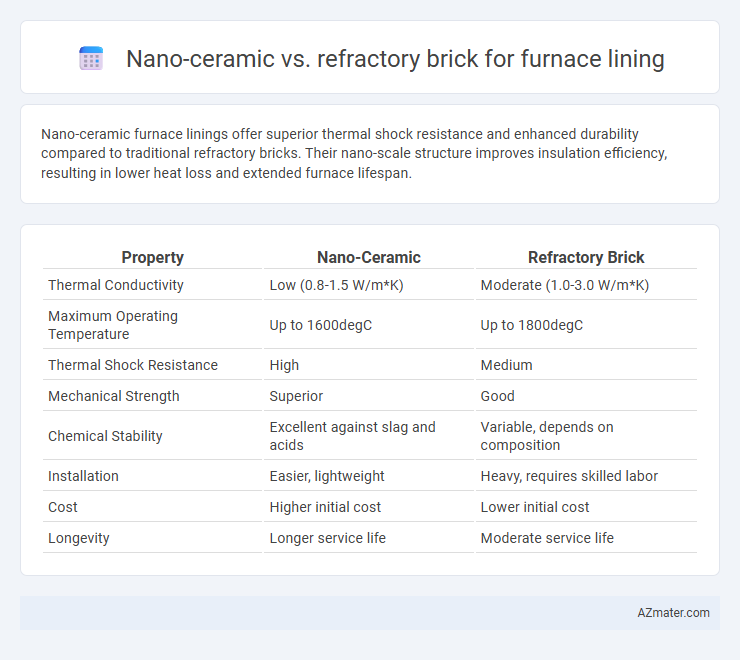
Nano-ceramic furnace linings offer superior thermal shock resistance and enhanced durability compared to traditional refractory bricks. Their nano-scale structure improves insulation efficiency, resulting in lower heat loss and extended furnace lifespan.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Nano-Ceramic | Refractory Brick |
|---|---|---|
| Thermal Conductivity | Low (0.8-1.5 W/m*K) | Moderate (1.0-3.0 W/m*K) |
| Maximum Operating Temperature | Up to 1600degC | Up to 1800degC |
| Thermal Shock Resistance | High | Medium |
| Mechanical Strength | Superior | Good |
| Chemical Stability | Excellent against slag and acids | Variable, depends on composition |
| Installation | Easier, lightweight | Heavy, requires skilled labor |
| Cost | Higher initial cost | Lower initial cost |
| Longevity | Longer service life | Moderate service life |
Introduction to Furnace Lining Materials
Furnace lining materials are critical for ensuring thermal insulation, structural integrity, and resistance to high temperatures in industrial furnaces. Nano-ceramic linings offer enhanced thermal shock resistance and lower thermal conductivity compared to traditional refractory bricks, resulting in improved energy efficiency and longer service life. Refractory bricks, typically composed of alumina, silica, or fireclay, provide proven durability and mechanical strength but may require more frequent maintenance under extreme thermal cycling.
What is Nano-ceramic Technology?
Nano-ceramic technology involves the use of ceramic materials engineered at the nanometer scale to enhance thermal resistance, mechanical strength, and durability in furnace linings. Compared to traditional refractory bricks, nano-ceramic linings offer superior insulation properties, reducing heat loss and improving energy efficiency in high-temperature environments. This technology enables finer microstructures and increased thermal shock resistance, extending the lifespan of furnace components under extreme operating conditions.
Overview of Refractory Bricks
Refractory bricks, also known as fire bricks, are primarily used for furnace lining due to their high heat resistance and ability to withstand thermal cycling. They are composed of materials such as alumina, silica, and fireclay, which provide strong structural integrity at temperatures exceeding 1500degC. Compared to nano-ceramic linings, refractory bricks offer proven durability and thermal insulation but generally have lower resistance to rapid temperature changes and chemical corrosion.
Thermal Insulation Efficiency Comparison
Nano-ceramic materials exhibit superior thermal insulation efficiency compared to refractory bricks due to their lower thermal conductivity and enhanced resistance to thermal shock. The nanostructured composition of nano-ceramics reduces heat transfer, resulting in improved energy conservation and prolonged furnace lining lifespan. In contrast, refractory bricks typically have higher density and thermal mass, which increases heat retention but reduces overall insulation performance.
Mechanical Strength and Durability
Nano-ceramic furnace linings exhibit superior mechanical strength due to their fine grain structure and enhanced bonding at the nano-scale, resulting in increased resistance to thermal shock and wear. Refractory bricks offer robust durability and high-temperature stability, but their coarser microstructure makes them more susceptible to cracking under rapid thermal cycling. The enhanced toughness of nano-ceramics extends furnace lifespan by minimizing spalling and deformation, outperforming traditional refractory bricks in demanding industrial environments.
Resistance to Thermal Shock
Nano-ceramic furnace linings exhibit superior resistance to thermal shock due to their fine-grained microstructure, which enhances crack resistance and improves durability under rapid temperature fluctuations. Refractory bricks, while robust, often have coarser grain sizes that make them more susceptible to cracking and spalling when exposed to sudden thermal changes. The enhanced thermal shock resistance of nano-ceramics leads to prolonged service life and reduced maintenance in high-temperature industrial furnace applications.
Installation and Maintenance Requirements
Nano-ceramic furnace linings provide superior ease of installation with their lightweight and precise fitting properties, reducing labor time compared to the heavier, bulkier refractory bricks that require skilled masonry for proper alignment and curing. Maintenance demands for nano-ceramic materials are lower due to their enhanced thermal shock resistance and minimal porosity, which limits crack formation and slag infiltration, whereas refractory bricks often need frequent inspections and repairs to address spalling and joint degradation. The advanced durability of nano-ceramics translates into longer service intervals and reduced downtime, optimizing operational efficiency in high-temperature furnace applications.
Cost Analysis: Nano-ceramic vs Refractory Brick
Nano-ceramic furnace linings typically incur higher initial costs due to advanced manufacturing and superior material properties but offer longer lifespans and reduced maintenance expenses. Refractory bricks present lower upfront expenses with easier installation, yet may require more frequent replacement and repairs, increasing long-term operational costs. Total cost analysis often favors nano-ceramic linings for high-temperature industrial applications where durability and maintenance savings outweigh initial investment.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Nano-ceramic furnace linings offer superior environmental benefits due to their energy-efficient thermal insulation properties, which reduce fuel consumption and lower greenhouse gas emissions during furnace operation. Refractory bricks, while durable, often require more frequent replacement and involve energy-intensive manufacturing processes that contribute to higher carbon footprints. Opting for nano-ceramic materials enhances sustainability by prolonging furnace life, minimizing waste, and supporting cleaner industrial practices.
Which is Better for Furnace Lining: Nano-ceramic or Refractory Brick?
Nano-ceramic furnace linings offer superior thermal shock resistance, higher durability, and enhanced insulating properties compared to traditional refractory bricks, making them ideal for high-performance applications requiring rapid temperature changes. Refractory bricks remain cost-effective and widely used due to their proven heat resistance and structural stability in steady high-temperature environments. Choosing between nano-ceramic and refractory brick depends on specific furnace operating conditions, with nano-ceramics best suited for advanced, high-efficiency systems demanding long-term reliability and energy savings.
Infographic: Nano-ceramic vs Refractory brick for Furnace Lining
 azmater.com
azmater.com