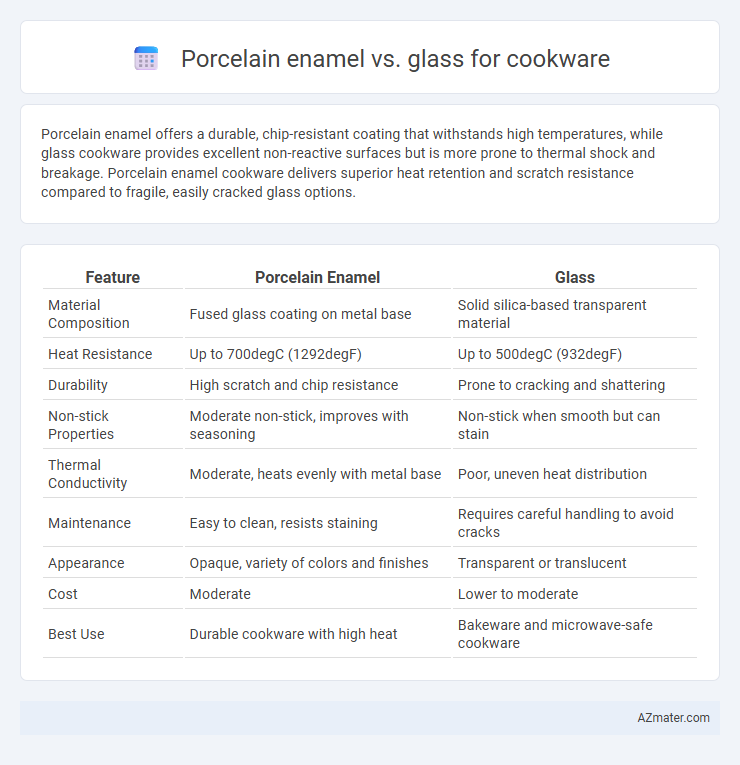
Porcelain enamel offers a durable, chip-resistant coating that withstands high temperatures, while glass cookware provides excellent non-reactive surfaces but is more prone to thermal shock and breakage. Porcelain enamel cookware delivers superior heat retention and scratch resistance compared to fragile, easily cracked glass options.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Porcelain Enamel | Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Fused glass coating on metal base | Solid silica-based transparent material |
| Heat Resistance | Up to 700degC (1292degF) | Up to 500degC (932degF) |
| Durability | High scratch and chip resistance | Prone to cracking and shattering |
| Non-stick Properties | Moderate non-stick, improves with seasoning | Non-stick when smooth but can stain |
| Thermal Conductivity | Moderate, heats evenly with metal base | Poor, uneven heat distribution |
| Maintenance | Easy to clean, resists staining | Requires careful handling to avoid cracks |
| Appearance | Opaque, variety of colors and finishes | Transparent or translucent |
| Cost | Moderate | Lower to moderate |
| Best Use | Durable cookware with high heat | Bakeware and microwave-safe cookware |
Overview: Porcelain Enamel vs Glass Cookware
Porcelain enamel cookware features a durable, chip-resistant coating fused to metal, offering excellent heat retention and an attractive, smooth surface ideal for high-temperature cooking. Glass cookware provides a non-reactive, transparent option that allows easy monitoring of food but is more prone to thermal shock and breakage under rapid temperature changes. Both materials deliver non-porous, stain-resistant qualities, but porcelain enamel outperforms glass in durability and heat conduction for versatile oven-to-stovetop use.
Material Composition and Manufacturing
Porcelain enamel cookware features a base of cast iron or steel coated with a layer of powdered glass fused at high temperatures, creating a durable, non-porous surface resistant to rust and scratches. Glass cookware is made from borosilicate or soda-lime glass, molded or blown into shape and tempered through controlled cooling processes to enhance resistance to thermal shock and mechanical stress. The manufacturing of porcelain enamel involves vitrification of glass powder onto metal, offering a robust hybrid material, whereas glass cookware relies solely on uniform glass composition and tempering techniques to ensure structural integrity and cooking performance.
