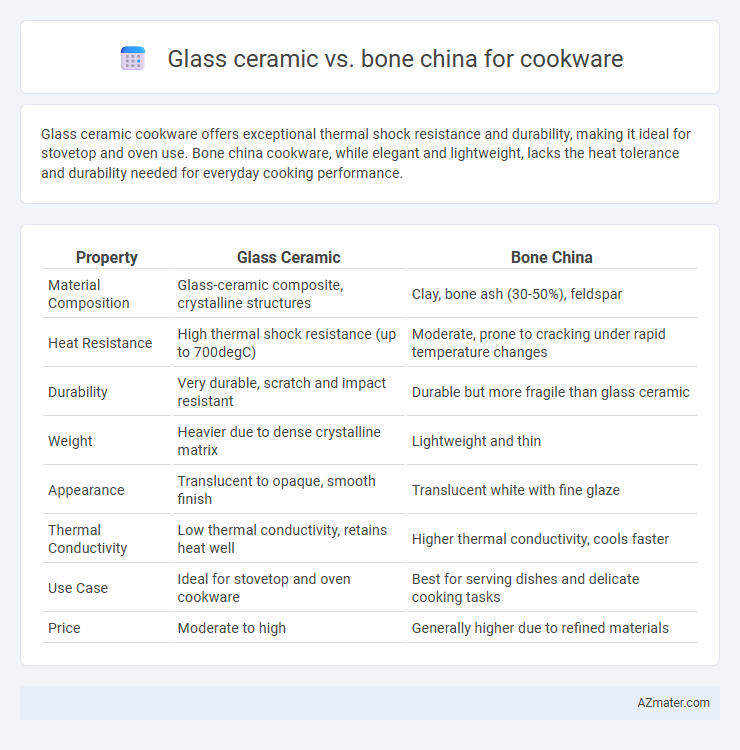
Glass ceramic cookware offers exceptional thermal shock resistance and durability, making it ideal for stovetop and oven use. Bone china cookware, while elegant and lightweight, lacks the heat tolerance and durability needed for everyday cooking performance.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Glass Ceramic | Bone China |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Glass-ceramic composite, crystalline structures | Clay, bone ash (30-50%), feldspar |
| Heat Resistance | High thermal shock resistance (up to 700degC) | Moderate, prone to cracking under rapid temperature changes |
| Durability | Very durable, scratch and impact resistant | Durable but more fragile than glass ceramic |
| Weight | Heavier due to dense crystalline matrix | Lightweight and thin |
| Appearance | Translucent to opaque, smooth finish | Translucent white with fine glaze |
| Thermal Conductivity | Low thermal conductivity, retains heat well | Higher thermal conductivity, cools faster |
| Use Case | Ideal for stovetop and oven cookware | Best for serving dishes and delicate cooking tasks |
| Price | Moderate to high | Generally higher due to refined materials |
Introduction to Glass Ceramic and Bone China Cookware
Glass ceramic cookware offers exceptional heat resistance and durability, making it suitable for high-temperature cooking and rapid temperature changes without cracking. Bone china cookware, known for its refined composition including bone ash, delivers superior whiteness, translucency, and lightweight strength, ideal for elegant serving and moderate cooking tasks. Both materials provide unique benefits, with glass ceramic excelling in thermal performance and bone china favored for its aesthetic appeal and chip resistance.
Material Composition and Manufacturing Processes
Glass ceramic cookware is made from a unique blend of silica, alumina, and other minerals that undergo controlled crystallization through rapid cooling, resulting in a hard, non-porous surface with excellent thermal shock resistance. Bone china, primarily composed of bone ash, kaolin, and feldspar, is fired at high temperatures to create a lightweight, translucent ceramic known for its strength and fine texture but less suited to withstand direct heat and rapid temperature changes. Manufacturing glass ceramic involves a precise thermal treatment to form embedded crystals that enhance durability and heat tolerance, whereas bone china's process relies on careful firing and glazing techniques to achieve its delicate appearance and mechanical properties.
Durability and Heat Resistance
Glass ceramic cookware offers exceptional heat resistance, withstanding sudden temperature changes up to 450degC, making it less prone to cracking or warping during cooking. Bone china, while elegant and lightweight, tends to be more fragile and less heat-resistant, often cracking under rapid temperature fluctuations or high heat exposure. For durability and thermal shock resistance, glass ceramic is the preferred choice for cookware designed for intensive and varied cooking conditions.
Cooking Performance and Heat Distribution
Glass ceramic cookware offers excellent heat retention and even heat distribution, making it ideal for slow, consistent cooking. Bone china, while elegant and durable for serving, lacks the thermal conductivity required for efficient cooking and can suffer from uneven heat distribution. For optimal cooking performance, glass ceramic is preferred due to its ability to maintain stable temperatures and resist thermal shock.
Microwave and Oven Compatibility
Glass ceramic cookware offers excellent microwave and oven compatibility due to its ability to withstand rapid temperature changes without cracking or warping, making it ideal for both cooking and reheating. Bone china cookware, while elegant and durable for serving purposes, typically has lower thermal resistance and is less suitable for direct oven use or intense microwave heating, risking damage or breakage. Choosing glass ceramic ensures safe, reliable performance across various cooking methods, including microwaving and oven baking.
Aesthetic Appeal and Design Options
Glass ceramic cookware offers a sleek, modern aesthetic with a smooth, often transparent or semi-translucent finish that enhances contemporary kitchen designs. Bone china, known for its delicate, fine texture and classic white or ivory tones, provides an elegant and timeless look ideal for traditional or formal settings. Both materials allow for diverse design options, but bone china often features intricate patterns and hand-painted details, while glass ceramic emphasizes minimalistic and clean lines.
Porosity, Stain Resistance, and Maintenance
Glass ceramic cookware features low porosity, offering excellent stain resistance and minimal absorption, which simplifies maintenance and prevents odor retention. Bone china, while elegant and durable for tableware, has higher porosity compared to glass ceramic, making it more susceptible to staining and requiring gentler cleaning methods. The dense, non-porous surface of glass ceramic ensures superior longevity and ease of care, making it a preferred choice for stain-resistant, low-maintenance cookware.
Health and Safety Considerations
Glass ceramic cookware offers superior thermal stability and non-porous surfaces, reducing the risk of chemical leaching and ensuring safer food preparation. Bone china, while elegant and durable, may contain trace amounts of lead or cadmium in older or lower-quality pieces, raising potential health concerns when used for cooking. Prioritizing certified lead-free and cadmium-free options in both materials is essential for maintaining optimal health and safety in the kitchen.
Cost Comparison and Value for Money
Glass ceramic cookware typically offers a lower price point compared to bone china, making it a budget-friendly option for everyday cooking. Bone china, known for its durability and elegant appearance, commands a higher cost but provides excellent heat retention and resistance to chipping, which can justify the investment over time. Evaluating factors like longevity, heat distribution, and aesthetic appeal helps determine the better value for money based on individual cooking needs and budget constraints.
Final Verdict: Choosing Between Glass Ceramic and Bone China Cookware
Glass ceramic cookware offers superior thermal shock resistance and durability, making it ideal for high-heat cooking and versatility in the kitchen. Bone china cookware, known for its elegant appearance and lightweight design, excels in serving and low to moderate temperature cooking but lacks the resilience needed for intense heat. For practical, everyday cooking, glass ceramic is the preferred choice, while bone china suits aesthetic-focused presentation and gentle cooking applications.
Infographic: Glass ceramic vs Bone china for Cookware
 azmater.com
azmater.com