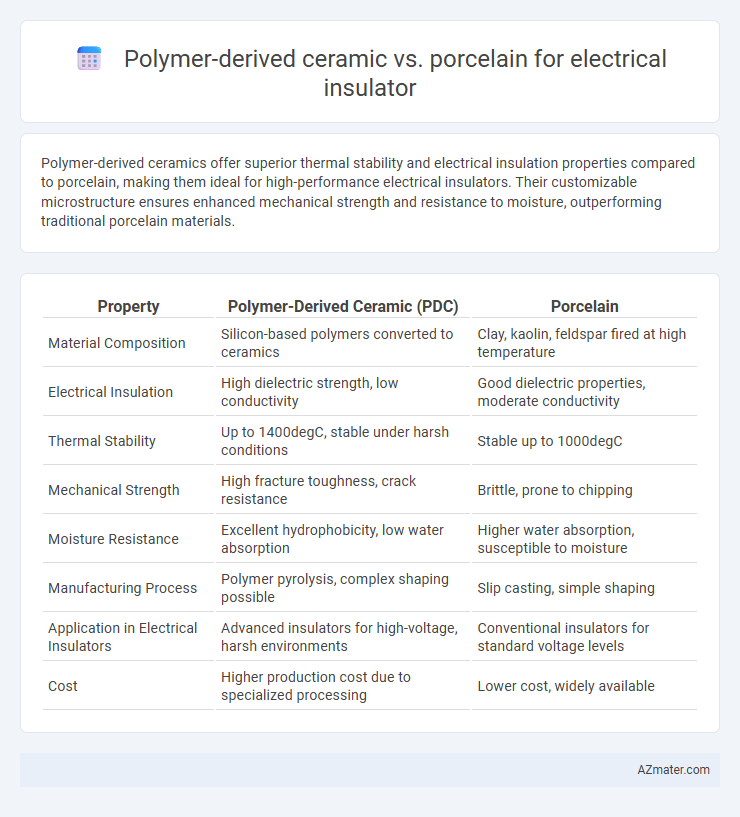
Polymer-derived ceramics offer superior thermal stability and electrical insulation properties compared to porcelain, making them ideal for high-performance electrical insulators. Their customizable microstructure ensures enhanced mechanical strength and resistance to moisture, outperforming traditional porcelain materials.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Polymer-Derived Ceramic (PDC) | Porcelain |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Silicon-based polymers converted to ceramics | Clay, kaolin, feldspar fired at high temperature |
| Electrical Insulation | High dielectric strength, low conductivity | Good dielectric properties, moderate conductivity |
| Thermal Stability | Up to 1400degC, stable under harsh conditions | Stable up to 1000degC |
| Mechanical Strength | High fracture toughness, crack resistance | Brittle, prone to chipping |
| Moisture Resistance | Excellent hydrophobicity, low water absorption | Higher water absorption, susceptible to moisture |
| Manufacturing Process | Polymer pyrolysis, complex shaping possible | Slip casting, simple shaping |
| Application in Electrical Insulators | Advanced insulators for high-voltage, harsh environments | Conventional insulators for standard voltage levels |
| Cost | Higher production cost due to specialized processing | Lower cost, widely available |
Introduction to Electrical Insulators
Electrical insulators are critical materials that prevent unwanted current flow and ensure safety in electronic devices and power systems. Polymer-derived ceramics offer advantages such as high thermal stability, chemical resistance, and excellent dielectric properties, making them suitable for advanced electrical insulation applications. Porcelain, traditionally used for insulators, provides mechanical strength and good insulation but lacks the enhanced performance of polymer-derived ceramics under extreme conditions.
Overview of Polymer-Derived Ceramics
Polymer-derived ceramics (PDCs) offer superior thermal stability, high electrical resistivity, and excellent mechanical strength compared to traditional porcelain used in electrical insulators. PDCs are synthesized through the pyrolysis of preceramic polymers, resulting in amorphous or nanocrystalline ceramic materials with tailored microstructures that provide enhanced dielectric properties and resistance to environmental degradation. These characteristics make polymer-derived ceramics a promising alternative for high-performance electrical insulation applications where durability and reliability are critical.
