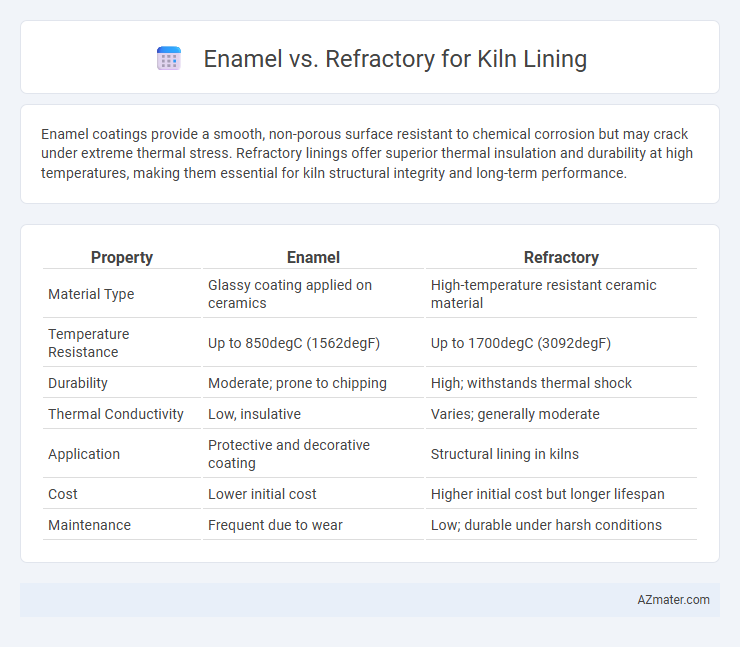
Enamel coatings provide a smooth, non-porous surface resistant to chemical corrosion but may crack under extreme thermal stress. Refractory linings offer superior thermal insulation and durability at high temperatures, making them essential for kiln structural integrity and long-term performance.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Enamel | Refractory |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Glassy coating applied on ceramics | High-temperature resistant ceramic material |
| Temperature Resistance | Up to 850degC (1562degF) | Up to 1700degC (3092degF) |
| Durability | Moderate; prone to chipping | High; withstands thermal shock |
| Thermal Conductivity | Low, insulative | Varies; generally moderate |
| Application | Protective and decorative coating | Structural lining in kilns |
| Cost | Lower initial cost | Higher initial cost but longer lifespan |
| Maintenance | Frequent due to wear | Low; durable under harsh conditions |
Introduction to Kiln Lining Materials
Kiln lining materials are critical for maintaining thermal efficiency and structural integrity in high-temperature environments. Enamel offers a smooth, protective coating with excellent resistance to chemical corrosion, while refractory materials provide superior thermal insulation and durability under extreme heat conditions. Selecting the appropriate kiln lining depends on factors such as operating temperature, chemical exposure, and mechanical stress.
Understanding Enamel as a Kiln Liner
Enamel as a kiln liner offers a smooth, non-porous surface that enhances thermal resistance and chemical stability under high temperatures. Its glass-like coating protects the kiln structure from corrosive fluxes and reduces maintenance needs compared to traditional refractory linings. Enamel's durability and ease of cleaning make it ideal for applications requiring consistent thermal performance and contamination-free environments.
Key Properties of Refractory Materials
Refractory materials for kiln lining are valued for their high melting points, thermal stability, and resistance to chemical corrosion, ensuring durability in extreme heat environments. Key properties include low thermal conductivity for energy efficiency, mechanical strength to withstand thermal cycling, and resistance to slag and molten metal infiltration. These characteristics help maintain structural integrity and prolong kiln lifespan compared to enamel linings, which are typically less heat-resistant and prone to cracking under thermal stress.
Thermal Resistance Comparison
Enamel coatings offer moderate thermal resistance, typically withstanding temperatures up to 850degC, making them suitable for lower-temperature kiln environments. Refractory linings, composed of firebrick or castable refractory materials, provide superior thermal resistance, often enduring temperatures exceeding 1700degC, which ensures durability in high-temperature kiln operations. The choice between enamel and refractory depends heavily on the maximum operating temperature and thermal shock resistance required for efficient kiln performance.
Durability and Longevity
Refractory materials offer superior durability and longevity for kiln lining due to their high resistance to thermal shock, chemical corrosion, and mechanical wear, maintaining structural integrity under extreme temperatures exceeding 1600degC. Enamel coatings provide a smooth, protective surface but tend to degrade faster under continuous high heat and abrasive conditions, reducing their effective lifespan in industrial kiln environments. Choosing refractory linings enhances operational efficiency by minimizing maintenance and replacement frequency, critical for high-temperature kiln applications.
Chemical Resistance: Enamel vs Refractory
Enamel coatings exhibit superior chemical resistance compared to refractory linings, effectively protecting kiln surfaces from corrosive slags and fluxes commonly encountered during high-temperature processes. Refractory materials, while durable against thermal shock and abrasion, may degrade faster when exposed to aggressive chemicals and molten materials. Selecting enamel for kiln lining enhances longevity by providing a non-porous, chemically inert barrier that minimizes contamination and structural damage.
Installation and Maintenance Ease
Enamel kiln linings offer a smoother surface that simplifies cleaning and requires less frequent maintenance due to their resistance to chemical corrosion and thermal shock. Refractory linings, while providing superior insulation and durability, demand more complex installation procedures involving careful layering and curing to avoid cracks. Maintenance of refractory materials often involves spot repairs and monitoring for wear, whereas enamel linings benefit from easier surface upkeep but may chip under mechanical stress.
Cost Analysis and Affordability
Enamel kiln linings generally offer lower upfront costs compared to refractory materials, making them more affordable for small-scale operations and short-term use. Refractory linings, while initially more expensive due to specialized fabrication and high-temperature resistance, provide superior durability and longer service life, reducing replacement frequency and long-term expenses. Cost-efficiency analysis favors enamel for budget-conscious projects with limited thermal demands, whereas refractory is cost-effective for industrial kilns requiring robust insulation and extended operational longevity.
Environmental and Safety Factors
Enamel kiln linings often contain lead and other heavy metals that pose significant environmental hazards during disposal and manufacturing, while refractory linings are generally made from natural, non-toxic minerals like alumina and silica, promoting eco-friendliness. From a safety perspective, refractory materials offer superior thermal stability and lower off-gassing, reducing exposure to harmful fumes compared to enamel coatings that may degrade at high temperatures. Choosing refractory linings contributes to safer kiln operation and aligns with stricter environmental regulations aiming to minimize hazardous waste and airborne contaminants.
Choosing the Right Kiln Lining for Your Needs
Choosing the right kiln lining involves evaluating the performance characteristics of enamel and refractory materials based on temperature tolerance, durability, and chemical resistance. Enamel linings provide a smooth, non-porous surface ideal for lower-temperature kilns with decorative needs, while refractory linings offer superior heat retention and structural support for high-temperature industrial applications. Selecting the appropriate lining depends on kiln operating temperatures, thermal conductivity requirements, and the specific heating cycles involved in your process.
Infographic: Enamel vs Refractory for Kiln Lining
 azmater.com
azmater.com