cooking temperatures and minimal heat loss. Earthenware pots excel in even heat distribution, as their porous nature absorbs and spreads heat gradually, reducing hotspots and promoting uniform cooking. Choosing between tile and earthenware depends on whether long-lasting heat retention or balanced heat distribution is prioritized for your cooking needs.
Durability and Lifespan
Tile cooking pots offer superior durability due to their glazed surface, making them resistant to cracks, stains, and thermal shock, which extends their lifespan significantly compared to earthenware. Earthenware pots, being porous and less vitrified, are prone to chipping, cracking, and absorbing moisture, leading to a shorter usable life under frequent cooking conditions. Proper maintenance can extend the durability of both, but tile pots generally provide longer-lasting performance for everyday cooking due to their dense, non-porous finish.
Cooking Performance and Food Flavor
Tile cooking pots excel in heat retention and even distribution, ensuring consistent cooking temperatures that enhance flavor development and prevent scorching. Earthenware pots offer porous material properties, enabling gradual moisture release that intensifies food aromas and produces tender textures. Both materials contribute uniquely to cooking performance, with tile favoring precise heat control and earthenware enhancing natural flavors through slow cooking.
Safety and Health Considerations
Tile cooking pots often feature glazed surfaces that provide a non-porous barrier, reducing the risk of bacterial contamination and making them easier to clean, but some glazes may contain harmful substances like lead or cadmium if not properly manufactured. Earthenware pots are naturally porous, promoting slow evaporation and moisture retention, which enhances flavor but requires thorough seasoning and careful maintenance to prevent cracks and bacterial growth. Choosing certified lead-free tiles or properly cured earthenware ensures safer cooking environments, minimizing health risks associated with toxic substances or microbial hazards.
Maintenance and Cleaning Tips
Tile cooking pots require gentle cleaning with non-abrasive sponges and mild detergents to preserve the glazed surface and prevent cracking. Earthenware pots demand thorough drying after washing to avoid moisture retention, which can cause mold or weakening of the porous material. Regular seasoning of earthenware enhances durability and non-stick properties, while tile pots benefit from occasional resealing to maintain water resistance.
Aesthetic Appeal and Design
Tile cooking pots offer a vibrant, glossy finish with intricate patterns that enhance kitchen aesthetics and complement modern decor styles. Earthenware pots provide a rustic, handcrafted look with natural earthy tones and textured surfaces, adding warmth and authenticity to traditional or farmhouse kitchens. Choosing between tile and earthenware depends on the desired visual impact, with tile emphasizing colorful elegance and earthenware highlighting organic charm.
Cost Comparison and Value
Tile cooking pots generally come at a higher price point than earthenware due to the specialized glazing and firing processes involved. Earthenware offers a more budget-friendly option with reliable heat retention and durability for everyday cooking needs. While tile pots provide aesthetic appeal and sometimes enhanced heat distribution, the cost-effectiveness of earthenware often makes it the preferred choice for value-conscious cooks.
Best Uses and Recommendations
Tile cooking pots provide excellent heat retention and are ideal for slow-cooked dishes like stews and casseroles, thanks to their even heat distribution and durability. Earthenware pots excel in natural moisture retention, making them perfect for recipes requiring gentle simmering or baking, such as tagines and bread. For versatile use and enhanced flavor infusion, tile cookware is recommended for stovetop and oven, while earthenware is preferred for low-temperature cooking and serving.
Infographic: Tile vs Earthenware for Cooking Pot
 azmater.com
azmater.com