Understanding Porcelain as an Insulator
Porcelain is a widely used electrical insulator due to its high dielectric strength, excellent thermal stability, and resistance to moisture and chemical corrosion. Its crystalline structure and composition of kaolin, feldspar, and silica contribute to superior mechanical strength and long-term durability under high voltage conditions. Compared to polymer-derived ceramics, porcelain offers proven reliability in outdoor and high-temperature applications, making it a standard choice for power transformers and insulator bushings.
Key Material Properties Comparison
Polymer-derived ceramics (PDCs) offer superior thermal stability and higher fracture toughness compared to traditional porcelain, making them more resistant to thermal shock and mechanical stress in electrical insulators. PDCs exhibit lower dielectric loss and higher dielectric strength, enhancing insulation performance at elevated temperatures and frequencies. Porcelain, while cost-effective and widely used, has lower mechanical strength and is more susceptible to moisture absorption, potentially compromising long-term electrical reliability.
Electrical Performance and Reliability
Polymer-derived ceramics (PDCs) exhibit superior electrical insulation properties with high dielectric strength and excellent thermal stability compared to traditional porcelain insulators. PDCs offer enhanced reliability in harsh environments due to their resistance to thermal shock, chemical corrosion, and mechanical stress, ensuring consistent electrical performance over time. Porcelain insulators, while widely used for their cost-effectiveness and mechanical toughness, generally have lower dielectric strength and are more susceptible to cracking and moisture ingress, which can compromise long-term reliability.
Mechanical Strength and Durability
Polymer-derived ceramics (PDCs) exhibit superior mechanical strength compared to porcelain due to their amorphous microstructure and enhanced fracture toughness, making them highly resistant to cracking under mechanical stress. PDCs also demonstrate excellent durability in harsh electrical environments, including high temperatures and corrosive conditions, outperforming porcelain's susceptibility to thermal shock and chemical degradation. This combination of mechanical robustness and durability positions PDCs as advanced materials for reliable and long-lasting electrical insulators.
Weather and Aging Resistance
Polymer-derived ceramics exhibit superior weather and aging resistance compared to porcelain due to their enhanced chemical stability and lower porosity, which reduces moisture ingress and surface degradation over time. Unlike porcelain, which can crack or degrade under prolonged exposure to ultraviolet radiation and environmental pollutants, polymer-derived ceramics maintain structural integrity and dielectric properties under harsh weather conditions. Their nanostructured composition and inherent resistance to thermal cycling make polymer-derived ceramics a more durable choice for long-term electrical insulation in outdoor applications.
Manufacturing Processes and Cost
Polymer-derived ceramics (PDCs) utilize a pyrolysis process where pre-ceramic polymers convert into ceramics at relatively lower temperatures compared to traditional porcelain firing, reducing energy consumption in manufacturing. Porcelain production involves high-temperature kilns and extensive shaping and glazing steps, which contribute to longer production cycles and higher operational costs. While PDCs offer cost benefits through simplified processing and scalability, porcelain remains economically viable due to well-established mass production infrastructure and material stability in electrical insulation applications.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Polymer-derived ceramics (PDCs) offer superior environmental benefits compared to traditional porcelain insulators due to their lower energy consumption during manufacturing and enhanced recyclability. The production of PDCs involves less greenhouse gas emissions and reduced raw material extraction, promoting sustainability in electrical insulation applications. In contrast, porcelain manufacturing requires high-temperature kilns and extensive mining, resulting in higher carbon footprints and environmental degradation.
Application Suitability and Industry Trends
Polymer-derived ceramics exhibit exceptional thermal stability and mechanical strength, making them ideal for high-performance electrical insulators in aerospace and automotive industries, where resistance to extreme temperatures and mechanical stress is critical. Porcelain electrical insulators remain prevalent in traditional power transmission and distribution due to their excellent dielectric properties and cost-effectiveness, supporting widespread infrastructure needs. Emerging industry trends highlight a gradual shift toward polymer-derived ceramics for next-generation insulators, driven by their versatility and enhanced durability in harsh environments.
Infographic: Polymer-derived ceramic vs Porcelain for Electrical insulator
 azmater.com
azmater.com