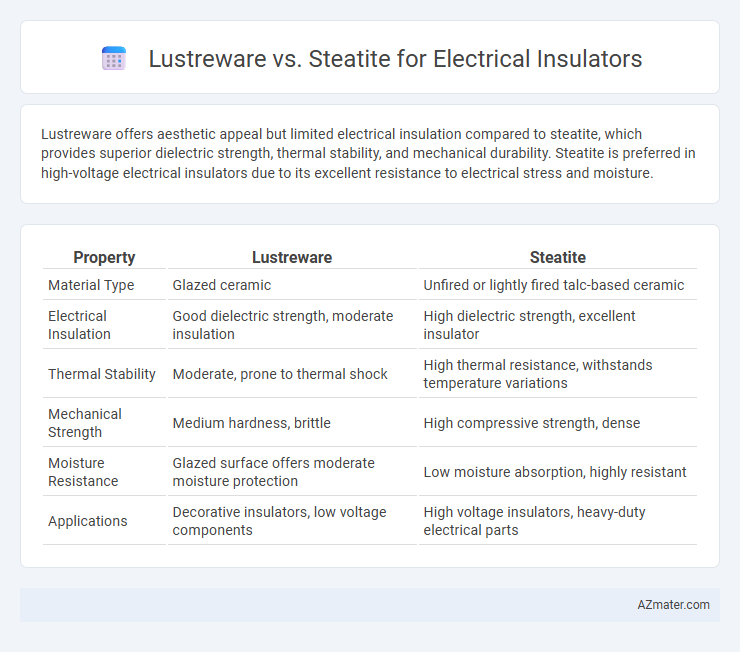
Lustreware offers aesthetic appeal but limited electrical insulation compared to steatite, which provides superior dielectric strength, thermal stability, and mechanical durability. Steatite is preferred in high-voltage electrical insulators due to its excellent resistance to electrical stress and moisture.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Lustreware | Steatite |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Glazed ceramic | Unfired or lightly fired talc-based ceramic |
| Electrical Insulation | Good dielectric strength, moderate insulation | High dielectric strength, excellent insulator |
| Thermal Stability | Moderate, prone to thermal shock | High thermal resistance, withstands temperature variations |
| Mechanical Strength | Medium hardness, brittle | High compressive strength, dense |
| Moisture Resistance | Glazed surface offers moderate moisture protection | Low moisture absorption, highly resistant |
| Applications | Decorative insulators, low voltage components | High voltage insulators, heavy-duty electrical parts |
Introduction to Electrical Insulators
Electrical insulators such as lustreware and steatite play crucial roles in preventing unwanted current flow and ensuring safety in electrical systems. Lustreware, known for its glazed finish and decorative appearance, offers moderate electrical resistance but is primarily valued for aesthetic applications. Steatite, composed of dense magnesium silicate, provides superior dielectric strength and mechanical durability, making it ideal for high-voltage and high-temperature insulator components.
What is Lustreware?
Lustreware, a type of ceramic with a metallic glaze, exhibits excellent insulating properties ideal for electrical applications. Compared to steatite, a dense, magnesium-rich ceramic known for high dielectric strength and thermal resistance, lustreware offers aesthetic appeal but generally lower electrical performance. Choosing between lustreware and steatite for electrical insulators depends on balancing decorative finish against superior insulating capabilities and mechanical durability.
What is Steatite?
Steatite, a dense and high-purity form of talc, is commonly used as an electrical insulator due to its excellent dielectric strength and thermal stability. Unlike lustreware, which is primarily a decorative ceramic, steatite offers superior mechanical strength and resistance to moisture, making it ideal for high-voltage and industrial applications. Its low electrical conductivity and heat resistance enhance the safety and performance of electrical components in demanding environments.
Material Composition and Properties
Lustreware electrical insulators are typically made from ceramic materials with a glazed surface, offering high dielectric strength and excellent resistance to moisture and chemical corrosion. Steatite insulators, composed primarily of magnesium silicate (MgSiO3), provide superior mechanical strength, low thermal expansion, and high electrical resistance, making them ideal for high-temperature applications. The choice between lustreware and steatite depends on the desired balance between insulating performance, thermal stability, and environmental durability.
Electrical Insulation Performance
Lustreware, primarily composed of ceramic materials with a glazed finish, offers moderate electrical insulation but can be susceptible to microcracks reducing dielectric strength. Steatite, a dense magnesium silicate ceramic, exhibits superior electrical insulation performance with high dielectric strength and excellent resistance to thermal shock and humidity, making it ideal for high-voltage applications. The low dielectric loss factor and stable insulating properties of steatite surpass the typically lower and more variable insulation characteristics found in lustreware.
Thermal Resistance and Stability
Lustreware and steatite are both used as electrical insulators, but steatite exhibits superior thermal resistance, typically withstanding temperatures up to 1300degC compared to lustreware's lower threshold around 800degC. Steatite's thermal stability is enhanced by its dense, crystalline structure, allowing it to maintain insulating properties under prolonged high-temperature exposure. Lustreware, while aesthetically appealing, offers limited stability under thermal stress, making steatite the preferred choice for high-temperature electrical applications.
Mechanical Strength and Durability
Lustreware exhibits superior mechanical strength with enhanced resistance to cracking and chipping compared to steatite, making it ideal for high-stress electrical insulator applications. Steatite, a dense ceramic material, offers good thermal stability but lower toughness and durability under mechanical load. The optimized toughness of lustreware provides longer service life and improved reliability in electrical insulation environments exposed to mechanical and thermal stresses.
Cost Comparison and Availability
Lustreware insulators generally have a higher cost due to their decorative glaze and limited production, making them less readily available in bulk compared to steatite insulators. Steatite, a dense ceramic material, offers a cost-effective alternative with widespread availability and superior mechanical strength, ideal for industrial electrical insulation applications. The cost efficiency and mass production capabilities of steatite result in a more accessible and economical choice for large-scale electrical projects.
Common Applications in the Industry
Lustreware, known for its decorative glazing, is rarely used in electrical insulation compared to steatite, which excels due to its high dielectric strength and thermal stability. Steatite is widely employed in industrial applications such as high-voltage insulators, ceramic capacitors, and electrical bushings. Its resistance to thermal shock and mechanical durability makes steatite the preferred choice for demanding electrical insulator components in power distribution and electronic devices.
Verdict: Choosing Between Lustreware and Steatite
Lustreware offers enhanced aesthetic appeal and moderate electrical insulation, making it suitable for decorative or low-voltage applications. Steatite provides superior thermal stability, high dielectric strength, and excellent mechanical durability, ideal for high-voltage and industrial insulator requirements. The verdict favors steatite for critical electrical insulation due to its reliability and performance under extreme conditions, while lustreware is best reserved for non-critical, decorative uses.
Infographic: Lustreware vs Steatite for Electrical Insulator
 azmater.com
azmater.com