Heat Conductivity and Distribution
Porcelain enamel cookware features a steel or cast iron base coated with a smooth, durable glass-like layer, offering moderate heat conductivity but excellent heat distribution due to the dense metal core. Glass cookware, typically made from tempered borosilicate, has lower heat conductivity and uneven heat distribution compared to metal-based cookware, which can lead to hot spots during cooking. The superior thermal properties of porcelain enamel-coated metals make them more efficient for consistent and controlled heat transfer in cooking applications.
Durability and Scratch Resistance
Porcelain enamel cookware offers superior scratch resistance due to its hard, glass-like coating fused to metal, making it highly durable against abrasive utensils and everyday use. Glass cookware, while non-porous and resistant to stains, is more prone to chipping and cracking under thermal shock or impact, reducing its long-term durability. Porcelain enamel's robust surface maintains appearance and functionality longer, making it a preferred choice for durability and scratch resistance in cookware.
Non-reactivity with Foods
Porcelain enamel cookware offers excellent non-reactivity with foods, preventing any metallic taste or chemical interaction during cooking, making it ideal for acidic ingredients. Glass cookware is also highly non-reactive, ensuring pure food flavors and safe cooking without leaching harmful substances. Both materials maintain food integrity and are safe choices for individuals sensitive to reactive metals like aluminum or cast iron.
Cleaning and Maintenance Needs
Porcelain enamel cookware offers a smooth, non-porous surface that resists staining and allows for easy cleaning with mild detergents, while glass cookware is highly resistant to scratches but may show smudges and requires careful handling to prevent chips. Porcelain enamel's durability withstands metal utensils and abrasive scrubbing, reducing maintenance efforts compared to glass, which is more prone to breakage and demands gentle cleaning to maintain clarity and integrity. Both materials provide dishwasher-safe options, but porcelain enamel's heat retention reduces residue buildup, simplifying routine maintenance over time.
Oven and Stovetop Compatibility
Porcelain enamel cookware offers excellent oven and stovetop compatibility due to its heat-resistant, non-reactive surface that withstands high temperatures without warping or discoloration. Glass cookware, while oven-safe, is typically unsuitable for stovetop use because direct flame can cause thermal shock, leading to cracking or shattering. Choosing porcelain enamel ensures versatile cooking options and durable performance across both stovetop and oven environments.
Aesthetics and Design Options
Porcelain enamel cookware offers a wide range of vibrant colors and glossy finishes, allowing for customizable and attractive kitchen aesthetics. Glass cookware provides a clear, transparent design that showcases the food while blending seamlessly with various kitchen decors. Each material enhances visual appeal differently, with porcelain enamel favoring bold, decorative looks and glass emphasizing simplicity and visibility.
Cost Comparison and Value
Porcelain enamel cookware typically offers a mid-range price point with durability and an attractive finish, providing excellent value for quality-conscious buyers. Glass cookware is often more affordable upfront but tends to lack the heat retention and scratch resistance of porcelain enamel, which can affect longevity and overall cost-effectiveness. Investing in porcelain enamel can lead to greater long-term savings due to its resistance to chipping and compatibility with various cooking surfaces, enhancing performance and durability.
Best Uses and Recommendations
Porcelain enamel cookware excels in even heat distribution and resistance to staining, making it ideal for slow-cooking, braising, and simmering acidic dishes like tomato sauces. Glass cookware is best suited for oven baking and microwave use, offering non-reactive surfaces that do not alter flavors but can be prone to thermal shock if exposed to sudden temperature changes. For versatile stovetop to oven use with durability, porcelain enamel is recommended, while glass is preferred for transparent baking needs and easy monitoring of food.
Infographic: Porcelain enamel vs Glass for Cookware
 azmater.com
azmater.com