Ferroelectric ceramic offers superior dielectric properties and temperature stability compared to traditional stoneware used in dinnerware. Stoneware provides durability and a rustic aesthetic but lacks the electrical responsiveness and precision of ferroelectric ceramics.
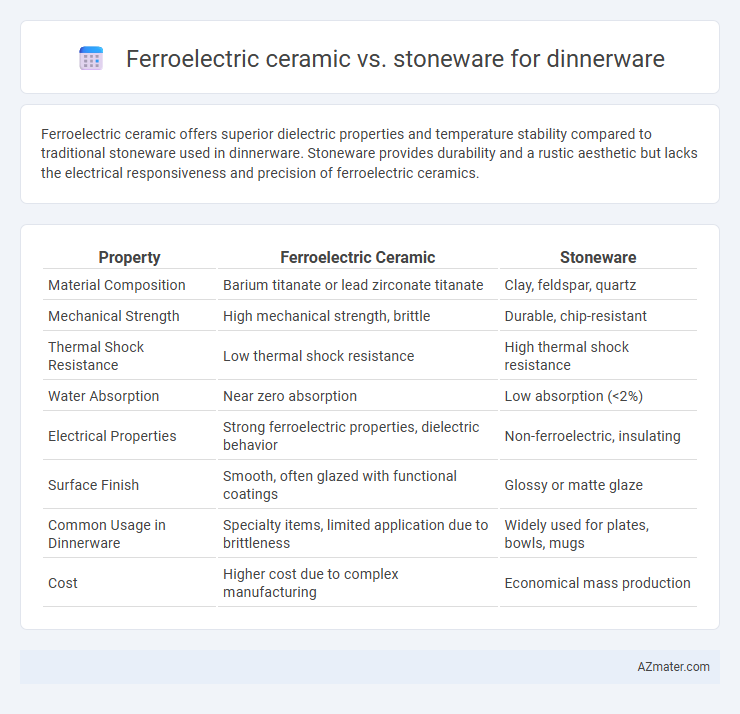
Table of Comparison
| Property | Ferroelectric Ceramic | Stoneware |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Barium titanate or lead zirconate titanate | Clay, feldspar, quartz |
| Mechanical Strength | High mechanical strength, brittle | Durable, chip-resistant |
| Thermal Shock Resistance | Low thermal shock resistance | High thermal shock resistance |
| Water Absorption | Near zero absorption | Low absorption (<2%) |
| Electrical Properties | Strong ferroelectric properties, dielectric behavior | Non-ferroelectric, insulating |
| Surface Finish | Smooth, often glazed with functional coatings | Glossy or matte glaze |
| Common Usage in Dinnerware | Specialty items, limited application due to brittleness | Widely used for plates, bowls, mugs |
| Cost | Higher cost due to complex manufacturing | Economical mass production |
Introduction to Ferroelectric Ceramics and Stoneware
Ferroelectric ceramics are advanced materials characterized by their spontaneous electric polarization, which can be reversed by an external electric field, making them ideal for sensor and actuator applications but less common in everyday dinnerware due to their brittleness. Stoneware, in contrast, is a durable, non-porous ceramic fired at high temperatures, valued for its strength, chip resistance, and ability to retain heat, making it a popular choice for everyday and formal dinnerware. While ferroelectric ceramics offer specialized electrical properties, stoneware provides practical benefits such as durability and thermal retention, catering to different functional needs in dinnerware use.
Material Composition and Properties
Ferroelectric ceramic dinnerware is composed of crystalline materials exhibiting spontaneous electric polarization, offering enhanced thermal resistance and mechanical strength compared to traditional ceramics. Stoneware consists primarily of dense, vitrified clay fired at high temperatures, resulting in a durable, non-porous surface ideal for everyday use but with lower thermal shock resistance. The unique electrical properties of ferroelectric ceramics provide superior resistance to cracking and chipping under rapid temperature changes, while stoneware excels in toughness and ease of maintenance.
Manufacturing Processes Compared
Ferroelectric ceramic dinnerware involves a complex manufacturing process that includes precise control of temperature and electrical polarization to achieve its unique properties, whereas stoneware is produced through high-temperature firing of clay and minerals to create a dense, durable, and non-porous final product. The ferroelectric ceramic process requires advanced sintering and annealing techniques to imbue the material with ferroelectric properties, making it less common and more specialized than stoneware. Stoneware manufacturing emphasizes consistent kiln temperatures and glazing methods to ensure chip resistance and robustness suitable for everyday use.
Durability and Wear Resistance
Ferroelectric ceramic dinnerware exhibits excellent durability due to its enhanced molecular structure, making it highly resistant to chipping and cracking over time. Stoneware is known for its robustness with a dense, non-porous composition that provides superior wear resistance against scratches and thermal shock. When comparing both, ferroelectric ceramic offers advanced toughness with added electrical properties, while stoneware remains a traditional choice valued for its natural hardness and longevity in everyday use.
Thermal Performance and Microwave Safety
Ferroelectric ceramic dinnerware excels in thermal performance due to its ability to withstand rapid temperature changes without cracking, making it ideal for microwave use where sudden heating occurs. Stoneware offers good heat retention but can suffer from thermal shock and may not always be microwave-safe depending on its glaze and composition. Choosing ferroelectric ceramic ensures consistent microwave safety and durability under high thermal stress, while stoneware requires careful selection to avoid damage during microwave heating.
Aesthetic Appeal and Design Options
Ferroelectric ceramic dinnerware offers a sleek, modern aesthetic with a smooth, glossy finish that enhances vivid colors and intricate patterns, making it ideal for contemporary table settings. Stoneware provides a rustic, earthy appeal with natural textures and muted tones, appealing to those who prefer a handcrafted, organic look. Both materials allow diverse design options, but ferroelectric ceramic supports high-definition printing and sharp detailing, while stoneware excels in unique glaze variations and artisanal craftsmanship.
Food Safety and Toxicity Concerns
Ferroelectric ceramic dinnerware, widely used for its durability and heat resistance, generally meets stringent food safety standards, but it may contain lead or cadmium in glazes if not certified as food-safe. Stoneware is also food-safe, commonly fired at high temperatures that minimize toxicity risks, resulting in non-porous surfaces that resist bacteria and chemical leaching. Consumers should verify certification labels such as FDA approval or similar food safety standards to ensure no harmful heavy metals are present in either material's finish.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Ferroelectric ceramic dinnerware typically involves complex manufacturing processes and the use of materials with higher energy consumption and environmental impact compared to stoneware. Stoneware is favored for sustainability due to its natural clay composition, longer durability, and lower energy requirements during production and firing. Choosing stoneware significantly reduces carbon footprint and supports eco-friendly practices in dinnerware manufacturing.
Cost Comparison and Market Availability
Ferroelectric ceramic dinnerware typically incurs higher production costs due to advanced material technology, resulting in price points above traditional stoneware, which remains more affordable for mass-market consumers. Market availability of stoneware is widespread with extensive distribution across retail outlets and online stores, while ferroelectric ceramic is less common, often found in specialty or high-end boutique shops. Cost efficiency and accessibility make stoneware the preferred choice for everyday use, contrasted with ferroelectric ceramic's niche appeal driven by innovation and durability.
Choosing the Right Dinnerware for Your Needs
Ferroelectric ceramic dinnerware offers superior durability with enhanced resistance to thermal shock and electrical properties, making it ideal for modern kitchens requiring advanced materials. Stoneware is known for its robustness, chip resistance, and classic aesthetic, providing a rustic charm perfect for everyday use and casual dining. Choosing between ferroelectric ceramic and stoneware depends on prioritizing technological benefits and heat tolerance or traditional styling and toughness for daily meals.
Infographic: Ferroelectric ceramic vs Stoneware for Dinnerware
 azmater.com
azmater.com